Abstract
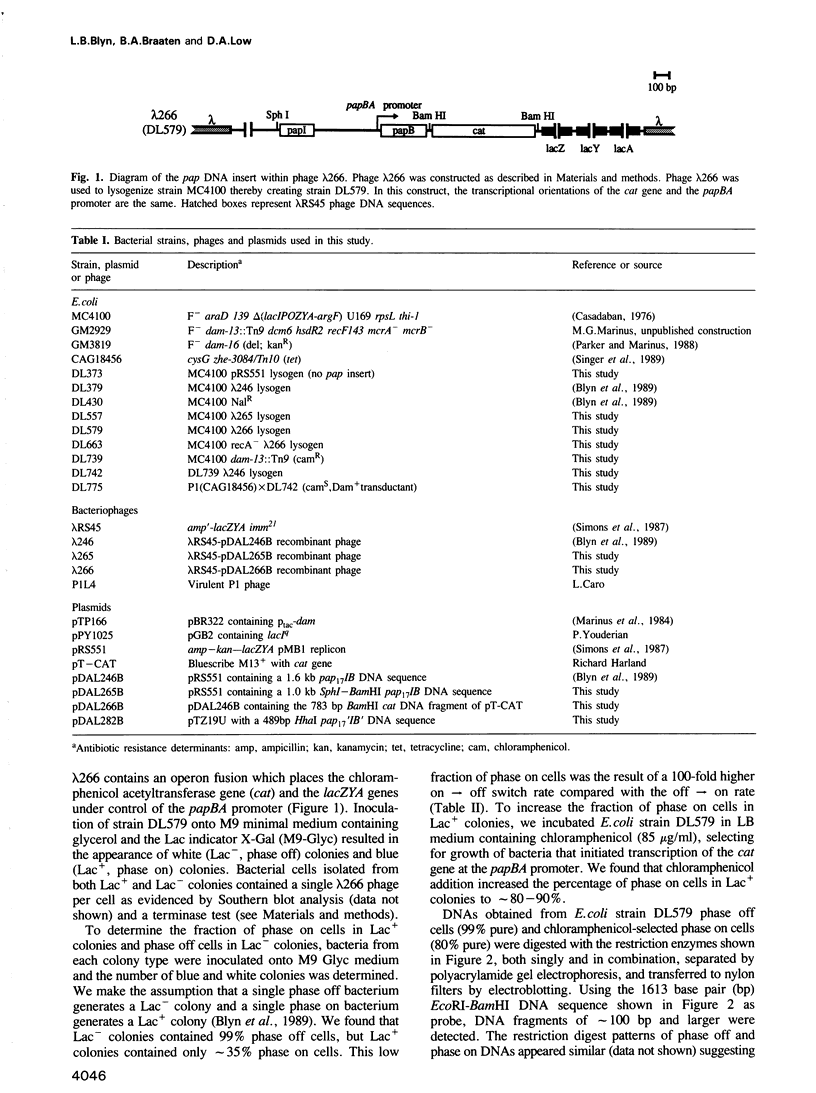
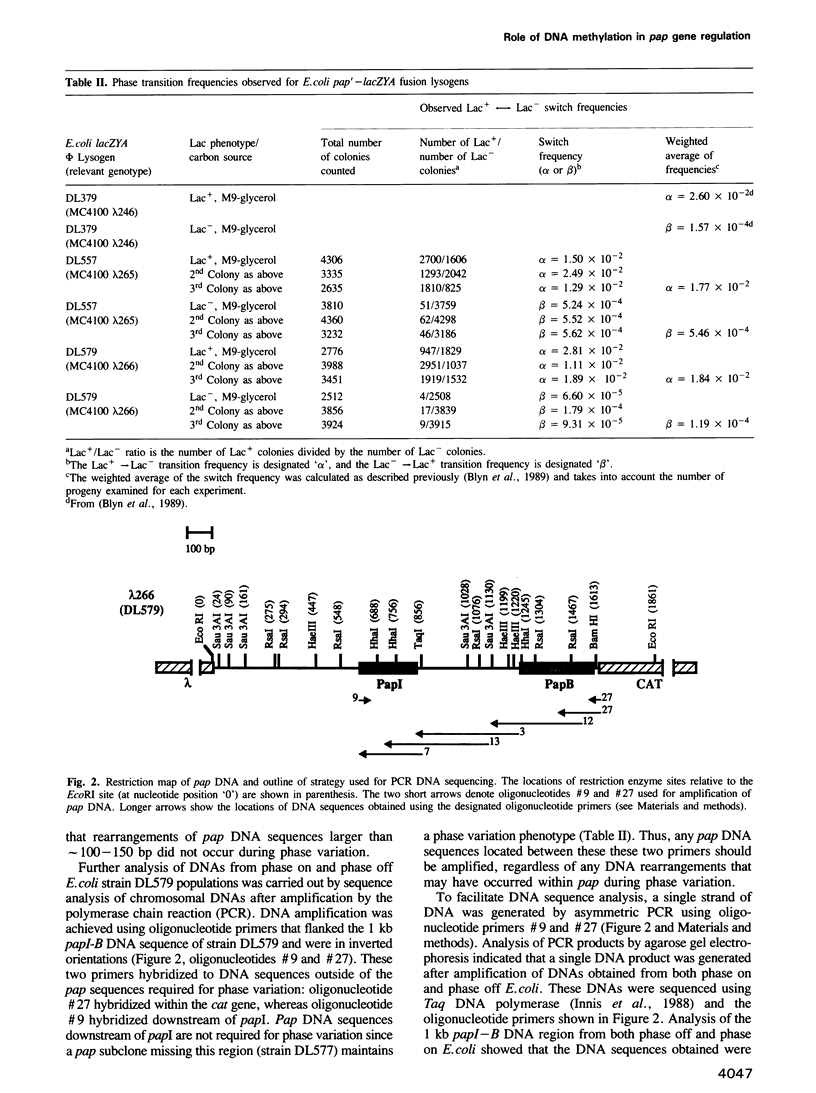
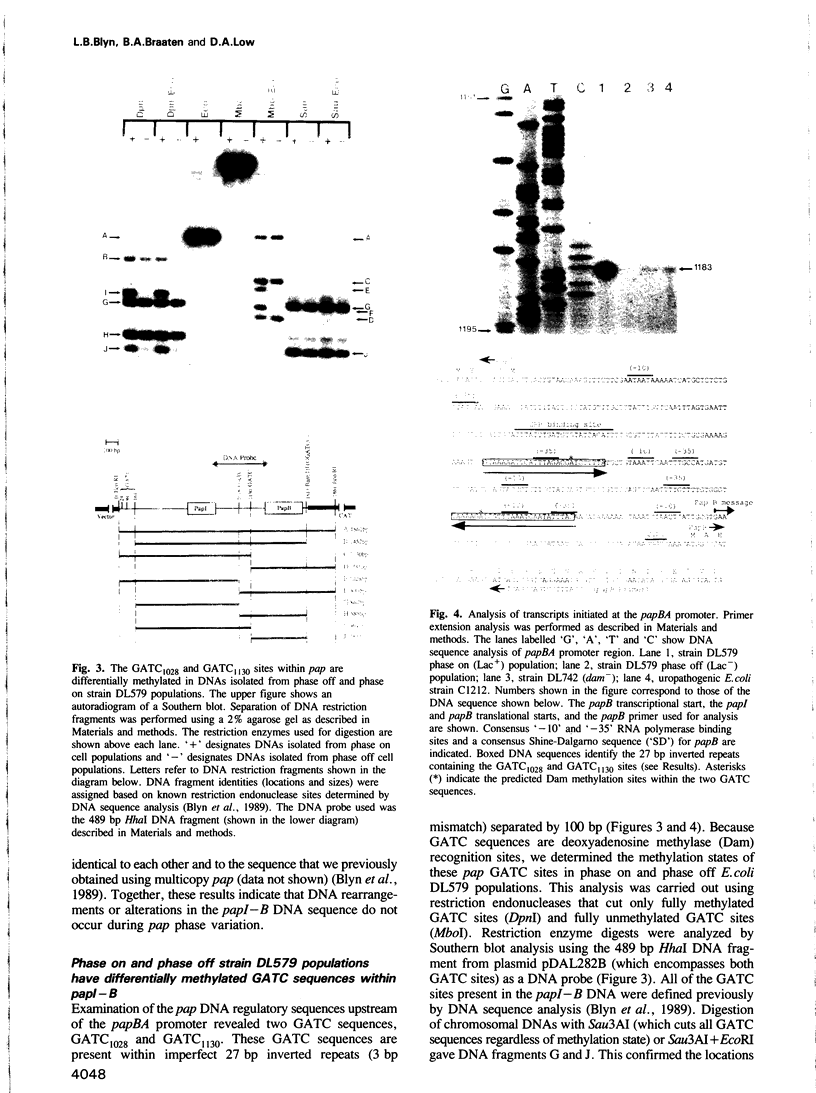
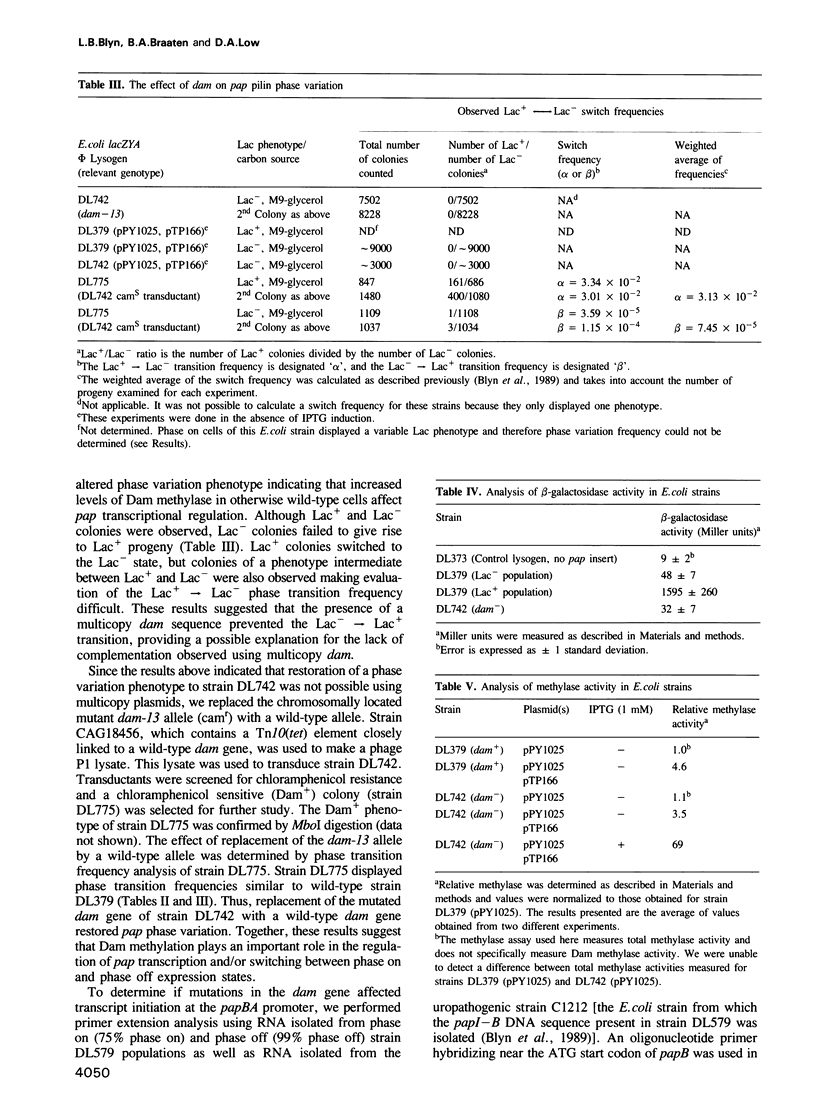
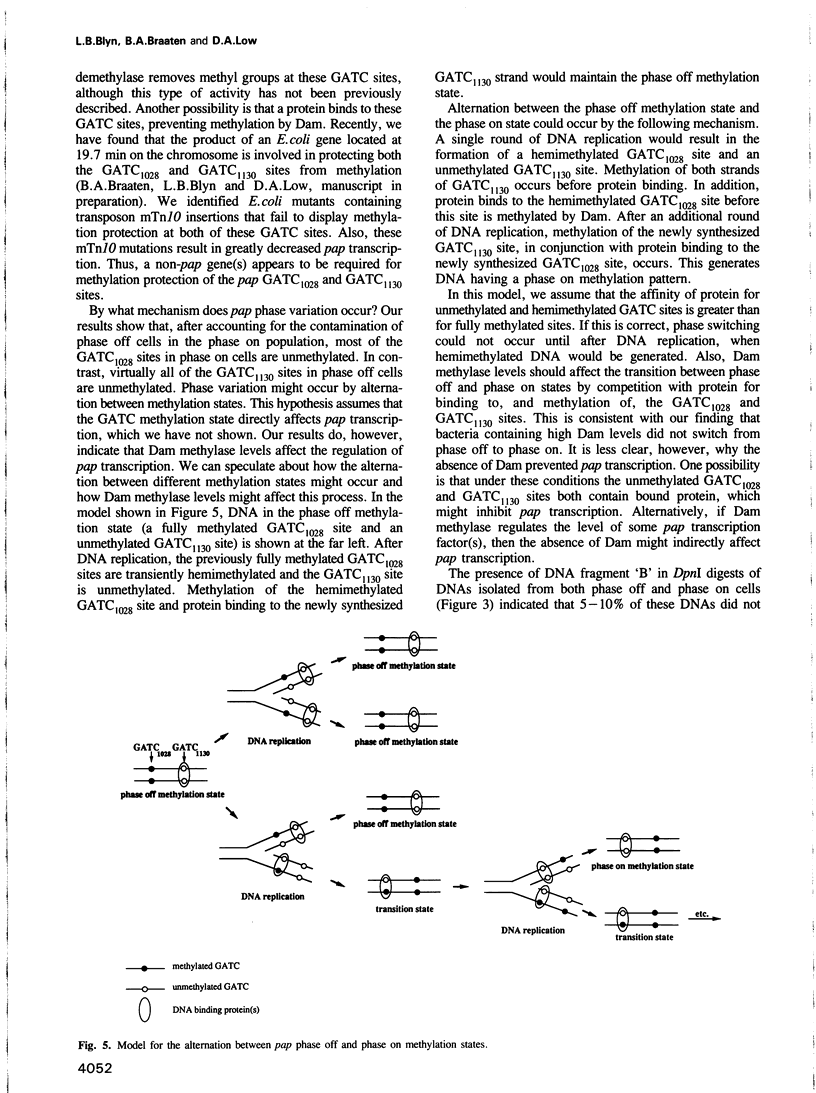
Transcription of the pap pilin (papA) gene in Escherichia coli is subject to control by a heritable phase variation mechanism in which alternation between transcriptionally active (phase on) and inactive (phase off) states occurs. Our results suggest that phase switching occurs without DNA rearrangement of pap DNA sequences, distinguishing this system from those described for E. coli type 1 pili and Salmonella flagellar phase variation. Analysis of the regulatory region upstream of papA in DNAs isolated from phase off and phase on cell populations showed that two deoxyadenosine methylase (Dam) sites, GATC1028 and GATC1130, were present. Southern blot analysis of MboI and DpnI restriction digests of DNAs showed that the GATC1028 site was unmethylated only in DNA isolated from phase on populations. Conversely, GATC1130 sites were unmethylated in DNA isolated from phase off populations. The presence of unmethylated GATC sites in E. coli is unusual and to our knowledge has not been previously reported. These results suggest that the methylation states of GATC1028 and GATC1130 may regulate pap transcription. Consistent with this hypothesis, Dam methylase levels affected the regulation of pap transcription; papA transcription was absent in dam- E. coli. Moreover, transition from the phase off to phase on state was not observed in E. coli expressing aberrantly high levels of Dam. A basic model is presented which outlines a possible mechanism by which alternation between phase off and phase on methylation states could occur.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Freitag C. S., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. An invertible element of DNA controls phase variation of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5724–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyn L. B., Braaten B. A., White-Ziegler C. A., Rolfson D. H., Low D. A. Phase-variation of pyelonephritis-associated pili in Escherichia coli: evidence for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):613–620. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Båga M., Göransson M., Normark S., Uhlin B. E. Transcriptional activation of a pap pilus virulence operon from uropathogenic Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3887–3893. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsman K., Göransson M., Uhlin B. E. Autoregulation and multiple DNA interactions by a transcriptional regulatory protein in E. coli pili biogenesis. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitag C. S., Abraham J. M., Clements J. R., Eisenstein B. I. Genetic analysis of the phase variation control of expression of type 1 fimbriae in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):668–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.668-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier G. E., Modrich P. Recognition sequence of the dam methylase of Escherichia coli K12 and mode of cleavage of Dpn I endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Forsman K., Uhlin B. E. Regulatory genes in the thermoregulation of Escherichia coli pili gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):123–130. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Forsman P., Nilsson P., Uhlin B. E. Upstream activating sequences that are shared by two divergently transcribed operons mediate cAMP-CRP regulation of pilus-adhesin in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1557–1565. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. S., Brinton C. C., Jr Identification and characterization of E. coli type-1 pilus tip adhesion protein. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):265–268. doi: 10.1038/332265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K. T., Youderian P., Simon M. I. Phase variation in Salmonella: analysis of Hin recombinase and hix recombination site interaction in vivo. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):937–948. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Myambo K. B., Gelfand D. H., Brow M. A. DNA sequencing with Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction-amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9436–9440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch H., Heesemann J., Laufs R., Kroll H. P., Kaper J. B., Levine M. M. Serological response to type 1-like somatic fimbriae in diarrheal infection due to classical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1987 Jun;2(6):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F. P., Lund B., Normark S. Genes of pyelonephritogenic E. coli required for digalactoside-specific agglutination of human cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1167–1173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low D., Robinson E. N., Jr, McGee Z. A., Falkow S. The frequency of expression of pyelonephritis-associated pili is under regulatory control. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):335–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Morris N. R. Biological function for 6-methyladenine residues in the DNA of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):309–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinus M. G., Poteete A., Arraj J. A. Correlation of DNA adenine methylase activity with spontaneous mutability in Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1984 Apr;28(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer W., Noyer-Weidner M. Timing and targeting: the biological functions of Dam methylation in E. coli. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90911-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Thomas R. Ter, a function which generates the ends of the mature lambda chromosome. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):242–244. doi: 10.1038/221242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden G. B., Pratt M. J., Schaechter M. The replicative origin of the E. coli chromosome binds to cell membranes only when hemimethylated. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B., Marinus M. G. A simple and rapid method to obtain substitution mutations in Escherichia coli: isolation of a dam deletion/insertion mutation. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. IS10 transposition is regulated by DNA adenine methylation. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Phase variation: genetic analysis of switching mutants. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):845–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Phase variation in Salmonella: genetic analysis of a recombinational switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):391–395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Zieg J., Simon M. Flagellar-phase variation: isolation of the rh1 gene. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):517–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.517-523.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N. Evidence that adenine methylation influences DNA-protein interactions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):490–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.490-493.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyf M., Avraham-Haetzni K., Reifman A., Shlomai J., Kaplan F., Oppenheim A., Razin A. DNA methylation pattern is determined by the intracellular level of the methylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Boslego J. W. Pilus vaccines. Vaccine. 1985 Mar;3(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(85)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Norgren M., Båga M., Normark S. Adhesion to human cells by Escherichia coli lacking the major subunit of a digalactoside-specific pilus-adhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1800–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Belasco J. G., Schottel J. L., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Decay of mRNA in Escherichia coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):653–657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]