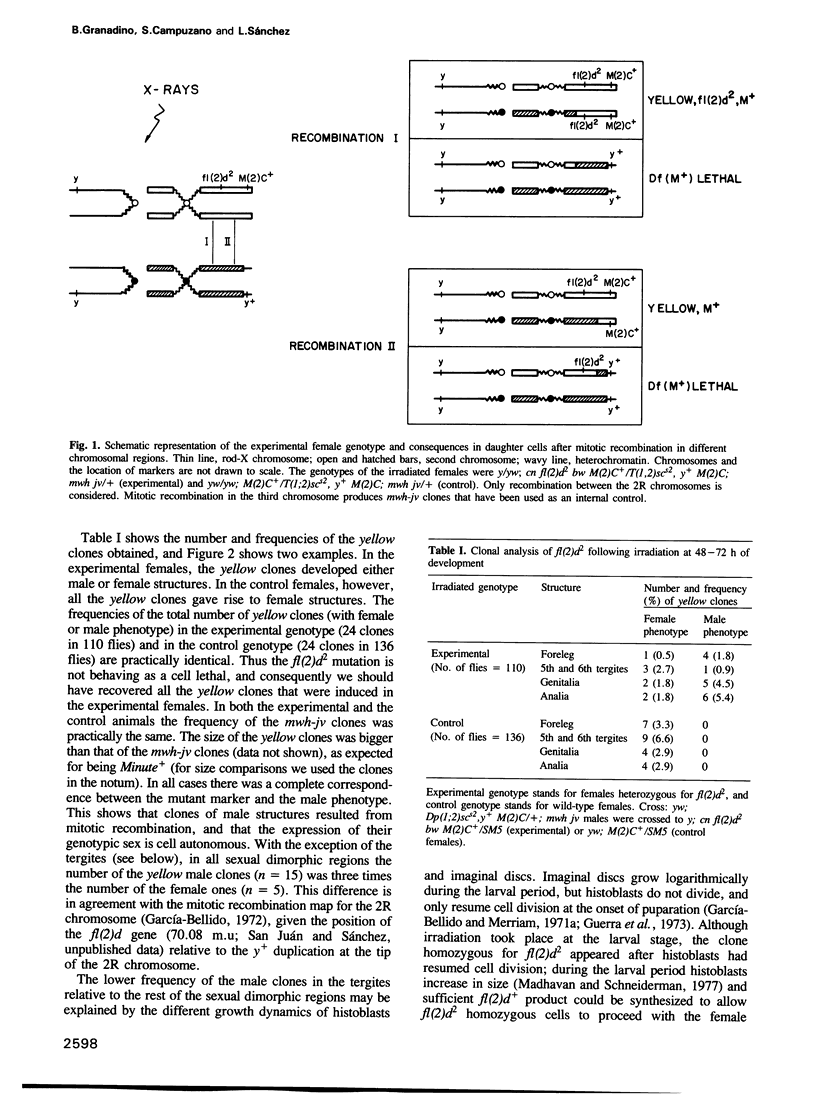
Abstract
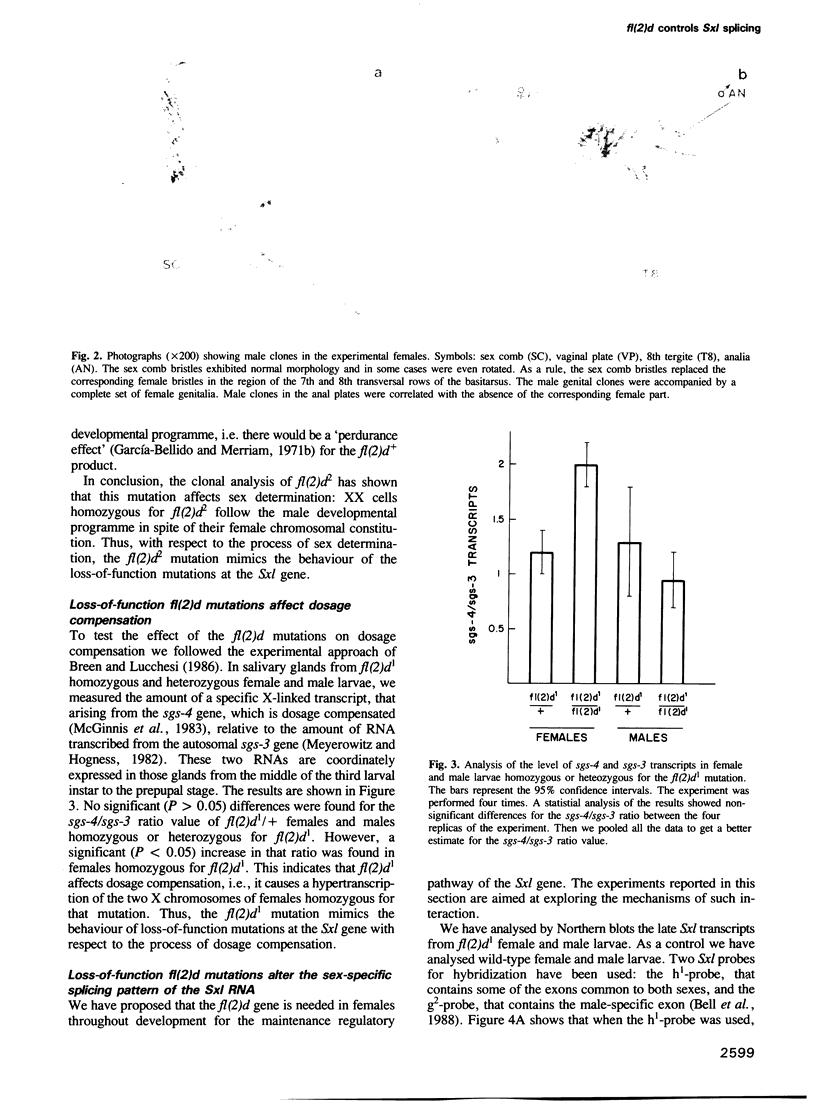
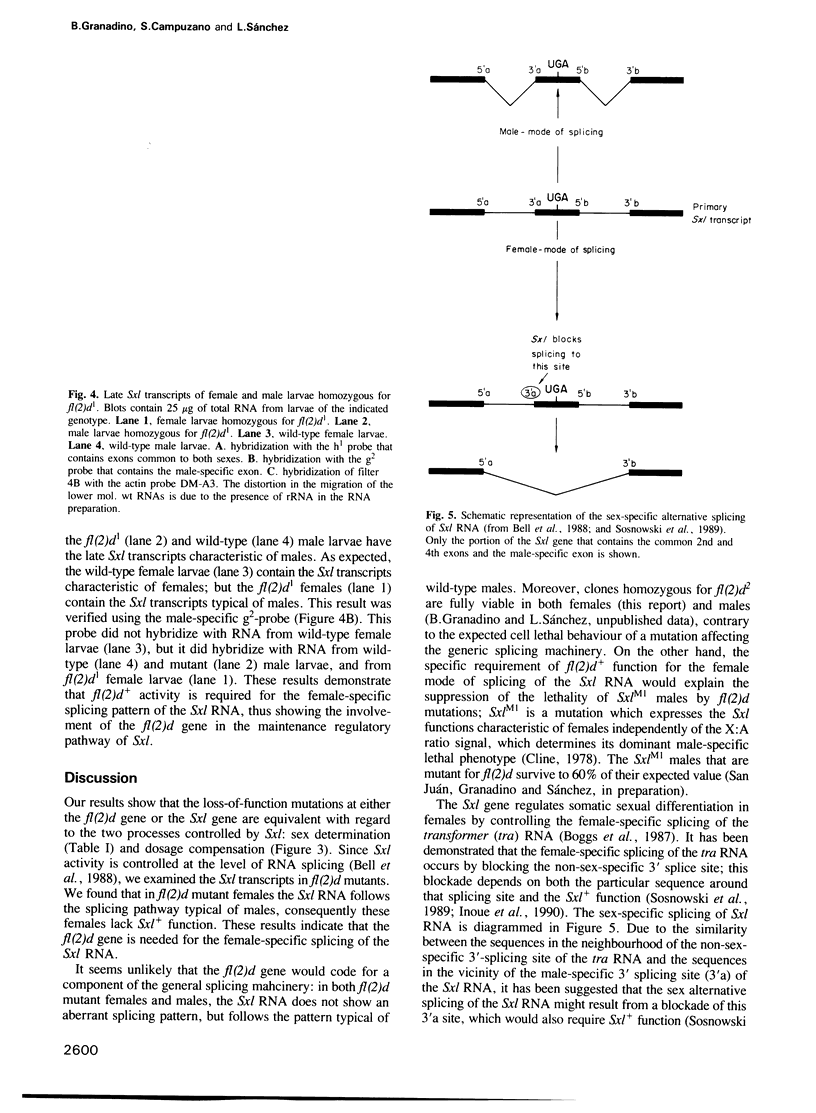
In Drosophila melanogaster, sex determination and dosage compensation are under the control of the Sex-lethal (Sxl) gene. We have identified a gene, female-lethal-2-d (fl(2)d), located in the second chromosome, that interacts with Sxl. fl(2)d homozygous clones, induced during the larval stage of fl(2)d/+ females, develop male structures instead of female ones. fl(2)d homozygous females hypertranscribe their two X chromosomes, as measured by comparing the level of the X-linked sgs-4 transcript, which is dosage compensated, with that of the autosomal sgs-3 transcript. Thus, with respect to the processes of sex determination and dosage compensation, loss-of-function mutations at the fl(2)d and at the Sxl genes are equivalent. Moreover, fl(2)d homozygous female larvae express the Sxl transcripts characteristic of males. These results indicate that the fl(2)d gene is needed for the sex-specific splicing pattern of the Sxl RNA that occurs in females, thus suggesting the involvement of the fl(2)d gene in the positive autoregulatory pathway of Sxl.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs R. T., Gregor P., Idriss S., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Regulation of sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster via alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):739–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen T. R., Lucchesi J. C. Analysis of the dosage compensation of a specific transcript in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):483–491. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Balcells L., Villares R., Carramolino L., García-Alonso L., Modolell J. Excess function hairy-wing mutations caused by gypsy and copia insertions within structural genes of the achaete-scute locus of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90764-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T., Daneholt B. The size of the transcription unit in Balbiani ring 2 of Chironomus tentans as derived from analysis of the primary transcript and 75 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. A female-specific lethal lesion in an X-linked positive regulator of the Drosophila sex determination gene, Sex-lethal. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):641–663. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. Autoregulatory functioning of a Drosophila gene product that establish es and maintains the sexually determined state. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):231–277. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. Evidence that sisterless-a and sisterless-b are two of several discrete "numerator elements" of the X/A sex determination signal in Drosophila that switch Sxl between two alternative stable expression states. Genetics. 1988 Aug;119(4):829–862. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.4.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline T. W. Two closely linked mutations in Drosophila melanogaster that are lethal to opposite sexes and interact with daughterless. Genetics. 1978 Dec;90(4):683–698. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bellido A., Merriam J. R. Clonal parameters of tergite development in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1971 Oct;26(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Bellido A. Some parameters of mitotic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(1):54–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00272218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra M., Postlethwait J. H., Schneiderman H. A. The development of the imaginal abdomen of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1973 Jun;32(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Hoshijima K., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Binding of the Drosophila sex-lethal gene product to the alternative splice site of transformer primary transcript. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):461–463. doi: 10.1038/344461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi J. C., Skripsky T. The link between dosage compensation and sex differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):217–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00286106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine E. M., Salz H. K., Cline T. W., Schedl P. The Sex-lethal gene of Drosophila: DNA alterations associated with sex-specific lethal mutations. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A transposable element inserted just 5' to a Drosophila glue protein gene alters gene expression and chromatin structure. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Hogness D. S. Molecular organization of a Drosophila puff site that responds to ecdysone. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Cline T. W., Schedl P. Functional changes associated with structural alterations induced by mobilization of a P element inserted in the Sex-lethal gene of Drosophila. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):221–231. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Maine E. M., Keyes L. N., Samuels M. E., Cline T. W., Schedl P. The Drosophila female-specific sex-determination gene, Sex-lethal, has stage-, tissue-, and sex-specific RNAs suggesting multiple modes of regulation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):708–719. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez L., Nöthiger R. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster: production of male clones in XX females. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):485–491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Sánchez L. The scute (T4) gene acts as a numerator element of the X:a signal that determines the state of activity of sex-lethal in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3079–3086. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]