Abstract
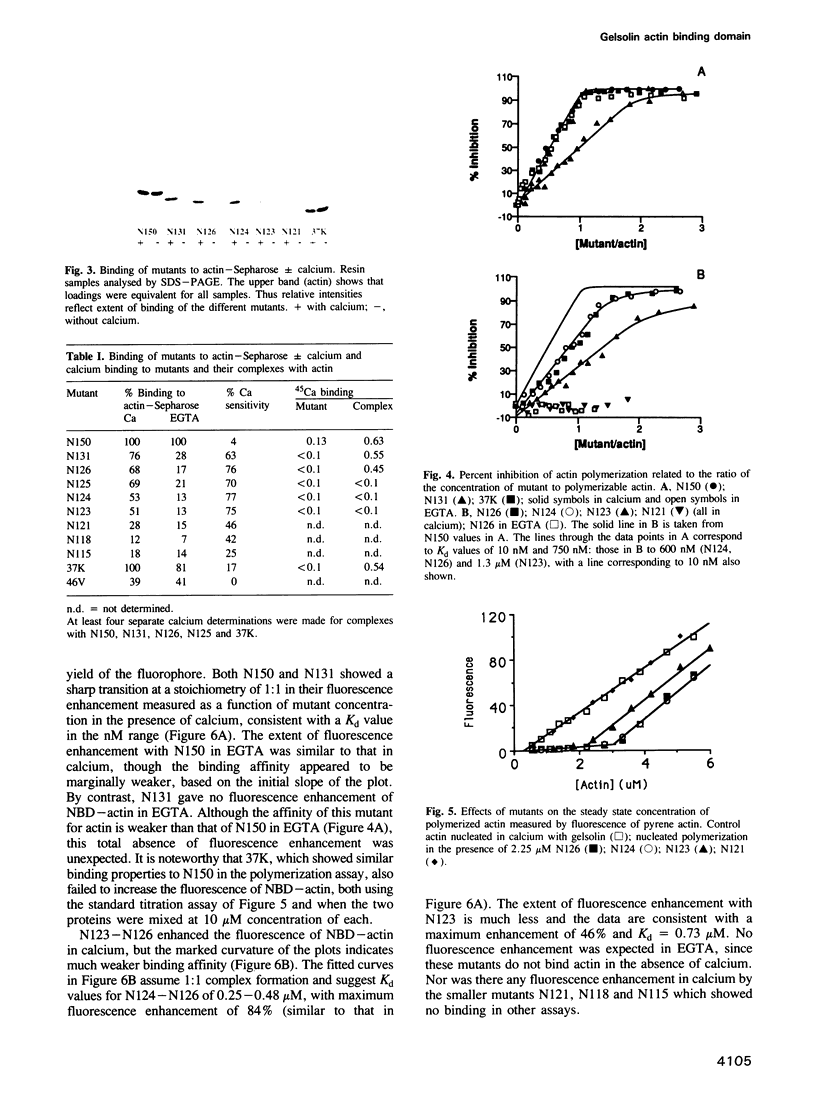
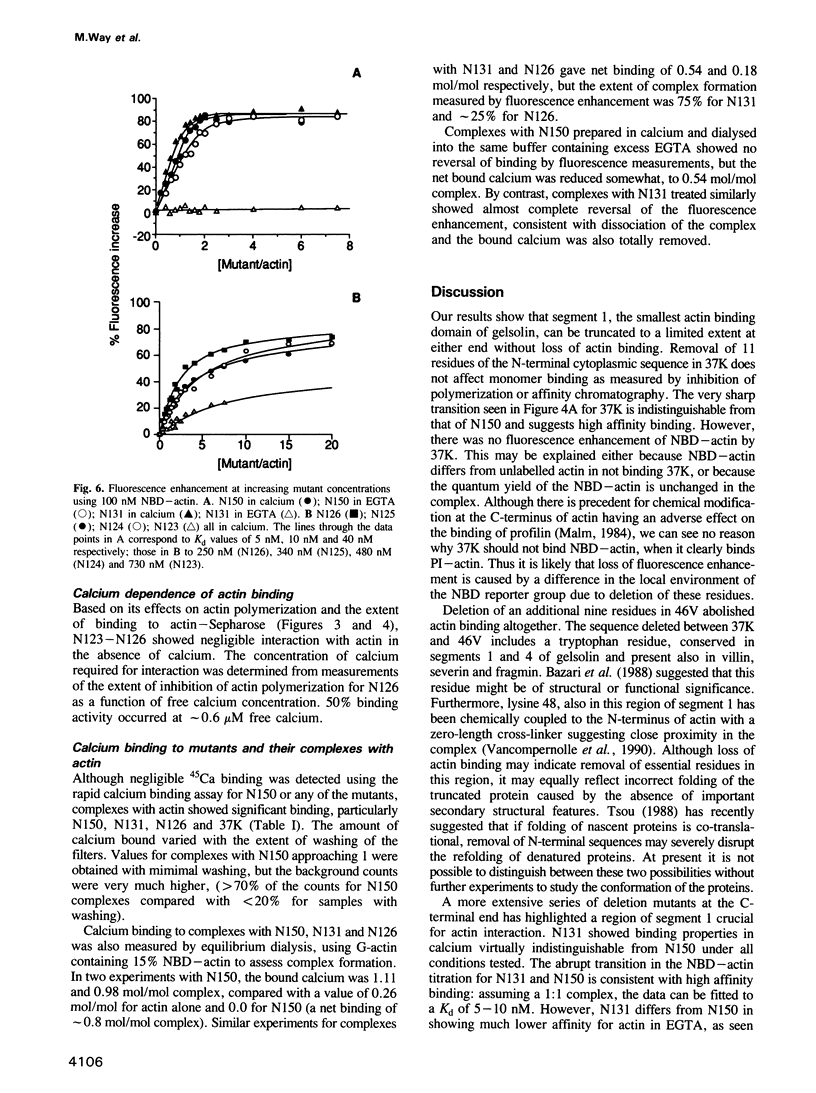
The actin severing and capping protein gelsolin contains three distinct actin binding sites. The smallest actin binding domain of approximately 15,000 Mr was originally obtained by limited proteolysis and it corresponds to the first of six repeating segments contained in the gelsolin sequence. We have expressed this domain (here termed segment 1 or N150 to define its amino acid length) in Escherichia coli, together with a series of smaller mutants truncated at either N- or C-terminal ends, in an attempt to localize residues critical of actin binding. Limited truncation of segment 1 by 11 residues at its N-terminal end has no observable effect on actin binding, but on removal of a further eight residues, actin binding is totally eliminated. Although this loss of actin binding may reflect ablation of critical residues, we cannot rule out the possibility that removal of these residues adversely affects the folding of the polypeptide chain during renaturation. Truncation at the C-terminus of segment 1 has a progressive effect on actin binding. Unlike intact segment 1, which shows no calcium sensitivity of actin binding within the resolution of our assays, a mutant with 19 residues deleted from its C-terminus shows unchanged affinity for actin in the presence of calcium, but approximately 100-fold weaker binding in its absence. Removal of an additional five residues from the C-terminus produces a mutant that binds actin only in calcium. Further limited truncation results in progressively weaker calcium dependent binding and all binding is eliminated when a total of 29 residues has been removed. Although none of the expressed proteins on their own binds calcium, 45Ca is trapped in the complexes, including the complex between actin and segment 1 itself. These results highlight a region close to the C-terminus of segment 1 that is essential for actin binding and demonstrate that calcium plays an important role in the high affinity actin binding by this domain of gelsolin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. E., Minamide L. S., Duester G., Bamburg J. R. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding chick brain actin depolymerizing factor. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 14;29(32):7414–7420. doi: 10.1021/bi00484a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The F-actin capping proteins of Physarum polycephalum: cap42(a) is very similar, if not identical, to fragmin and is structurally and functionally very homologous to gelsolin; cap42(b) is Physarum actin. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4149–4157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André E., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Noegel A. Severin, gelsolin, and villin share a homologous sequence in regions presumed to contain F-actin severing domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazari W. L., Matsudaira P., Wallek M., Smeal T., Jakes R., Ahmed Y. Villin sequence and peptide map identify six homologous domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4986–4990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. Gelsolin has three actin-binding sites. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1553–1562. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Kurth M. C. Actin-gelsolin interactions. Evidence for two actin-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7480–7487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. F., Pantaloni D., Korn E. D. Fluorescence measurements of the binding of cations to high-affinity and low-affinity sites on ATP-G-actin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10778–10784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Blum J. D., Pollard T. D. Acanthamoeba castellanii capping protein: properties, mechanism of action, immunologic cross-reactivity, and localization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):217–225. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershman L. C., Selden L. A., Estes J. E. High affinity binding of divalent cation to actin monomer is much stronger than previously reported. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Matsudaira P. T. Functional comparison of villin and gelsolin. Effects of Ca2+, KCl, and polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16738–16743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Janmey P. A., Yin H. L. Identification of critical functional and regulatory domains in gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1717–1726. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Mehl R., Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Yin H. L. Muscle is the major source of plasma gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8239–8243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Stossel T. P., Orkin S. H., Mole J. E., Colten H. R., Yin H. L. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):455–458. doi: 10.1038/323455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malm B. Chemical modification of Cys-374 of actin interferes with the formation of the profilactin complex. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 6;173(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki F., Matsumoto S., Yahara I., Yonezawa N., Nishida E., Sakai H. Cloning and characterization of porcine brain cofilin cDNA. Cofilin contains the nuclear transport signal sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11564–11568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama K., Nishida E., Yonezawa N., Sakai H., Matsumoto S., Iida K., Yahara I. Destrin, a mammalian actin-depolymerizing protein, is closely related to cofilin. Cloning and expression of porcine brain destrin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5768–5773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B., Gooch J., Hinssen H., Weeds A. G. Loss of calcium sensitivity of plasma gelsolin is associated with the presence of calcium ions during preparation. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81524-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B., Weeds A. G. Binding of pig plasma gelsolin to F-actin and partial fractionation into calcium-dependent and calcium-independent forms. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K., Yin H. L. End-label fingerprintings show that the N- and C-termini of actin are in the contact site with gelsolin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5269–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobacman L. S., Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. Effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on the pre-steady state kinetics of actin polymerization and on the concentration of F-actin at steady state. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8806–8812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou C. L. Folding of the nascent peptide chain into a biologically active protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1809–1812. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J. S., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D. Acanthamoeba actin and profilin can be cross-linked between glutamic acid 364 of actin and lysine 115 of profilin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J. Structural principles of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Gooch J., Pope B., Weeds A. G. Expression of human plasma gelsolin in Escherichia coli and dissection of actin binding sites by segmental deletion mutagenesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):593–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Weeds A. Actin-binding proteins. Cytoskeletal ups and downs. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):292–294. doi: 10.1038/344292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Weeds A. Nucleotide sequence of pig plasma gelsolin. Comparison of protein sequence with human gelsolin and other actin-severing proteins shows strong homologies and evidence for large internal repeats. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Harris H., Gratzer W., Gooch J. Interactions of pig plasma gelsolin with G-actin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):77–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Hartwig J. H., Maruyama K., Stossel T. P. Ca2+ control of actin filament length. Effects of macrophage gelsolin on actin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9693–9697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Iida K., Janmey P. A. Identification of a polyphosphoinositide-modulated domain in gelsolin which binds to the sides of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):805–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerle C. T., Patane K., Frieden C. Divalent cation binding to the high- and low-affinity sites on G-actin. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6545–6552. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]