Abstract
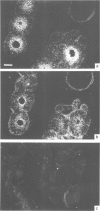
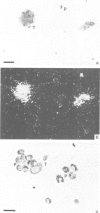
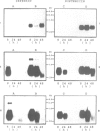
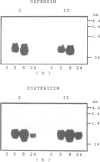
Injections of low doses of bacteria into larvae of Phormia terranovae induce the appearance of potent bactericidal peptides in the blood, among which predominate the anti-Gram positive insect defensins and the anti-Gram negative diptericins. Insect defensins show significant homologies to mammalian (including human) microbicidal peptides present in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages. We report the molecular cloning of cDNAs and primer extension studies which indicate that insect defensin is produced as a prepro-peptide yielding mature defensin A (40 residues) after cleavage of a putative signal peptide (23 residues) and a prosequence (34 residues). Previous studies have established that diptericin (82 residues) is matured from a pre-peptide by cleavage of a putative signal peptide (19 residues) and C-terminal amidation. Using oligonucleotide probes complementary to the sequences of the mRNAs for defensin and diptericin, we show by in situ hybridization that both antibacterial peptides are concomitantly synthesized by the same cells: thrombocytoids, a specialized blood cell type, and adipocytes. Transcriptional studies based on hybridization of RNAs to cDNAs of defensin and diptericin indicate that the transcription of both genes is induced regardless of the nature of the stimulus (injection of Gram positive or Gram negative bacteria, lipopolysaccharides). Even a sterile injury applied to axenically raised larvae is efficient in inducing the transcription of both genes suggesting that the local disruption of the integument aspecifically initiates a signalling mechanism which the thrombocytoids and the adipocytes are able to interpret. The transcription of immune genes is relatively short lived and a second challenge yields a response similar to that of the first stimulus, indicating that the experimental insects do not keep a 'memory' of their first injection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Natori S. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and characterization of cDNA for sarcotoxin IIA, an inducible antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1715–1721. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels P., Ampe C., Jacobs F., Vaeck M., Tempst P. Apidaecins: antibacterial peptides from honeybees. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2387–2391. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daher K. A., Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Kronenberg M. Isolation and characterization of human defensin cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7327–7331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daher K. A., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Direct inactivation of viruses by human granulocyte defensins. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1068-1074.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson L., Russell V., Dunn P. E. A family of bacteria-regulated, cecropin D-like peptides from Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19424–19429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarcq J. L., Keppi E., Dunbar B., Lambert J., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann D., Rankine S. M., Fothergill J. E., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity. Purification and characterization of a family of novel inducible antibacterial proteins from immunized larvae of the dipteran Phormia terranovae and complete amino-acid sequence of the predominant member, diptericin A. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye I., Wyatt G. R. The synthesis of antibacterial proteins in isolated fat body from Cecropia silkmoth pupae. Experientia. 1980 Nov 15;36(11):1325–1326. doi: 10.1007/BF01969615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Lehrer R. I. Antimicrobial activity of phagocyte granule proteins. Semin Respir Infect. 1986 Jun;1(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Szklarek D., Harwig S. S., Daher K., Bainton D. F., Lehrer R. I. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1427–1435. doi: 10.1172/JCI112120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Melvold R. W., Nathenson S. G. Mitotic recombination in germ cells generated two major histocompatibility complex mutant genes shown to be identical by RNA sequence analysis: Kbm9 and Kbm6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3371–3375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Daher K., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Direct inactivation of viruses by MCP-1 and MCP-2, natural peptide antibiotics from rabbit leukocytes. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):467–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.467-472.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto N., Okada M., Takahashi H., Ming Q. X., Nakajima Y., Nakanishi Y., Komano H., Natori S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA and assignment of the C-terminal of sarcotoxin IA, a potent antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):717–722. doi: 10.1042/bj2390717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for sapecin and unique expression of the sapecin gene during the development of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17117–17121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart J. M., Essrich M., Dimarcq J. L., Hoffmann D., Hoffmann J. A., Lagueux M. Insect immunity. Isolation of cDNA clones corresponding to diptericin, an inducible antibacterial peptide from Phormia terranovae (Diptera). Transcriptional profiles during immunization. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 15;182(2):423–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Brown D. M., DeLange R. J., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of six antimicrobial peptides of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4579–4584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S., Ganz T., Schilling J. W., Lehrer R. I. Primary structures of three human neutrophil defensins. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1436–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI112121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsted M. E., Harwig S. S. Purification, primary structure, and antimicrobial activities of a guinea pig neutrophil defensin. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2281–2286. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2281-2286.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner H., Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):246–248. doi: 10.1038/292246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
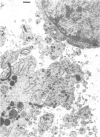
- Zachary D., Hoffmann J. A. The haemocytes of Calliphora erythrocephala (Meig.) (Diptera). Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Jul 26;141(1):55–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00307396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]