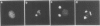Abstract
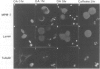
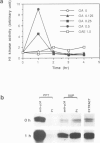
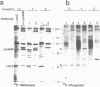
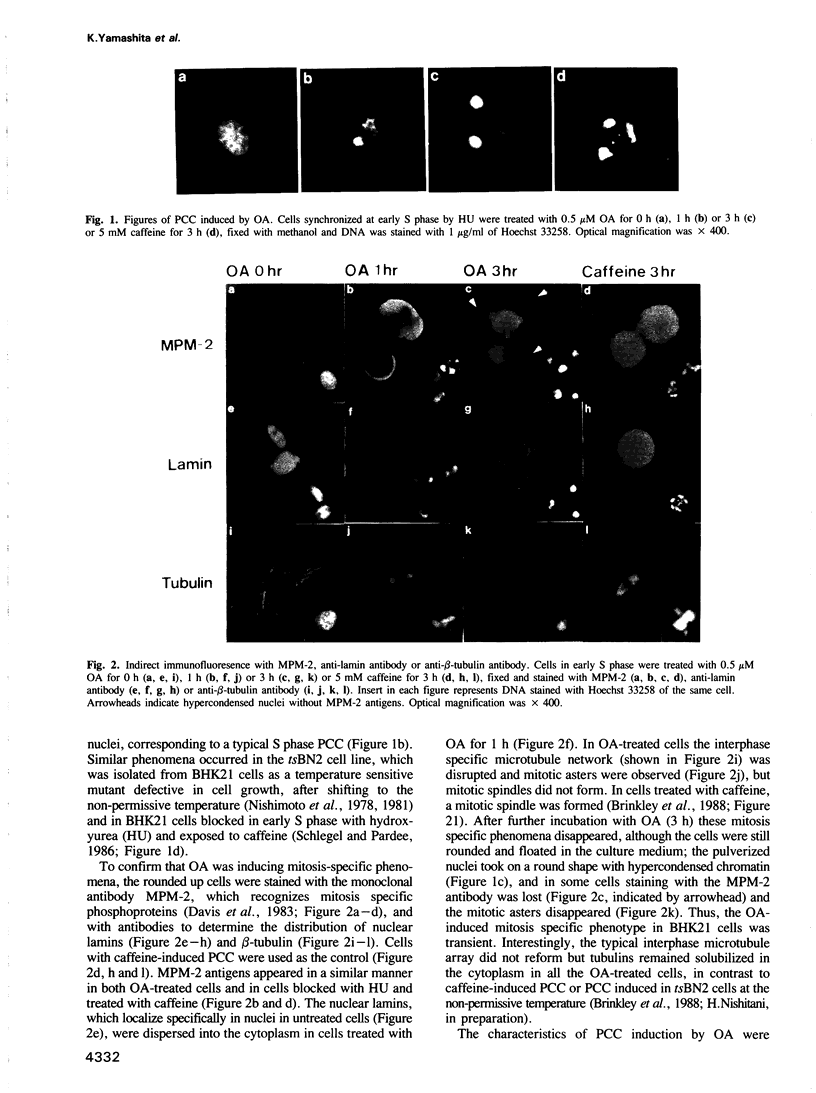
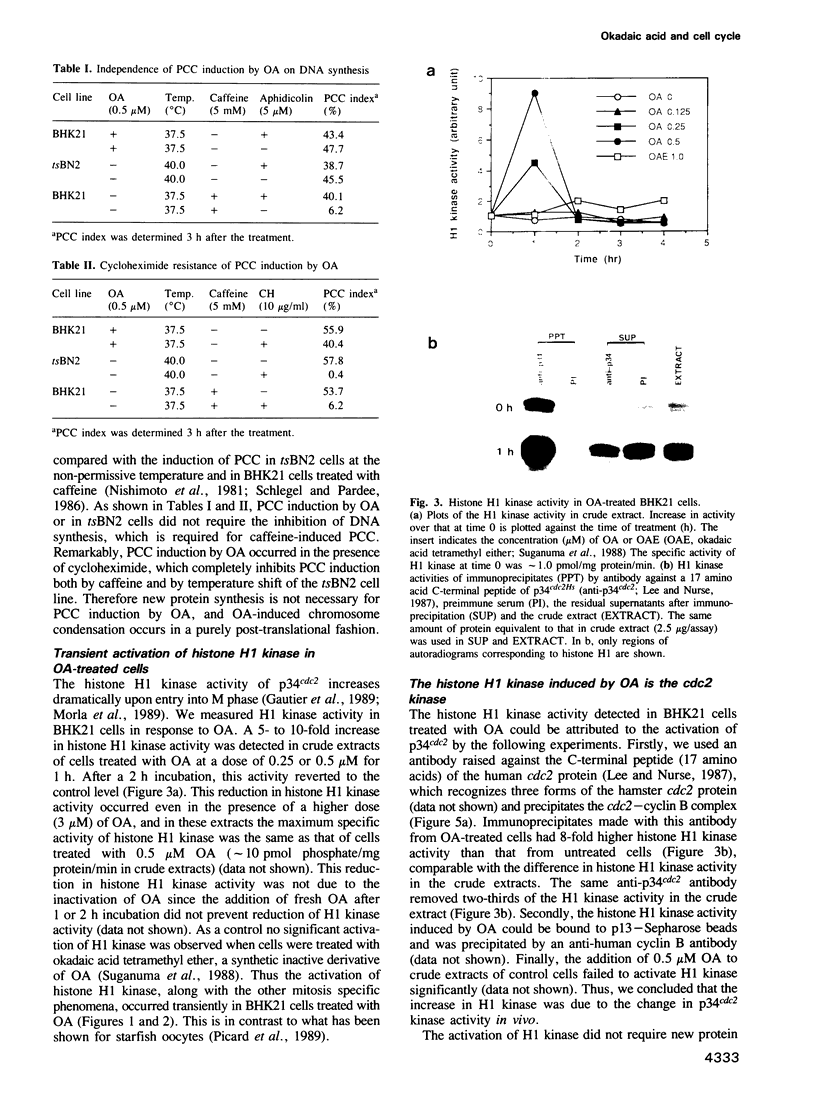
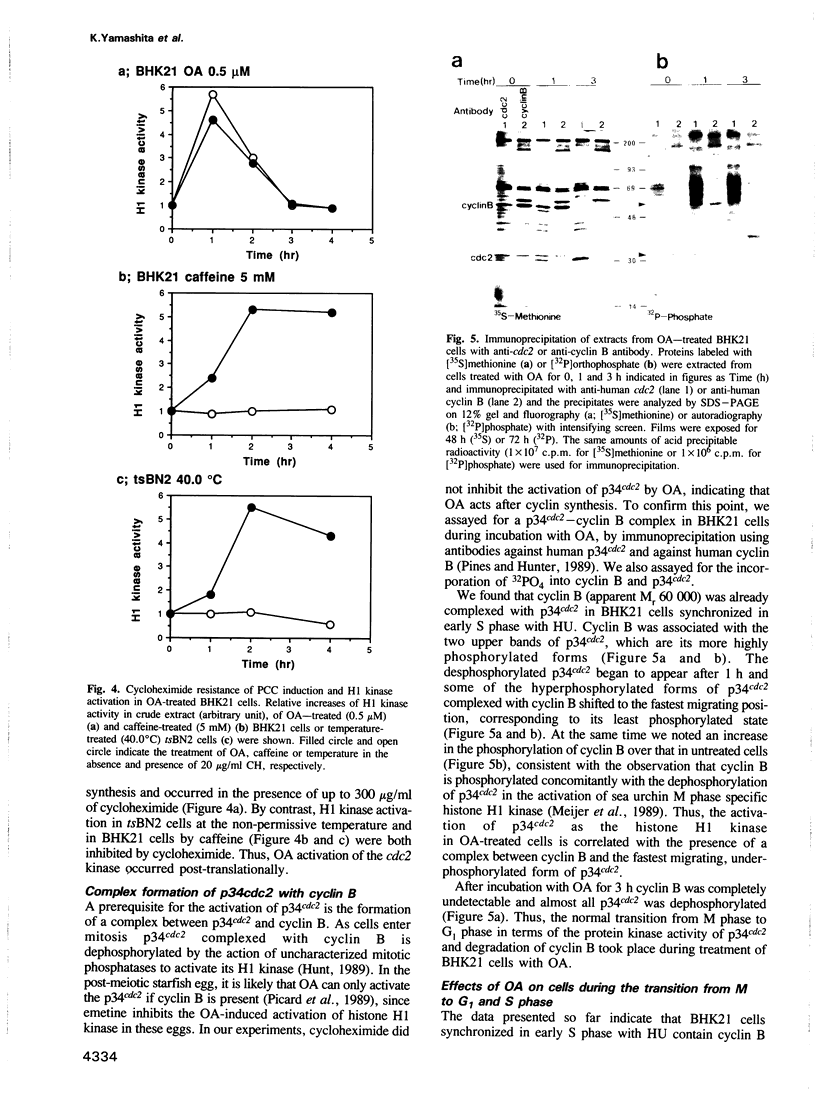
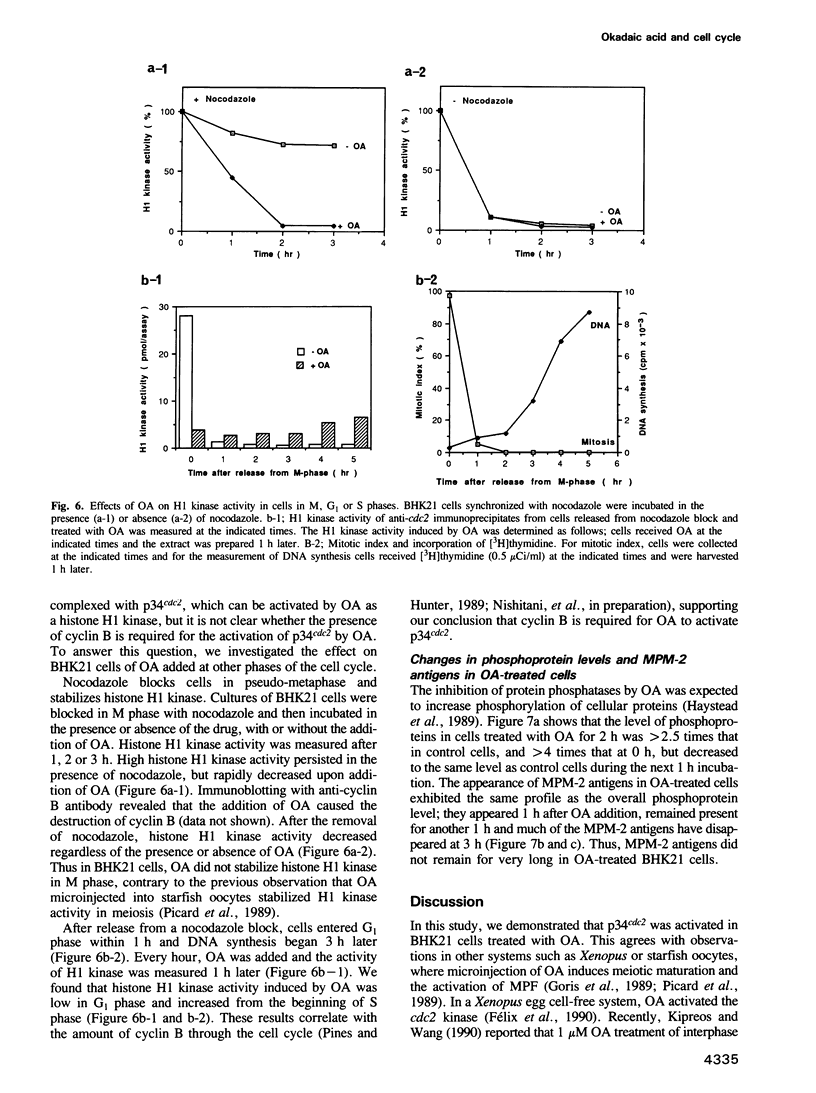
When BHK21 cells synchronized in early S phase were exposed to okadaic acid (OA), an inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, mitosis specific events such as premature chromosome condensation, the production of MPM-2 antigens, dispersion of nuclear lamins and the appearance of mitotic asters were induced, and then disappeared upon further incubation. These mitosis specific events occurred even in the presence of cycloheximide. Within 1 h of exposure to OA, cdc2/histone H1 kinase activity rose 10-fold compared with untreated controls, but returned to the control level upon further incubation. Using antibodies against either p34cdc2 or cyclin B it was found that p34cdc2 complexed with cyclin B was dephosphorylated after OA treatment concomitant with the activation of cdc2 kinase, and that cyclin B was subsequently degraded concomitant with a decrease in cdc2 kinase activity, as in normal mitosis. In contrast, when cells in G1 phase were treated with OA no increase in cdc2 kinase activity was observed. Moreover when cells in pseudo-metaphase induced by nocodazole were treated with OA, cdc2 kinase was inactivated. These results suggest that OA sensitive protein phosphatases control both the activation and inactivation of the p34cdc2 kinase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R., Zinkowski R. P., Mollon W. L., Davis F. M., Pisegna M. A., Pershouse M., Rao P. N. Movement and segregation of kinetochores experimentally detached from mammalian chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):251–254. doi: 10.1038/336251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of MPF activity in vitro. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. The bimG gene of Aspergillus nidulans, required for completion of anaphase, encodes a homolog of mammalian phosphoprotein phosphatase 1. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Picard A. M phase-promoting factor: its identification as the M phase-specific H1 histone kinase and its activation by dephosphorylation. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:39–51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Matsukawa T., Nurse P., Maller J. Dephosphorylation and activation of Xenopus p34cdc2 protein kinase during the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):626–629. doi: 10.1038/339626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Hermann J., Hendrix P., Ozon R., Merlevede W. Okadaic acid, a specific protein phosphatase inhibitor, induces maturation and MPF formation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heald R., McKeon F. Mutations of phosphorylation sites in lamin A that prevent nuclear lamina disassembly in mitosis. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):579–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Embryology. Under arrest in the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):483–484. doi: 10.1038/342483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Martin T., Richter W. W., Olson M., Fujiki H. Hyperphosphorylation of N-60, a protein structurally and immunologically related to nucleolin after tumour-promoter treatment. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1621–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipreos E. T., Wang J. Y. Differential phosphorylation of c-Abl in cell cycle determined by cdc2 kinase and phosphatase activity. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2183353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Capony J. P., Caput D., Cavadore J. C., Derancourt J., Kaghad M., Lelias J. M., Picard A., Dorée M. MPF from starfish oocytes at first meiotic metaphase is a heterodimer containing one molecule of cdc2 and one molecule of cyclin B. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Watrin A., Labbé J. C., Cavadore J. C. Microinjection of p34cdc2 kinase induces marked changes in cell shape, cytoskeletal organization, and chromatin structure in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):151–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90725-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Spurr N. K., Nurse P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):676–679. doi: 10.1038/333676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Nurse P. Cell cycle control genes in fission yeast and mammalian cells. Trends Genet. 1988 Oct;4(10):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. l., Gautier J., Langan T. A., Lohka M. J., Shenoy S., Shalloway D., Nurse P. Maturation-promoting factor and the regulation of the cell cycle. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:53–63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Arion D., Golsteyn R., Pines J., Brizuela L., Hunt T., Beach D. Cyclin is a component of the sea urchin egg M-phase specific histone H1 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2275–2282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Eilen E., Basilico C. Premature of chromosome condensation in a ts DNA- mutant of BHK cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Ishida R., Ajiro K., Yamamoto S., Takahashi T. The synthesis of protein(s) for chromosome condensation may be regulated by a post-transcriptional mechanism. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Nov;109(2):299–308. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C. J., Nurse P. Control of the higher eukaryote cell cycle by p34cdc2 homologues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Nakagawa J., Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Nigg E. A. Identification of major nucleolar proteins as candidate mitotic substrates of cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90093-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Nakagawa J., Dorée M., Labbé J. C., Nigg E. A. In vitro disassembly of the nuclear lamina and M phase-specific phosphorylation of lamins by cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90471-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Capony J. P., Brautigan D. L., Dorée M. Involvement of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A in the control of M phase-promoting factor activity in starfish. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3347–3354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pondaven P., Meijer L., Beach D. Activation of M-phase-specific histone H1 kinase by modification of the phosphorylation of its p34cdc2 and cyclin components. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):9–17. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Pardee A. B. Caffeine-induced uncoupling of mitosis from the completion of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2422760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Bialojan C., Troschka M., Rüegg J. C. Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase inhibition and force enhancement by black sponge toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde F., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Karsenti E. Regulation of microtubule dynamics by cdc2 protein kinase in cell-free extracts of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):233–238. doi: 10.1038/343233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Kirschner M. W. Identification of cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation sites on nuclear lamin C. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90469-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]