Abstract
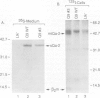
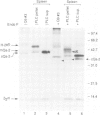
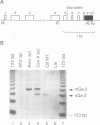
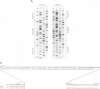
Among the best characterized non-classical mouse major histocompatibility antigens are the Qa-2 molecules. These proteins can serve as targets for allogenic cytotoxic T cells and as signal transducing molecules. They are structurally similar to H-2 transplantation antigens in their N-terminal and beta 2-microglobulin binding domains but differ at their C-termini. While the H-2 antigens span the cell membrane, the Qa-2 molecules are attached to the cell surface via phospholipid anchors. The genetic information encoding this attachment is contained in exon 5. In concanavalin A activated splenocytes the expression of membrane bound Qa-2 antigens declines and, simultaneously, soluble forms of Qa-2 molecules are secreted. We demonstrate here that the soluble Qa-2 polypeptides are translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs lacking exon 5, while the membrane forms are encoded by the full-size transcripts. In cultured cells the alternative splicing of the Qa-2 message is induced by T-cell activation splicing of the Qa-2 message is induced by T-cell activation with concanavalin A. The canonical mRNA encoding the membrane form of Qa-2 predominates in unstimulated mouse tissues but the cultured cell lines, like activated T cells, express enhanced levels of the truncated mRNA. In some cell lines almost all Qa-2 transcripts lack exon 5. For example, in L cells, mRNAs encoding soluble Qa-2 molecules are at least 10 times more abundant than Qa-2 transcripts encoding phospholipid anchored antigens. These findings are discussed in terms of potential functions of membrane bound and secreted Qa-2 molecules.
Full text
PDF

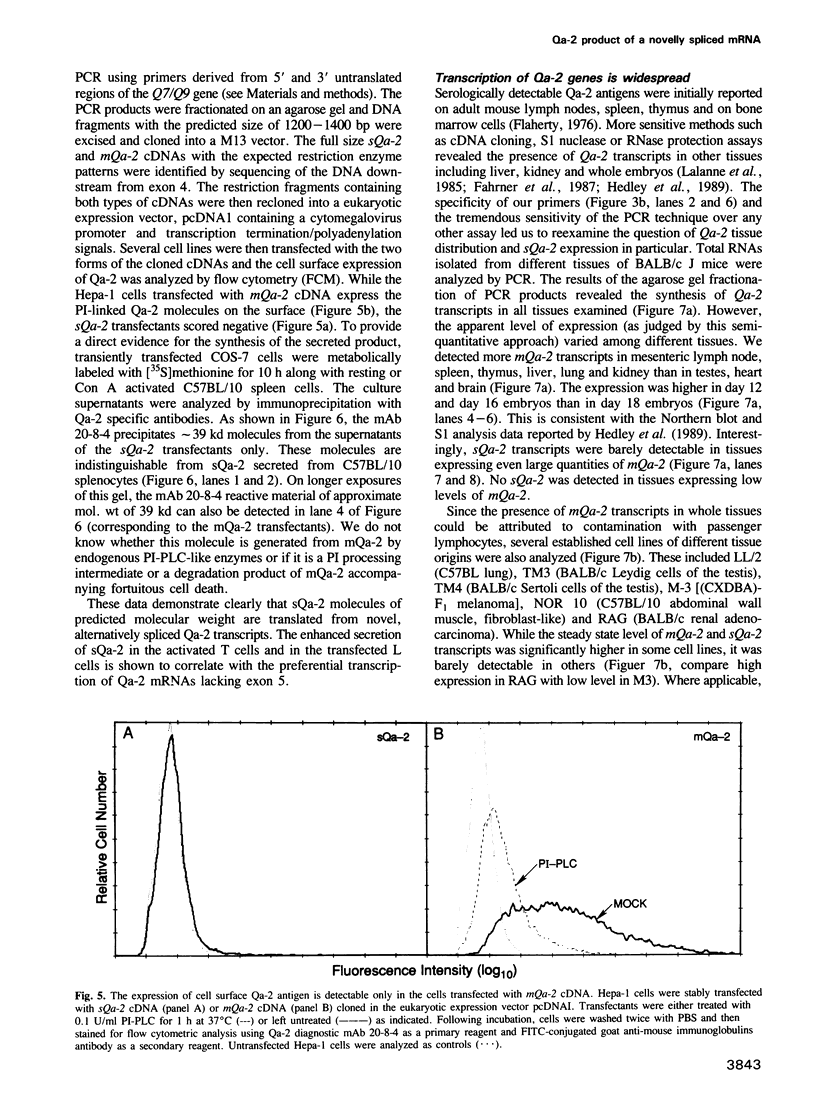
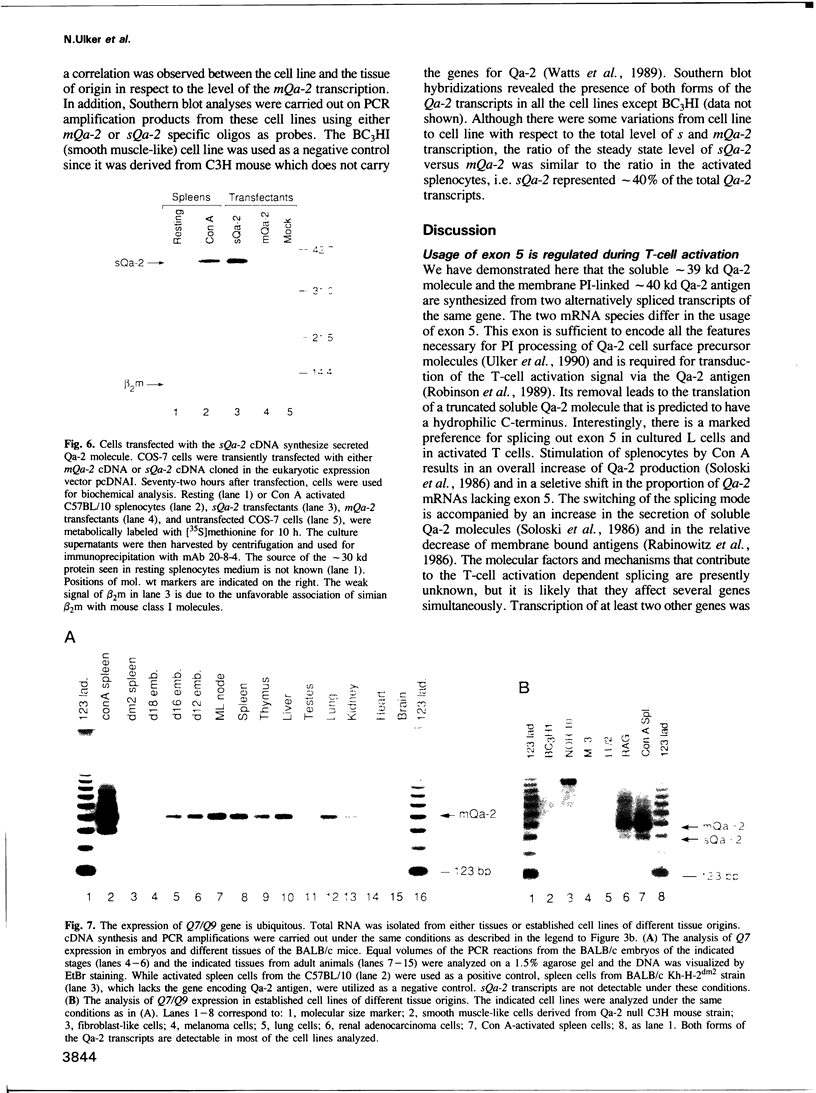



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asarnow D. M., Kuziel W. A., Bonyhadi M., Tigelaar R. E., Tucker P. W., Allison J. P. Limited diversity of gamma delta antigen receptor genes of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoncello I., Bartelmez S. H., Bradley T. R., Hodgson G. S. Increased Qa-m7 antigen expression is characteristic of primitive hemopoietic progenitors in regenerating marrow. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkeland M. L., Johnson P., Trowbridge I. S., Puré E. Changes in CD45 isoform expression accompany antigen-induced murine T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6734–6738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone J. A., Cron R. Q., Cotterman M., Houlden B. A., Matis L. A. Structure and specificity of T cell receptor gamma/delta on major histocompatibility complex antigen-specific CD3+, CD4-, CD8- T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1899–1916. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Weiss E. H., Paulson M., Flavell R. A. Duplicated gene pairs and alleles of class I genes in the Qa2 region of the murine major histocompatibility complex: a comparison. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3203–3207. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrner K., Hogan B. L., Flavell R. A. Transcription of H-2 and Qa genes in embryonic and adult mice. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty L., DiBiase K., Lynes M. A., Seidman J. G., Weinberger O., Rinchik E. M. Characterization of a Q subregion gene in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1503–1507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Guise J., Tucker P. W., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site choice rather than splice site choice governs the regulated production of IgM heavy-chain RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2439–2443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn A. B., Soloski M. J. Anti-Qa-2-induced T cell activation. The parameters of activation, the definition of mitogenic and nonmitogenic antibodies, and the differential effects on CD4+ vs CD8+ T cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Drake B. L., Head J. R., Tucker P. W., Forman J. Differential expression of the class I MHC genes in the embryo and placenta during midgestational development in the mouse. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4046–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bonneville M., Takagaki Y., Nakanishi N., Kanagawa O., Krecko E. G., Tonegawa S. Different gamma delta T-cell receptors are expressed on thymocytes at different stages of development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):631–635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S. Secretion of HLA-A and -B antigens via an alternative RNA splicing pathway. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalanne J. L., Transy C., Guerin S., Darche S., Meulien P., Kourilsky P. Expression of class I genes in the major histocompatibility complex: identification of eight distinct mRNAs in DBA/2 mouse liver. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Maloy W. L., Coligan J. E. Characteristics of the expression of the murine soluble class I molecule (Q10). J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loveland B., Wang C. R., Yonekawa H., Hermel E., Lindahl K. F. Maternally transmitted histocompatibility antigen of mice: a hydrophobic peptide of a mitochondrially encoded protein. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):971–980. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90345-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura A., Schloss R., Shen F. W., Tung J. S., Hunt S. W., 3rd, Fisher D. A., Hood L. E., Boyse E. A. Expression of the Q8/9d gene by T cells of the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(3):156–161. doi: 10.1007/BF02421200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey J., Boyd L. F., Maloy W. L., Coligan J. E., Margulies D. H. Alternative processing of H-2Dd pre-mRNAs results in membrane expression of differentially phosphorylated protein products. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2477–2483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norment A. M., Lonberg N., Lacy E., Littman D. R. Alternatively spliced mRNA encodes a secreted form of human CD8 alpha. Characterization of the human CD8 alpha gene. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3312–3319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrand-Rosenberg S., Nickerson D. A., Clements V. K., Garcia E. P., Lamouse-Smith E., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Embryonal carcinoma cells express Qa and Tla class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5084–5088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz R., Sharrow S. O., Chatterjee-Das S., Rogers M. J., Sachs D. H. Qa alloantigen expression on functional T lymphocytes from spleen and thymus. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(6):391–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00377958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Millrain M., Antoniou J., Simpson E., Mellor A. L. A glycophospholipid anchor is required for Qa-2-mediated T cell activation. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):85–87. doi: 10.1038/342085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. J., Siwarski D. F., Shacter E., Maloy W. L., Lillehoj E. P., Coligan J. E. Three distinct H-2Ks molecules differing at the carboxy terminus are expressed on a tumor from SJL/J mice. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):3006–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrow S. O., Flaherty L., Sachs D. H. Serologic cross-reactivity between Class I MHC molecules and an H-2-linked differentiation antigen as detected by monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):21–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
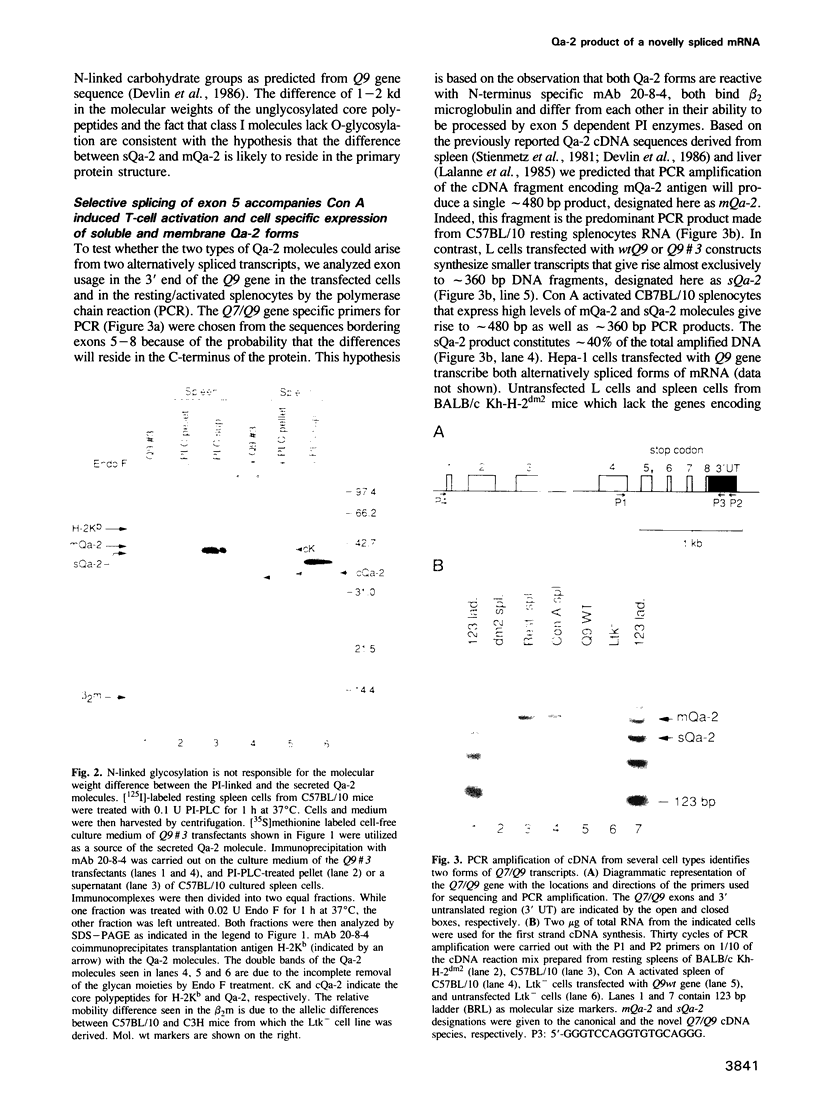
- Soloski M. J., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Qa-region class I gene expression: identification of a second class I gene, Q9, encoding a Qa-2 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3100–3104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloski M. J., Vernachio J., Einhorn G., Lattimore A. Qa gene expression: biosynthesis and secretion of Qa-2 molecules in activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2949–2953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Moore K. W., Frelinger J. G., Sher B. T., Shen F. W., Boyse E. A., Hood L. A pseudogene homologous to mouse transplantation antigens: transplantation antigens are encoded by eight exons that correlate with protein domains. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. The gamma delta T cell receptor and class Ib MHC-related proteins: enigmatic molecules of immune recognition. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):895–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I. Molecules related to class-I major histocompatibility complex antigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I., Soloski M., Low M. G., Hood L. A single gene encodes soluble and membrane-bound forms of the major histocompatibility Qa-2 antigen: anchoring of the product by a phospholipid tail. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
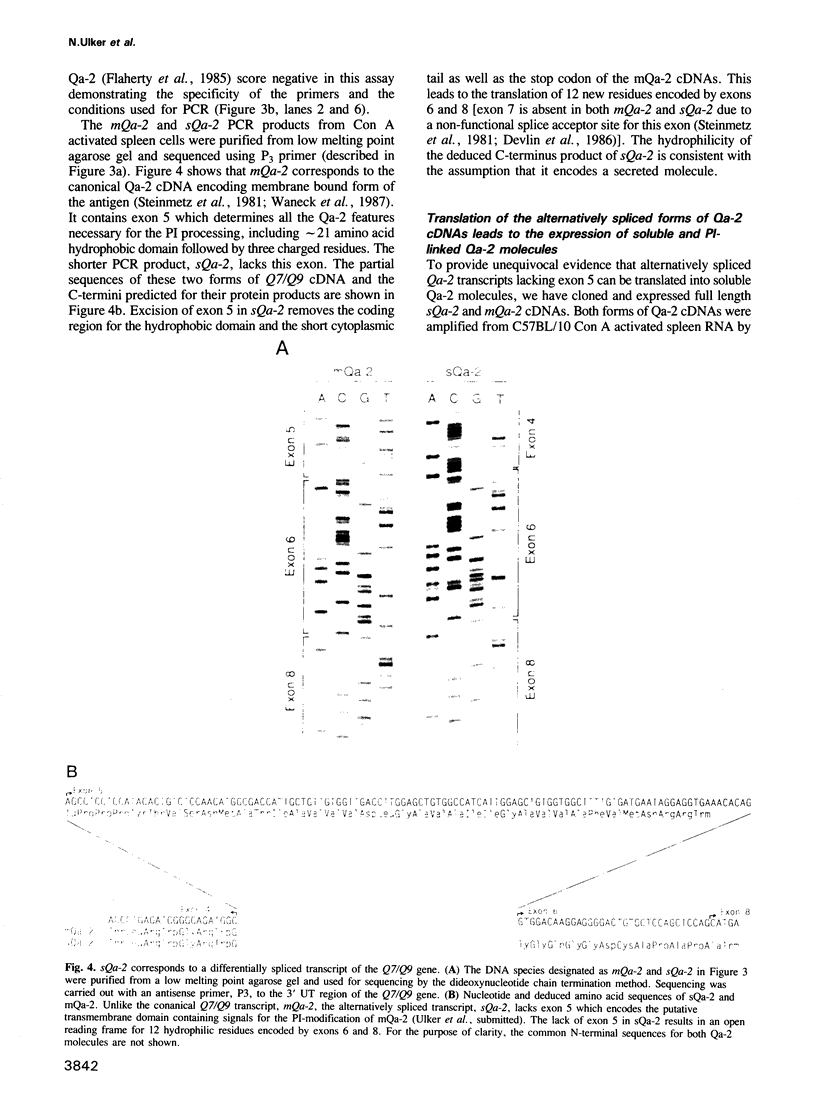
- Ulker N., Hood L. E., Stroynowski I. Molecular signals for phosphatidylinositol modification of the Qa-2 antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2214–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulker N., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus replication in human amnion U cells by cloned human gamma-interferon. I. Effect on early and late stages of the viral multiplication cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4319–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernachio J., Li M., Donnenberg A. D., Soloski M. J. Qa-2 expression in the adult murine thymus. A unique marker for a mature thymic subset. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):48–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waneck G. L., Sherman D. H., Calvin S., Allen H., Flavell R. A. Tissue-specific expression of cell-surface Qa-2 antigen from a transfected Q7b gene of C57BL/10 mice. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1358–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waneck G. L., Sherman D. H., Kincade P. W., Low M. G., Flavell R. A. Molecular mapping of signals in the Qa-2 antigen required for attachment of the phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):577–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S., Davis A. C., Gaut B., Wheeler C., Hill L., Goodenow R. S. Organization and structure of the Qa genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the C3H mouse: implications for Qa function and class I evolution. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1749–1759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamoyska R., Vollmer A. C., Sizer K. C., Liaw C. W., Parnes J. R. Two Lyt-2 polypeptides arise from a single gene by alternative splicing patterns of mRNA. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Scholl R., Browse J., Somerville C. Double stranded DNA sequencing as a choice for DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1220–1220. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]