Abstract
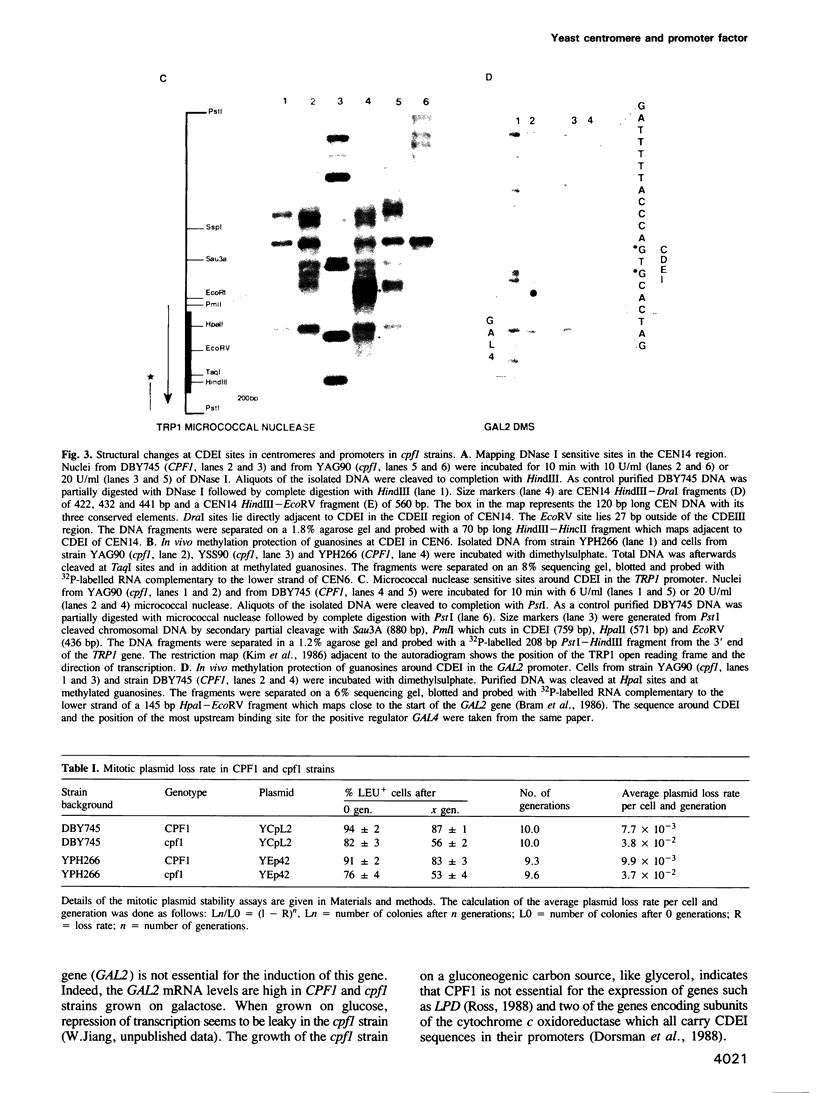
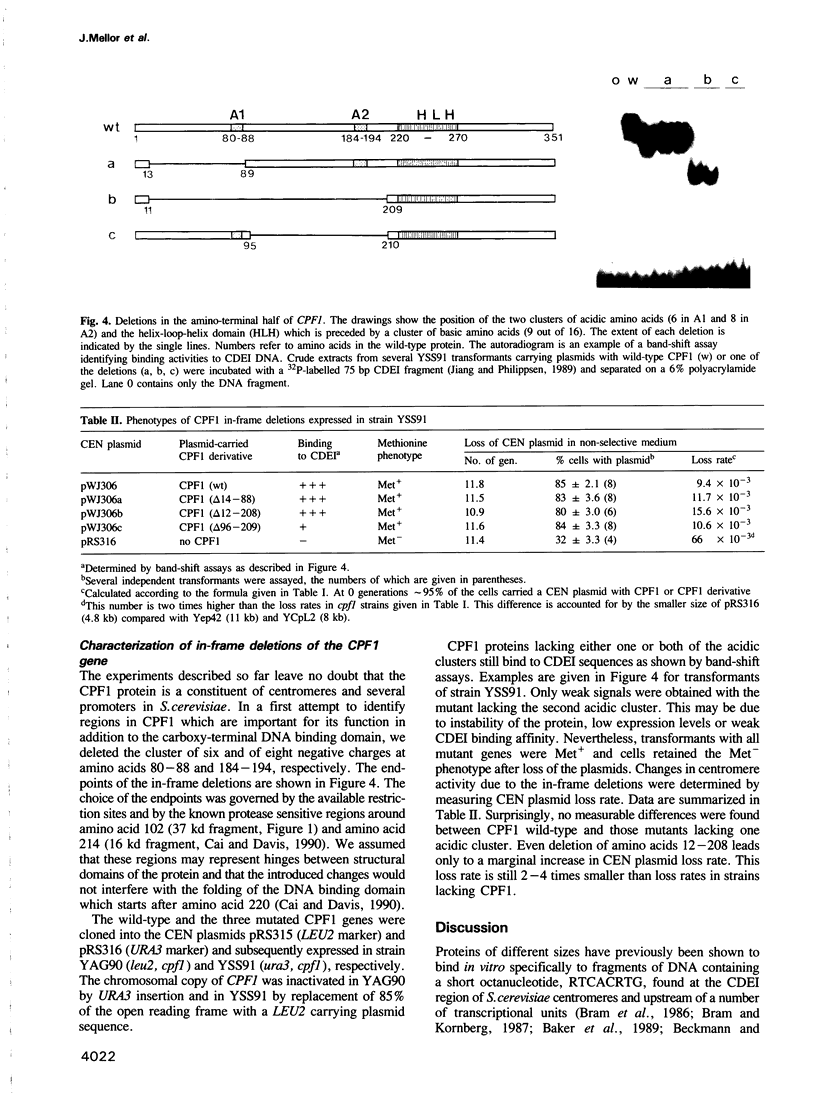
Centromeres and several promoters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae contain a highly conserved octanucleotide, RTCACRTG, called CDEI. Using biochemical, genetic and structural analyses, we show that the same protein binds in vivo to CDEI sites in centromeres and in promoters. This protein, called CPF1 for centromere promoter factor, binds DNA as a dimer. Inactivation of the gene is not lethal but leads to a partial loss of the centromere function and to a Met- phenotype. Changes of the chromatin structure due to inactivation of CPF1 are seen at centromeres and at several CDEI-carrying promoters (e.g. MET25, TRP1, GAL2). However promoter activities are affected in diverse ways making it presently difficult to describe a function for CPF1 in gene expression. The sequence of the cloned gene reveals in the carboxy-terminal part two potential amphipathic helices preceded by a positively charged stretch of amino acids very similar to the helix-loop-helix domains recently identified in factors controlling tissue specific transcription in higher eukaryotes. Carboxy-terminal truncations of CPF1 lacking this domain no longer bind to CDEI. The amino-terminal half of CPF1 carries two clusters of negatively charged amino acid residues. Surprisingly, deletions of these clusters still render cells Met+ and lead only to a marginal decrease in centromere activity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Fitzgerald-Hayes M., O'Brien T. C. Purification of the yeast centromere binding protein CP1 and a mutational analysis of its binding site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10843–10850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Masison D. C. Isolation of the gene encoding the Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere-binding protein CP1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2458–2467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Kadesch T. Identification of a yeast protein with properties similar to those of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer-binding protein NF-muE3. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4535–4540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Isolation of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA-binding protein, its human homolog, and its possible role as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):403–409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. A yeast ARS-binding protein activates transcription synergistically in combination with other weak activating factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M. J., Davis R. W. Purification of a yeast centromere-binding protein that is able to distinguish single base-pair mutations in its recognition site. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2544–2550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai M., Davis R. W. Yeast centromere binding protein CBF1, of the helix-loop-helix protein family, is required for chromosome stability and methionine prototrophy. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):437–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90525-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Cheng J. T., Tasi L. H., Schneider N., Buchanan G., Carroll A., Crist W., Ozanne B., Siciliano M. J., Baer R. The tal gene undergoes chromosome translocation in T cell leukemia and potentially encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):415–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A. A yeast protein possesses the DNA-binding properties of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):820–822. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottarel G., Shero J. H., Hieter P., Hegemann J. H. A 125-base-pair CEN6 DNA fragment is sufficient for complete meiotic and mitotic centromere functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3342–3349. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberledge S., Carbon J. Mutational analysis of meiotic and mitotic centromere function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):203–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Identification of two factors which bind to the upstream sequences of a number of nuclear genes coding for mitochondrial proteins and to genetic elements important for cell division in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7287–7301. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Statistical positioning of nucleosomes by specific protein-binding to an upstream activating sequence in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 5;204(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90603-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita A., Kikuchi Y., Kuhara S., Misumi Y., Matsumoto S., Kobayashi H. Domains of the SFL1 protein of yeasts are homologous to Myc oncoproteins or yeast heat-shock transcription factor. Gene. 1989 Dec 28;85(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk M., Hegemann J. H., Philippsen P. Chromatin digestion with restriction endonucleases reveals 150-160 bp of protected DNA in the centromere of chromosome XIV in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):153–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00261171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Mutants of GAL4 protein altered in an activation function. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann J. H., Shero J. H., Cottarel G., Philippsen P., Hieter P. Mutational analysis of centromere DNA from chromosome VI of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2523–2535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Pridmore D., Hegemann J. H., Thomas M., Davis R. W., Philippsen P. Functional selection and analysis of yeast centromeric DNA. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. D., Philippsen P. Purification of a protein binding to the CDEI subregion of Saccharomyces cerevisiae centromere DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5585–5593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. An AT rich region of dyad symmetry is a promoter element in the yeast TRP1 gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Mar;211(3):472–476. doi: 10.1007/BF00425703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Multiple control elements in the TRP1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4251–4258. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa N., Oshima Y. Functional domains of a positive regulatory protein, PHO4, for transcriptional control of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2224–2236. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzeri L., Landonio L., Stotz A., Philippsen P. Role of conserved sequence elements in yeast centromere DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1867–1874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen J., Mellor J. Characterisation of sequences required for RNA initiation from the PGK promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3219–3225. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H., Jost J. P. Optimized genomic sequencing as a tool for the study of cytosine methylation in the regulatory region of the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Gene. 1986;42(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D., Cherest H., Surdin-Kerjan Y. Elements involved in S-adenosylmethionine-mediated regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae MET25 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3292–3298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K., Hörz W., Hinnen A. The two positively acting regulatory proteins PHO2 and PHO4 physically interact with PHO5 upstream activation regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2050–2057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]