Figure 6. AML1-ETO and miR-29b-1 form a regulatory circuit that modulates leukemic phenotype.
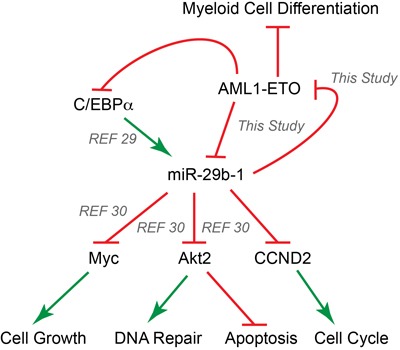
Our results establish a regulatory circuit between the AML1-ETO oncogene and the miR-29b-1 tumor suppressor; AML1-ETO transcriptionally regulates miR-29b-1, and miR-29b-1 translationally inhibits AML1-ETO. MicroRNA-29b-1 has been implicated in hematological malignancies and is a direct transcriptional target of the hematopoietic C/EBPα transcription factor [29]. Our results suggest that AML1-ETO regulates the expression of miR-29b-1 directly by binding to the promoter regulatory region of the miR-29a/b-1 locus, as well as indirectly through down-regulation of C/EBPα, which activates the miR-29a/b-1 locus [29]. It has been shown that miR-29b-1 directly inhibits the expression of Myc, a key regulator of cell cycle and cell growth, Akt2, an upstream sensor in the DNA repair/damage pathways and a regulator of cell apoptosis, and Cyclin D2 (CCND2), which mediates cell cycle control [30]. The current study provides evidence of a complex interplay between AML1-ETO and miR-29b-1 that leads to partial apoptosis, decreased BrdU incorporation, and release from AML1-ETO-mediated myeloid differentiation block. Our study and others together implicate miR-29b-1 as a key modulator of leukemic phenotype in acute myeloid leukemia. Green arrows indicate an activating event, while red symbols show an inhibitory event.
