Abstract
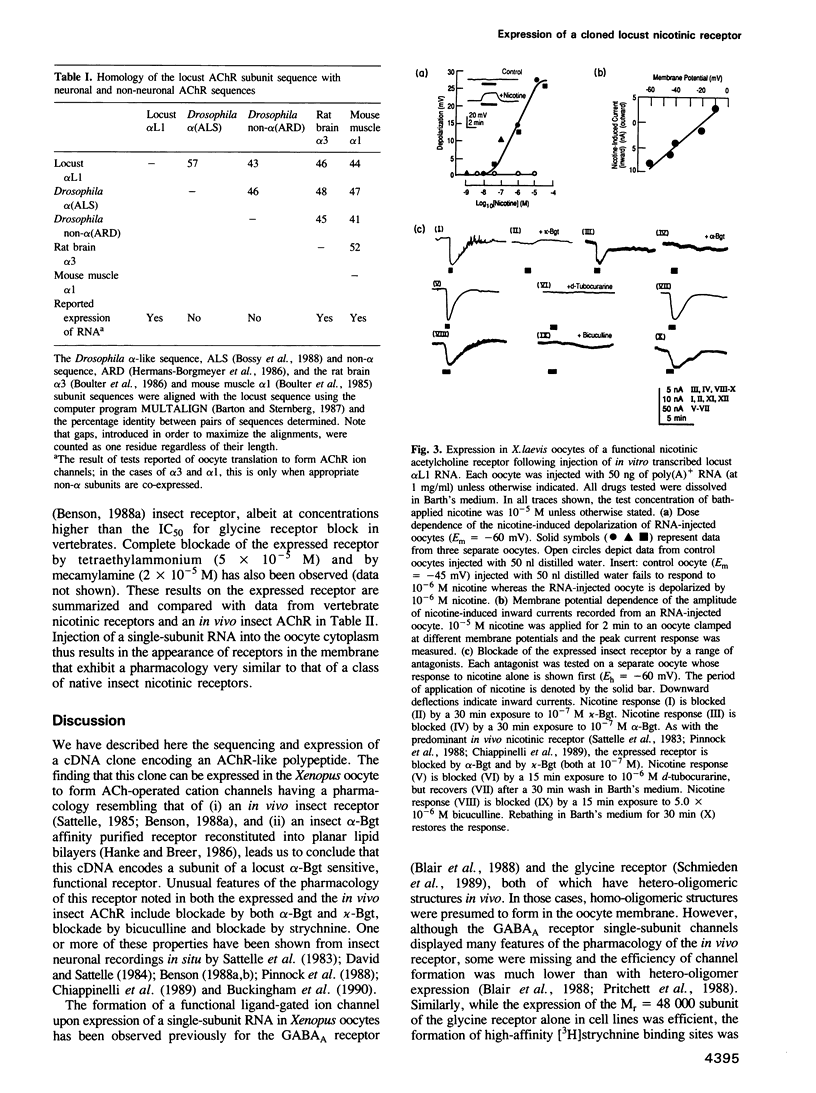
We report the isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone that encodes a locust (Schistocerca gregaria) nervous system nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) subunit (alpha L1). The calculated molecular weight of the unglycosylated polypeptide, which contains in the proposed extracellular domain two adjacent cysteine residues which are characteristic of alpha (ligand binding) subunits, is 60,641 daltons. Injection into Xenopus oocytes, of RNA synthesized from this clone in vitro, results in expression of functional nicotinic receptors in the oocyte membrane. In these, nicotine opens a cation channel; the receptors are blocked by both alpha-bungarotoxin (alpha-Bgt) and kappa-bungarotoxin (kappa-Bgt). Reversible block of the expressed insect AChR by mecamylamine, d-tubocurarine, tetraethylammonium, bicuculline and strychnine has also been observed. These data are entirely consistent with previously reported electrophysiological studies on in vivo insect nicotinic receptors and also with biochemical studies on an alpha-Bgt affinity purified locust AChR. Thus, a functional receptor exhibiting the characteristic pharmacology of an in vivo insect nicotinic AChR can be expressed in Xenopus oocytes by injection with a single subunit RNA.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton G. J., Sternberg M. J. A strategy for the rapid multiple alignment of protein sequences. Confidence levels from tertiary structure comparisons. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Ballivet M., Rungger D. Activation and blocking of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor reconstituted in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1993–1997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blagburn J. M., Sattelle D. B. Internal presynaptic tetraethylammonium (TEA+) blocks cholinergic transmission at a synapse between identified neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair L. A., Levitan E. S., Marshall J., Dionne V. E., Barnard E. A. Single subunits of the GABAA receptor form ion channels with properties of the native receptor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):577–579. doi: 10.1126/science.2845583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossy B., Ballivet M., Spierer P. Conservation of neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors from Drosophila to vertebrate central nervous systems. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):611–618. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Connolly J., Deneris E., Goldman D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Functional expression of two neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors from cDNA clones identifies a gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7763–7767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Evans K., Goldman D., Martin G., Treco D., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a cDNA clone coding for a possible neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):368–374. doi: 10.1038/319368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Luyten W., Evans K., Mason P., Ballivet M., Goldman D., Stengelin S., Martin G., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Isolation of a clone coding for the alpha-subunit of a mouse acetylcholine receptor. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2545–2552. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H., Kleene R., Hinz G. Molecular forms and subunit structure of the acetylcholine receptor in the central nervous system of insects. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3386–3392. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03386.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Mudd J., Shah V., Merlie J. P. A universal oligonucleotide probe for acetylcholine receptor genes. Selection and sequencing of cDNA clones for the mouse muscle beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16451–16458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiappinelli V. A., Hue B., Mony L., Sattelle D. B. Kappa-bungarotoxin blocks nicotinic transmission at an identified invertebrate central synapse. J Exp Biol. 1989 Jan;141:61–71. doi: 10.1242/jeb.141.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneris E. S., Boulter J., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Beta 3: a new member of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family is expressed in brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6268–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneris E. S., Connolly J., Boulter J., Wada E., Wada K., Swanson L. W., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Primary structure and expression of beta 2: a novel subunit of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1988 Mar;1(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Armstrong J., Colman A. The effect of capping and polyadenylation on the stability, movement and translation of synthetic messenger RNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7375–7394. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. M., Deneris E. S., Patrick J., Heinemann S. The functional diversity of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is increased by a novel subunit: beta 4. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filbin M. T., Lunt G. G., Donnellan J. F. Partial purification and characterisation of an acetylcholine receptor with nicotinic properties from the supraoesophageal ganglion of the locust (Schistocerca gregaria). Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 15;132(1):151–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. A., Schmidt J. T., Oswald R. E. Effect of alpha-bungarotoxin on retinotectal synaptic transmission in the goldfish and the toad. Neuroscience. 1980;5(5):929–942. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Deneris E., Luyten W., Kochhar A., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):965–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Breer H. Channel properties of an insect neuronal acetylcholine receptor protein reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):171–174. doi: 10.1038/321171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Zopf D., Ryseck R. P., Hovemann B., Betz H., Gundelfinger E. D. Primary structure of a developmentally regulated nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protein from Drosophila. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1503–1508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Dwork A. J., Kaldany R. R., Silver M. L., Wideman J., Stein S., Karlin A. Identification of the alpha subunit half-cystine specifically labeled by an affinity reagent for the acetylcholine receptor binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11662–11665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao P. N., Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor binding site contains a disulfide cross-link between adjacent half-cystinyl residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8085–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane N. J., Swales L. S., David J. A., Sattelle D. B. Differential accessibility to two insect neurones does not account for differences in sensitivity to alpha-bungarotoxin. Tissue Cell. 1982;14(3):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(82)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Schoepfer R., Whiting P. Molecular studies of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor family. Mol Neurobiol. 1987 Winter;1(4):281–337. doi: 10.1007/BF02935740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Zigmond R. E. Characterization of neuronal nicotinic receptors by snake venom neurotoxins. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Feb;11(2):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J., Darlison M. G., Lunt G. G., Barnard E. A. Cloning of putative nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes from the locust. Biochem Soc Trans. 1988 Aug;16(4):463–465. doi: 10.1042/bst0160463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nef P., Oneyser C., Alliod C., Couturier S., Ballivet M. Genes expressed in the brain define three distinct neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):595–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann D., Barchan D., Safran A., Gershoni J. M., Fuchs S. Mapping of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site within the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3008–3011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. A slowly inactivating potassium current in native oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 22;238(1293):369–381. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnock R. D., Lummis S. C., Chiappinelli V. A., Sattelle D. B. Kappa-bungarotoxin blocks an alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic receptor in the insect central nervous system. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 16;458(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90494-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Gorman C. M., Kettenmann H., Seeburg P. H., Schofield P. R. Transient expression shows ligand gating and allosteric potentiation of GABAA receptor subunits. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1306–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.2848320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattelle D. B., Pinnock R. D., Wafford K. A., David J. A. GABA receptors on the cell-body membrane of an identified insect motor neuron. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jan 22;232(1269):443–456. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss P., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Betz H., Gundelfinger E. D. Neuronal acetylcholine receptors in Drosophila: the ARD protein is a component of a high-affinity alpha-bungarotoxin binding complex. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2889–2894. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieden V., Grenningloh G., Schofield P. R., Betz H. Functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of the strychnine binding 48 kd subunit of the glycine receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bennett J. P., Jr Neurotransmitter receptors in the brain: biochemical identification. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Becker C. M., Pritchett D. B., Schofield P. R., Grenningloh G., Kettenmann H., Betz H., Seeburg P. H. Functional chloride channels by mammalian cell expression of rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Ballivet M., Boulter J., Connolly J., Wada E., Deneris E. S., Swanson L. W., Heinemann S., Patrick J. Functional expression of a new pharmacological subtype of brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):330–334. doi: 10.1126/science.2832952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Sattelle D. B., Abalis I., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-activated 36Cl- influx: a functional in vitro assay for CNS gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors of insects. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):177–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. M., Mayne K. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Mouse-Torpedo hybrid acetylcholine receptors: functional homology does not equal sequence homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4852–4856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Garza R., McGuire T. J., Freedman R., Hoffer B. J. Selective antagonism of nicotine actions in the rat cerebellum with alpha-bungarotoxin. Neuroscience. 1987 Dec;23(3):887–891. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



