Abstract
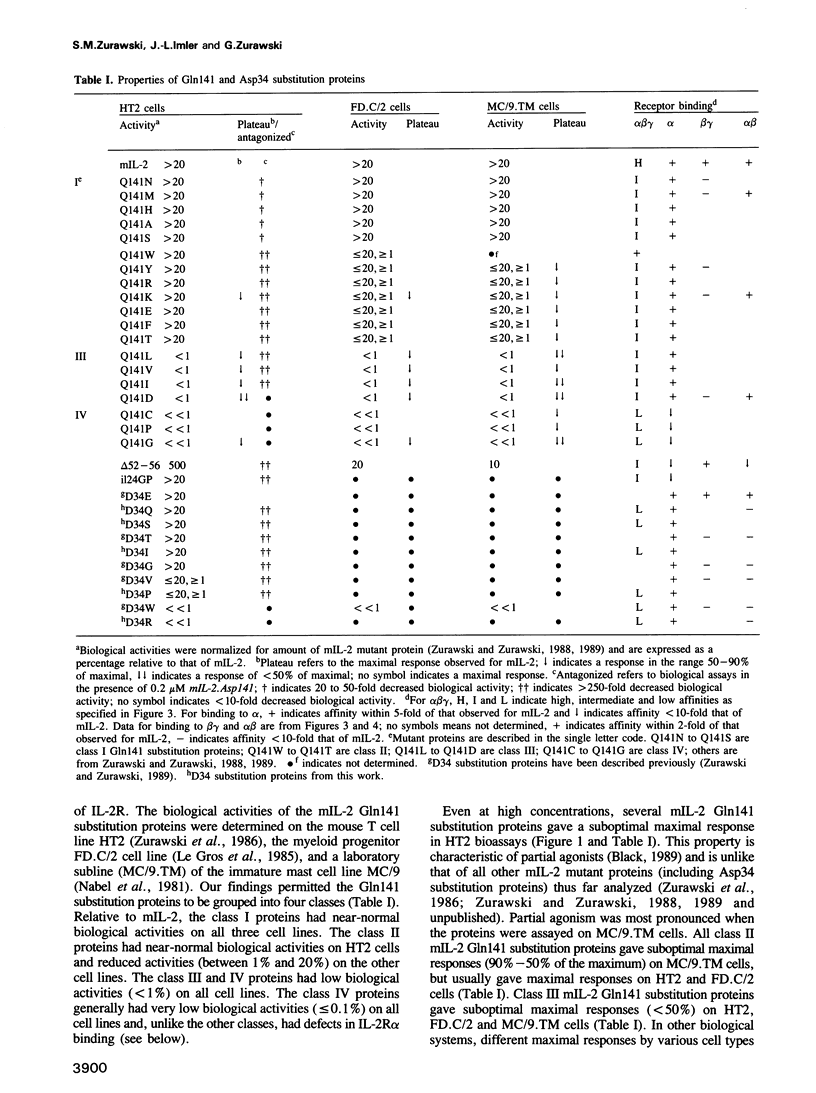
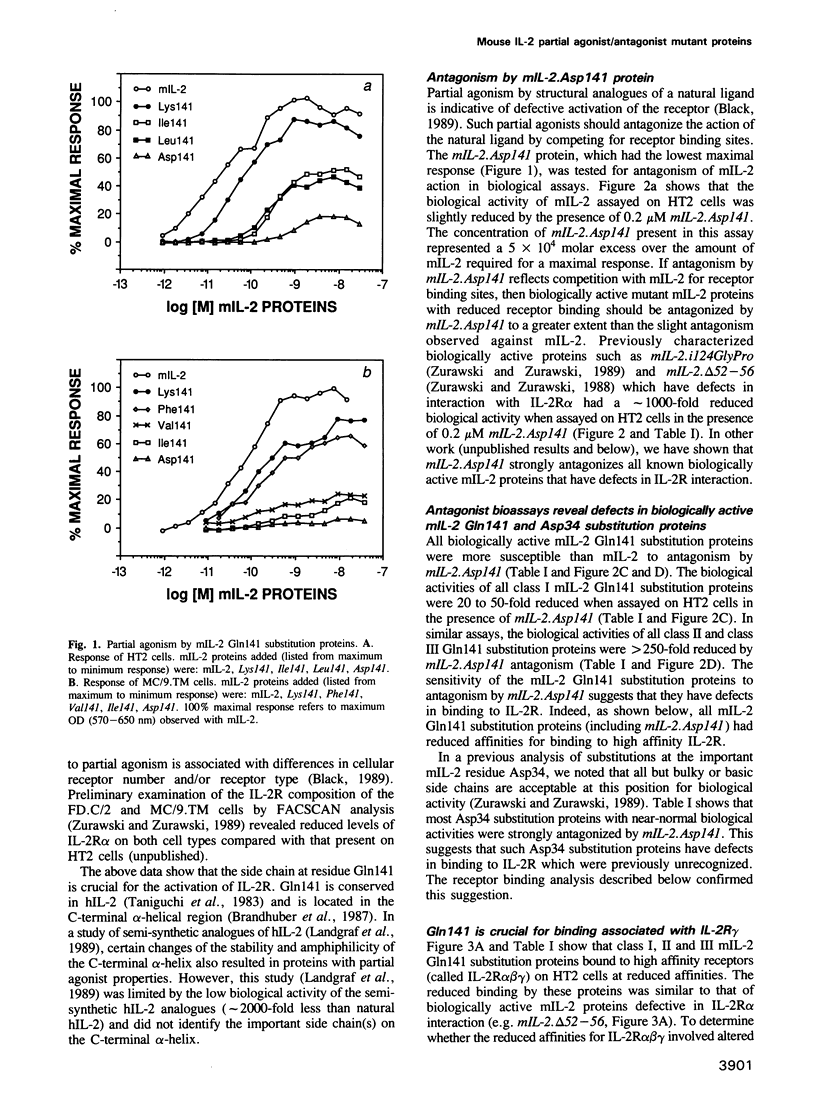
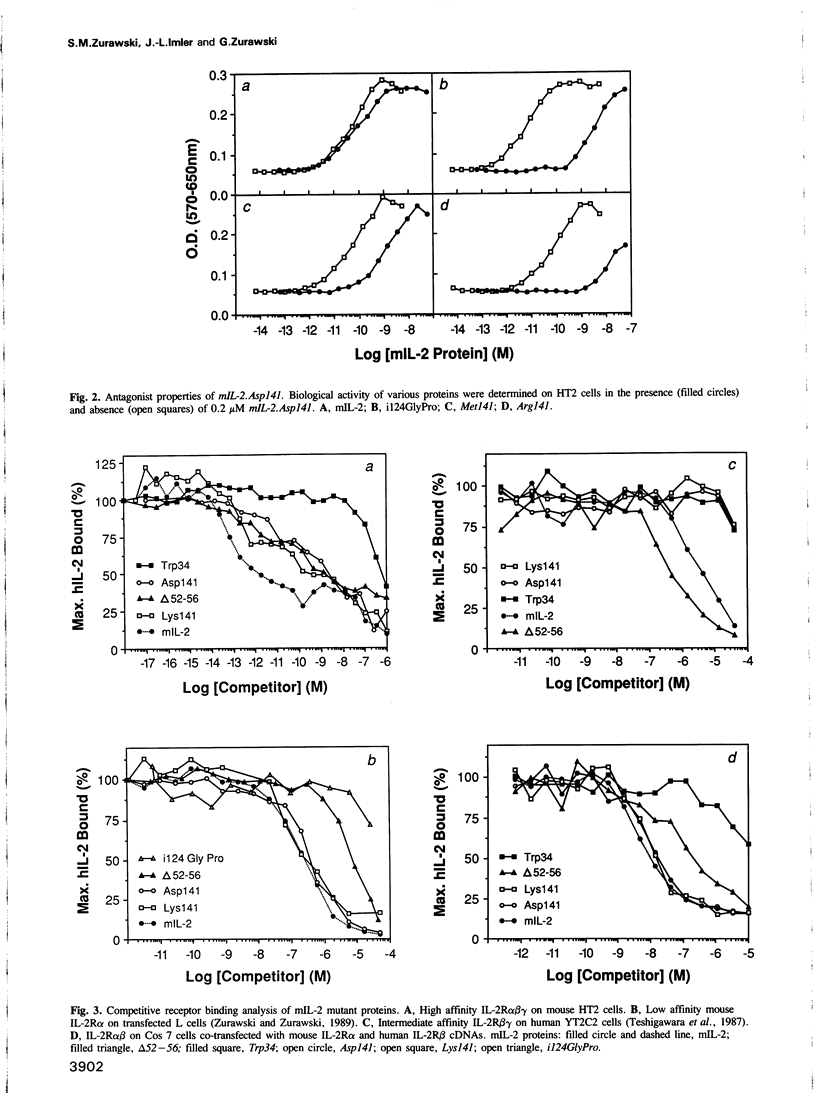
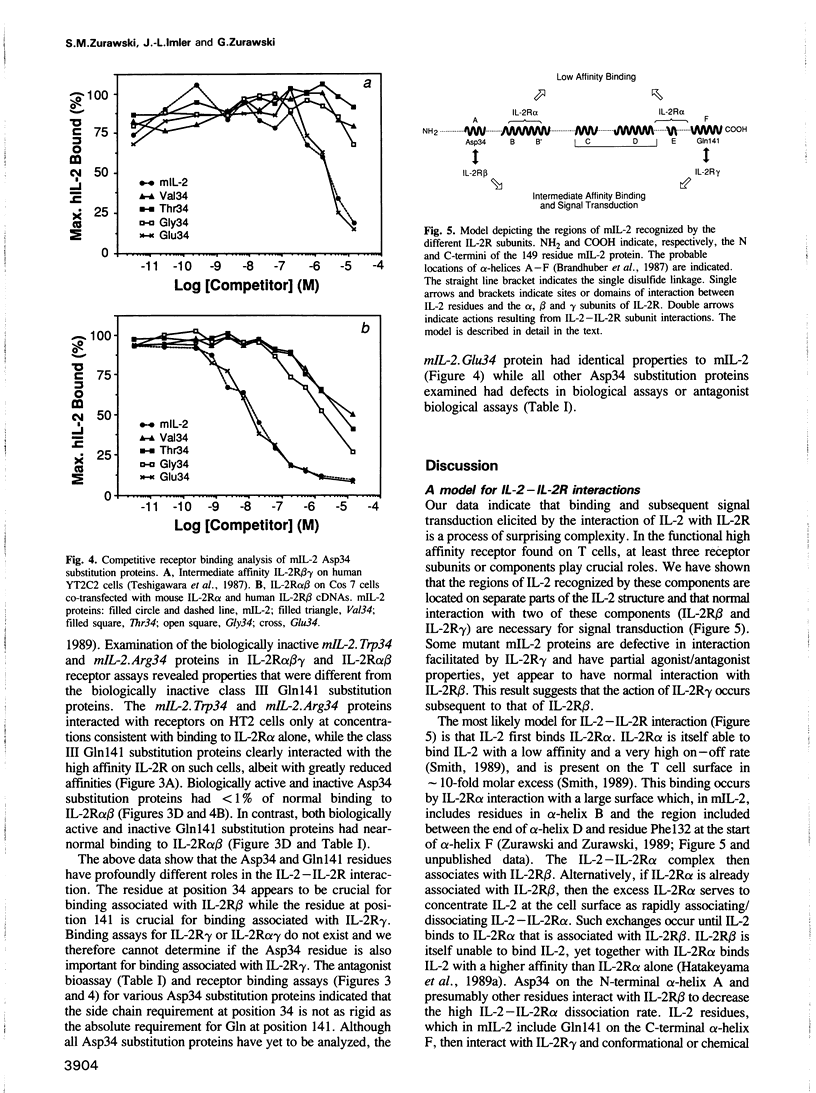
Some mouse interleukin-2 (mIL-2) proteins with substitutions at residue Gln141 are unable to trigger a maximal biological response. The Asp141 protein induces the lowest maximal response. The Asp141 protein can weakly antagonize the biological activity of mIL-2 and strongly antagonizes the biological activity of active mIL-2 mutant proteins that have defects in interactions with the high affinity receptor. Residue 141 mutant proteins bind with reduced affinity to T cells expressing the high affinity IL-2 receptor, yet bind normally to transfected fibroblasts expressing only the alpha and beta chains of the receptor. These results suggest that a third receptor component is important for both binding and signal transduction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bich-Thuy L. T., Dukovich M., Peffer N. J., Fauci A. S., Kehrl J. H., Greene W. C. Direct activation of human resting T cells by IL 2: the role of an IL 2 receptor distinct from the Tac protein. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1550–1556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. Drugs from emasculated hormones: the principle of syntopic antagonism. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):486–493. doi: 10.1126/science.2569237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandhuber B. J., Boone T., Kenney W. C., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of interleukin-2. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1707–1709. doi: 10.1126/science.3500515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L., Tsien W. H., Seals C., Hakimi J., Weber D., Bailon P., Hoskings J., Greene W. C., Toome V., Ju G. Identification of specific residues of human interleukin 2 that affect binding to the 70-kDa subunit (p70) of the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7709–7713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Tsudo M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Doi T., Miyata T., Miyasaka M., Taniguchi T. Interleukin-2 receptor beta chain gene: generation of three receptor forms by cloned human alpha and beta chain cDNA's. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):551–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2785715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Collins L., Kaffka K. L., Tsien W. H., Chizzonite R., Crowl R., Bhatt R., Kilian P. L. Structure-function analysis of human interleukin-2. Identification of amino acid residues required for biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5723–5731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf B., Cohen F. E., Smith K. A., Gadski R., Ciardelli T. L. Structural significance of the C-terminal amphiphilic helix of interleukin-2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):816–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gros G. S., Gillis S., Watson J. D. Induction of IL 2 responsiveness in a murine IL 3-dependent cell line. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4009–4014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Malek T. R., Leonard W. J., Greene W. C., Shevach E. M., Germain R. N. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a mouse interleukin 2 receptor cDNA. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4212–4217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Dvorak H. F., Cantor H. Inducer T lymphocytes synthesize a factor that stimulates proliferation of cloned mast cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):332–334. doi: 10.1038/291332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Shimizu A., Ishida N., Sabe H., Teshigawara K., Maeda M., Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Honjo T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):631–635. doi: 10.1038/311631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragovi H., Malek T. R. Evidence for additional subunits associated to the mouse interleukin 2 receptor p55/p75 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel U., Meyer M., Sebald W. Mutant proteins of human interleukin 2. Renaturation yield, proliferative activity and receptor binding. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Mosmann T. R., Benedik M., Zurawski G. Alterations in the amino-terminal third of mouse interleukin 2: effects on biological activity and immunoreactivity. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3354–3360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Identification of three critical regions within mouse interleukin 2 by fine structural deletion analysis. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1061–1069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Mouse interleukin-2 structure-function studies: substitutions in the first alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p70 receptor binding and mutations in the fifth alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p55 receptor binding. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2583–2590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



