Abstract
Members of the Dickkopf (Dkk) family of Wnt antagonists interrupt Wnt-induced receptor assembly and participate in axial patterning and cell fate determination. One family member, DKK3, does not block Wnt receptor activation. Loss of Dkk3 expression in cancer is associated with hyperproliferation and dysregulated ß-catenin signaling, and ectopic expression of Dkk3 halts cancer growth. The molecular events mediating the DKK3-dependent arrest of ß-catenin-driven cell proliferation in cancer cells are unknown. Here we report the identification of a new intracellular gene product originating from the Dkk3 locus. This Dkk3b transcript originates from a second transcriptional start site located in intron 2 of the Dkk3 gene. It is essential for early mouse development and is a newly recognized regulator of ß-catenin signaling and cell proliferation. Dkk3b interrupts nuclear translocation ß-catenin by capturing cytoplasmic, unphosphorylated ß-catenin in an extra-nuclear complex with ß-TrCP. These data reveal a new regulator of one of the most studied signal transduction pathways in metazoans and provides a novel, completely untapped therapeutic target for silencing the aberrant ß-catenin signaling that drives hyperproliferation in many cancers.
Introduction
The Dickkopf family of secreted glycoproteins is composed of four members that first appeared in early metazoans as key regulators of the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway [1–4]. Three family members DKK1, DKK2 and DKK4 bind to the LRP5/6 and Kremen subunits of the receptor [5] and prevent assembly of a functional Wnt receptor complex [6–8]. The remaining family member, DKK3, apparently evolved divergently [2, 9] and does not bind to LRP5/6 or modulate Wnt receptor assembly/signaling [10–13], even though it retains the two cysteine rich domains common to all family members [10]. Despite its inability to disrupt Wnt receptor binding, DKK3 is the best-known tumor suppressor in the family [11, 12]. DKK3 expression is frequently silenced in cancer, often by the hyper-methylation of CpG islands located in the Dkk3 locus [13–15] and ectopic over-expression of DKK3 slows ß-catenin driven cancer cell proliferation in vitro [16–19]. To date, the molecular details of the mechanism DKK3 action remain elusive. Despite its presumed role in regulating ß-catenin driven cancer cell proliferation, targeted inactivation of the mouse Dkk3 gene failed to provide a direct link between DKK3, the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling, and control of cell proliferation. The Dkk3tm1Cni mutant mouse is viable, fertile, shows no ß-catenin signaling defects or any increase in cancer susceptibility [20] and failed to phenocopy other Dickkopf deletion mutants [21–25] or deletion mutants of individual components the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway [26–32].
In this study, we show that the Dkk3 gene encodes a second vital intracellular isoform, DKK3b, that inhibits hyperproliferation in cancer cells by blocking the ß-catenin nuclear translocation downstream of the Wnt-regulated ß-catenin destruction complex. In normal mouse fibroblasts, loss of DKK3b disrupts cell adhesion. This newly discovered Dkk3 gene product is an obligatory negative regulatory element in the ß-catenin signaling axis that adds a non-canonical attenuating mechanism to one of the most studied signal transduction pathways in metazoan systems. DKK3b captures ß-catenin in an extra nuclear complex with ß-TrCP preventing its nuclear translocation and serving as a gatekeeper for ß-catenin nuclear entry that modulates ß-catenin-dependent gene expression.
Materials and methods
Animals
Pregnant Sprague Dawley rats were purchased from Charles-River Labs. C57Bl/6J and CD1 mice were obtained from Jackson Labs and Charles River respectively. All rodents used in this study were maintained in an AALAC-accredited facility. The Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of Massachusetts Medical School (Assurance #A3306-01) approved the use of animals. All rodents were euthanized by CO2 asphyxiation followed by decapitation. Frozen whole brain from homozygous and heterozygous Dkk3tm1Cni were the gift of Dr. C. Niehrs.
Generation of Dkk3CFP mutant mice
Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN) target sites within intron 2 of mouse Dkk3 gene (NCBI: NC_000073.6) were identified (nt8312-nt8341: AGCCCCTTTTCttcacctCAGTTGTAACTG) [33, 34] and two four finger nucleases were assembled. The cDNAs encoding the zinc fingers were generated by gene synthesis (IDT) and then cloned into a pCS2 expression vector bearing the heterodimeric DD and RR versions of FokI [35]: The complete amino acid sequences of the ZFNs are 5’ HA-ZFN (5’-GAAAAGGGGCT; DD FokI): NH2 YPYDVPDYATERPYKCPECGKSFSRSDTLKEHQRTHTGEKPYAC
PVESCDRRFSRSSHLTRHIRIHTGQKPFQCRICMRNFSRSDHLTQHIRTHTGEKPFACDICGRKFAQRGNLTRHTKIHTGGSQLVKSELEEKKSELRHKLKYVPHEYIELIEIARNSTQDRILEMKVMEFFMKVYGYRGKHLGGSRKPDGAIYTVGSPIDYGVIVDTKAYSGGYNLPIGQADEMQDYVEENQTRNKHINPNEWWKVYPSSVTEFKFLFVSGHFKGNYKAQLTRLNHITNCNGAVLSVEELLIGGEMIKAGTLTLEEVRRKFNNGEINF-COOH and the 3’ Flag-ZFN (5’-CAGTTGTAACTG; DD FokI): NH2-DYKDDDKTERPYKCPECGKSFSRSDTLV
EHQRTHTGEKPYACPVESCDRRFSQRGNLTTHIRIHTGQKPFQCRICMRNFSRSDALRSHIRTHTGEKPFACDICGRKFARSDNLSEHTKIHTGGSQLVKSELEEKKSELRHKLKYVPHEYIELIEIARNSTQDRILEMKVMEFFMKVYGYRGKHLGGSRKPDGAIYTVGSPIDYGVIVDTKAYSGGYNLPIGQAREMQRYVEENQTRNKHINPNEWWKVYPSSVTEFKFLFVSGHFKGNYKAQLTRLNHITNCNGAVLSVEELLIGGEMIKAGTLTLEEVRRKFNNGEINF-COOH. The homologous recombination donor DNA for the mouse target Dkk3 locus was assembled by PCR amplification. PCR primers are listed in (Table 1).
Table 1. Primers used in this study.
| Primer | use | sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 5HR7351F | 5 HR arm | 5’-AGAGAGAGAGAGACTAAGGTACTGGC |
| 5HR38275R | 5 HR arm | 5’-GATCCTGAACCGGTATAACTTCGTATAATGTATGCTATACGAAG-TTATCAGTTACAACTGAGGTGAAGAAAAGG |
| 3HR8276LAF | 3 HR arm | 5’-CCTGACTTAAGATAACTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAAGTTA-TAAAGAAACCGTTTTGTGTCTTTGATTTG |
| 3HR9050 | 3 HR arm | 5’-GATCCTGACTTAAGTCAAGTCATTCAGGCTGGTTG |
| LF | Dkk3 locus | 5’-AAGGACCCTGCCTTGGCCACTTGG |
| LR | Dkk3 locus | 5’- ACGGCATGGACGAGCTGTACC |
| RF | Dkk3 locus | 5’- GCTGTACCGCTAAAGCGGCCGC |
| RR | Dkk3 locus | 5’- CTCCACCCAGCTCCTGATTC |
| DPF1 | genotyping | 5’-TTTGGCTTGCTGGCTAAGAT |
| DPR2 | genotyping | 5’-GAGGGTGGTCACCAGGGT |
| DCF3 | genotyping | 5’-CGCCACAACATCGAGG |
| DCF4 | genotyping | 5’-ACCATGAGGTCTCGTCAACC |
| Dkk3F | Off-target PCR | 5'-TGTGCCACGGCCCTTACCTT |
| Dkk3R | Off-target PCR | 5'-GGCTAAGATAACCCTTCTGAGGTC |
| DlstF | Off-target PCR | 5’GCAGAGGAAGTGCAAGTTTAAGGCTAGATC |
| DlstR | Off-target PCR | 5’CAGCCATTCTAGAAACCCTGATCAAG |
| Rnu6F | Off-target PCR | 5'-AAACTGGCTCTCGTGGGGGT |
| Rnu6R | Off-target PCR | 5'-CACAGGTGACAGTGTGGTGG |
| Tcf7l2F | Off-target PCR | 5'-ATGTCAGCCCACAGTGATGAGAG |
| Tcf7l2R | Off-target PCR | 5'-CTCCCTGGAAATTGGCAGCTTG |
| Akap9F | Off-target PCR | 5'-CCTACAGATCCGTTAAGGGTACAG |
| Akap9R | Off-target PCR | 5'-CTCAGAGGAGGAGTCATCAAGTG |
| Drb1F | Off-target PCR | 5’-CTCACTGTTTCTAGGAACCTTGGTTCTGTC |
| Drb1R | Off-target PCR | 5’-GAACAGAGAAAGAAAGTCTGAGCTCAGTCC |
| Aldoart1F | Off-target PCR | 5’-GCAGTGGCTATAGCAGAGAGGAAGAA |
| Aldoart1R | Off-target PCR | 5’-TGCCGATGTCAAATGTAGCATGGCACTATC |
| Fam168bF | Off-target PCR | 5'-GCATCTGTCTGCAGACCACATTTG |
| Fam168bR | Off-target PCR | 5'-GCACGTTCACAATACTGTGGGG |
| Mett21eF | Off-target PCR | 5’GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAAGAA |
| Mett21eR | Off-target PCR | 5’CAGAGTTAGCATTTCTTCTAGGCTCCACC |
| Rps6ka5F | Off-target PCR | 5'-GAGGCGCATGCAGAAACTTCAC |
| Rps6ka5R | Off-target PCR | 5'-CCTGAAAAGCCTACTAGGTCTCTC |
| Arhgef2F | Off-target PCR | 5'-AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAG |
| Arhgef2R | Off-target PCR | 5'-GGTGGCAAGAACCAGATGTGCT |
| TSS2F | CHiP | 5’-AGATGGCCCCTTTTCTTCAC |
| TSS2R | CHiP | 5’-TGGTCTCGTTGTGGTAGTTGG |
| EXF2 | qPCR | 5’-CCAGCTCTCAACTACCCTCA |
| EXR2 | qPCR | 5’-CATCAGCTCCTCCACCTCTCG |
| EXF3 | qPCR | 5’-GCTGCTAAAACGTCCTCTGAGG |
| EXR3 | qPCR | 5’-GTCTCCGTGCTGGTCTCATT |
| RActF | qPCR | 5’-CTAAGGCCAACCGTGAAAAG |
| RActR | qPCR | 5’-GGGGTGTTGAAGGTCTCAAA |
| GAPDHF | qPCR | 5’-TGCCACTCAGAAGACTGTGG |
| GAPDHR | qPCR | 5’-GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTCT |
| DKSF | loxP scar | 5'-GAGAAGGCAGCCCCTTTTCT |
| DKSR | loxP scar | 5'-CTTCTTCCGCCTCCATCTATCAAATC |
The 824 bp 5’ homology arm (nt7415-nt8239) and 722 bp 3’homology arm (nt8342-nt9064) were appended to a loxP-TagCFP-pA-loxP cassette to create a linear 2.7 kb Dkk3b HR Donor DNA ZFN and HR Donor DNA. Validation was performed in the C8D1A cells (ATCC) derived from the C57Bl/6J mouse cerebellum. C8D1A cells were transfected with Dkk3 targeted ZFN plasmids and genomic DNA was isolated 48 h later. The 681 bp target locus was PCR amplified, heat denatured, re-annealed and indel formation evaluated by Cel-1 assay [36] (Transgenomic, Inc.). HR repair of the ZFN generated DSB was validated using ssDNA oligonucleotides to insert a unique restriction site at the DSB [37]. C8D1A cells were transfected with a 96-mer ssDNA oligo with a unique EcoRI site bracketed by 45 nt long homology arms (5’CAGTCTTGGCACCTATAGAAGAGGGGAAGAGAAGGCAGCCCCTTTTGAATTCTTGTAACTGAAAGAAACCGTTTGTGTCTTTGATTTGATAGATG) along with the Dkk3 targeted ZFN plasmids using Fugene6. The Dkk3 target sequence was PCR amplified from gDNA isolated 48 h after transfection. HR mediated repair of the ZFN generated DSB was confirmed by the EcoRI restriction of the PCR amplified target sequence.
Capped, polyadenylated ZFN mRNAs were synthesized in vitro (Ambion), purified (Qiagen) and injected along with the 2.7 kb linear Dkk3b HR Donor DNA into the nucleus and cytoplasm of C57Bl/6J zygotes (UMMS Transgenic Core). Injected zygotes were implanted into the uteri of pseudo-pregnant C57Bl/6J dams and gene edited pups were identified by genotyping (see Fig 1A and Table 1 for genotyping primer pairs: DPF1:DPR2, mut-407 bp; D3F3:D3R4, mut-1031 bp; DPF1:D3R4, wt-618 bp, mut-1747bp). Insertion of the CFP cDNA at the target locus was confirmed by DNA sequencing of PCR products generated with primers LL (nt7259-nt7284) and RR (nt9058-nt9027) located 166 nt and 444 nt respectively, outside the HR region.
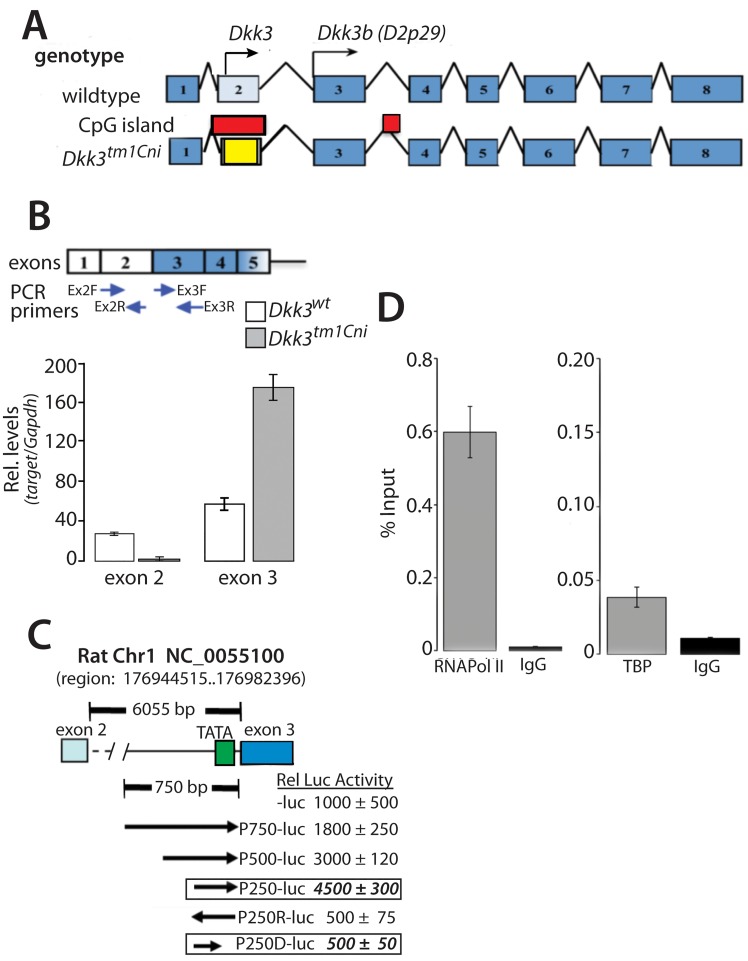
Fig 1. Identification of multiple transcripts originating for the Dkk3 gene locus.
(A) Schematic diagram of the Dkk3 gene (NC_000073.6) in the wild type and Dkk3tm1Cni mouse. Initiator methionine’s for Dkk3 (NM_0154814) and D2p29 (AF245040) indicated by arrows; CpG islands indicated by red box; LacZ-pA stop cassette in yellow. (B) Quantitative PCR of Dkk3 containing exon 2 and exon 3 transcripts in total brain RNA from the Dkk3tm1Cni mouse. Arrows indicate PCR primer sites. Data reported as means ± se of 3 individuals; each sample determined in quadruplicate. (C) Schematic diagram of rat Dkk3 intron 2-luciferase reporter constructs. Arrows indicate orientation and location of intron 2 segments upstream of exon 3; data reported as means ± se of 3 independent experiments, each sample determined in triplicate. (D) ChIP analysis of RNA pol II and TATA box binding protein (TBP) binding to the ~66 nucleotides (nt6682-nt6948) of intron 2 adjacent to exon 3 in the rat astrocyte Dkk3 gene; data reported as means ± se of 3 independent experiments; each sample determined in quadruplicate.
Predicted off-target sites were identified by PROGNOS [38]. Potential off-target sites were PCR amplified from liver gDNA (founder #19) and cloned into the pCR4 vector (Life Technologies). Eight to twelve independent clones of each potential off-target site were DNA sequenced in both directions.
The transcription initiation site in exon 2 of the mouse Dkk3 gene was captured by 5’RACE of mRNA purified from the mutant mouse Dkk3CFP cerebral cortex using the SMARTer® RACE 5’/3’ kit from Clontech laboratories following manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, mRNA was purified using the Dynabeads® mRNA Direct™Kit from ThermoFisher according to manufacturer’s instructions. Mouse brain mRNA (500 ng) was used for 1st cDNA synthesis and the 5’UTR of the Cfp mRNA was amplified from the 1st strand cDNA by 5’RACE PCR using the kit upstream UPM primer (5’-GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT) and two, independent, Cfp-specific downstream primers each with an appended infusion cloning sequence (bolded nucleotides): one located 384 nucleotides downstream from the Cfp ATG start site CFP384R (5’-gattacgccaagcttCTCGCCCTTCAGCTCGACGCGGTTCACC) and a second located 234 nucleotides downstream of the Cfp ATG start site CFP234R (5’- gattacgccaagcttCATGTGCTCGGGGTAGCGGGCGAAGC). Specific PCR products of ~500 bp and ~300 bp, respectively, were gel isolated, cloned into the pRACE vector (TaKaRa) and 15 clones from each Cfp primer were DNA sequenced.
Cell culture and transfection
Primary astrocytes were prepared from one-day-old neonatal rat or mouse [39]. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were prepared from 13.5–14.5 day old fetuses [40]. Cells were maintained at 37°C under 5% CO2 in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) containing 10% bovine calf serum (BCS), 50 units/ml penicillin, 90 units/ml streptomycin. All cell cultures were passaged every 5–7 days for up to 3 passages.
PC3, HEK293, HeLa and C8D1A cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 units/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin and 2 mM L-glutamine. Cells were seeded at a density of 15,000 cells/cm2 24 h prior to transfection.
Transient transfections were done with Fugene6 according to manufacturer’s instructions. Cell lysates were prepared 48 h after transfection. Each transfection experiment repeated at least 3 times and each assay point was determined in triplicate.
Tunable ectopic protein(s) expression was done using the Tet-ON expression system (Life Technologies). The Tet Repressor Protein (TR) was integrated in the genome of PC3 cells by lentivirus infection (pLenti3.3/TR, Life Technologies) and cell selected with G418. TR expressing PC3 cells were transfected with pTREX-DKK3-HA or pTREX-Flag-IBS and ectopic protein expression induced by addition of increasing concentrations of doxycycline to the growth medium.
Luciferase reporter assays
Promoter analysis was done with PCR isolated segments of intron 2 of the rat Dkk3 gene. The Tcf promoter [41] (M50 Super 8x TOPflash) was a gift from Randall Moon (Addgene plasmid # 12456)); the E-Cad promoter [42] was a gift from Eric Fearon (Addgene plasmid # 19290)); and the E2F promoter[43] was the gift of Jason Chen. All promoter cDNAs were cloned into the pGL4 firefly luciferase vector (Promega). Cells were transfected with the individual promoter-reporter plasmids using Fugene6. After 48 h, cell lysates were prepared and luciferase assays were done according to manufacturer’s instructions (Promega). ß-catenin signaling was evaluated in cells co-transfected with the Wnt expression plasmid, pcDNA-Wnt1 [44]; pcDNA-Wnt1 was a gift from Marian Waterman (Addgene plasmid # 35905). Each promoter-reporter experiment was performed in triplicate, and each experiment was repeated at least three times.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was done as described [45] with modifications. Primary rat astrocytes were cross-linked with 1% formaldehyde. Washed cell pellets were lysed on ice in hypo-osmotic lysis buffer, nuclei collected by centrifugation, and DNA sheared (average size 200–400 bp) by sonication in iso-osmotic sonication buffer. Clarified extracts were pre-cleared with A/G plus-agarose beads pre-coated with 2 μg/ml sonicated salmon sperm DNA and 1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin. Thirty A260 units of the pre-cleared nuclear lysate was then incubated with 3 μg of anti-RNA pol II, anti-TBP or normal Rabbit IgG and immune complexes isolated by A/G plus-agarose beads (Santa Cruz Biotech.). Immune complexes were eluted in 50 mM Tris, pH 8, 1 mM EDTA, 1% (v/v) SDS at 65°C for 15 min, adjusted to 200 mM NaCl, and cross-links broken by heating at 65°C for 16 h. Immune complexes were then treated with RNase I (1 unit/ml) and Proteinase K (20 μg/ml) and DNA purified (Qiagen). Immune-precipitated DNA and input DNA (10% total) were analyzed by real time PCR (MJ Research Thermal Cycler) using the SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen) and primers TSS2F and TSS2R (Table 1). μ
Immunocytochemistry
Cells were seeded onto on poly-d-lysine (10 μg/ml) coated coverslips and grown for 24 h prior to transfection. All transfections were done with Fugene6 according to manufacturer’s instructions. After 48 h, cells were washed with ice cold PBS, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 minutes and quenched with 10 mM glycine. Fixed cells were permeabilized with Triton X-100, blocked with 1% BSA in TRIS buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 and then incubated with primary antibodies (0.2–1 μg/ml) for 1 h at room temperature. After washing, immune complexes were visualized with secondary antibody-Alexafluor conjugates for 1 h. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Coverslips were mounted with Prolong® Gold mountant (ThermoFisher). Tissue sections (5 μm) were prepared by the Morphology Core (UMMS) from paraffin embedded, formalin fixed organs from a Dkk3CFP/+ mutant mouse. Dewaxed sections were stained with anti-CFP antibody (1 μg/ml) and counter stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Antibodies used in this study were: anti-HA (ab1424), anti- ß-tubulin (ab6046), anti-DKK3 (ab186409) (Abcam), anti-FLAG (M2; F3165), anti-Myc (SAB4300320) anti-ß-catenin (04–958) (Sigma), anti-CFP (cat#632381) (TaKaRa), anti-ß-TrCP (mAB #4394), anti-GAPDH (mAB #2118) (Cell Signaling), and anti-Dkk3b [46]. Alexfluor488 and Alexafluor568 conjugated and HRP-conjugated secondary IgGs (cat#: A-11008, A-11034, A-11004, A11036, 31430, 31460) were purchased from Life Technologies; RDye680CW and IRDye800CW conjugated secondary IgGs (cat#: 925–68020, 925–68022, 925–32210, 925-32211were purchased from Li-COR Biosciences.
RNAi knockdown
MEFs were infected with pools of lentiviral shRNAs in pGIPZ from (Dharmacon) archived by UMMS RNAi Core. Lentiviral pools of shRNAs (>1 x 106 pfu/ml per shRNA target) targeting the open reading frame of mouse DKK3 and Dkk3b transcripts (exons 4 and 8) (V3LMM_518668, V3LMM_487209, V3LMM_487206, V3LMM_487207), mouse ß-catenin (exons 5 and 8) (V2LMM_16708, V3LMM_491202, V2LMM_4912040), and human ß-TrCP (V2LHS_33325, V2LHS_33330, V2LHS_33325) and a non-silencing control (RHS4348) were used. Cells were infected with lentiviral pools of shRNAs (>1 x 106 pfu/ml per shRNA target), grown for 2 days and selected with puromycin. GFP positive shRNA expressing cells were used in all experiments.
Total RNA isolation, and real time PCR
Total cellular RNA was isolated using Trizol Reagent (Life Technologies) or RNeasy (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer instructions. RT-PCR was performed with SuperScript First-Strand Synthesis System (Life Technologies) and primed with either Oligo(dT) or random hexamers. First strand cDNAs primed with either Oligo(dT) or random hexamers yielded identical results. Initially, real time PCR (MJ Research Thermal Cycler) was done with a SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen). All subsequent experiments were done using multiplexed TaqMan® Probes and the VIIA Real Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). TaqMan® Fast Advanced Master Mix and taqMan® probes for mus Dkk3 exons 1–2, Mm01269624; mus Dkk3 exons 3–4, Mm00443801; mus Cyclin D1; Mm00432359; mus c-Myc, Mm00487804; human Cyclin D1, Hs00765553; human c-Myc, Hs00153408; human Axin2, Hs00610344; human Cox2, Hs000153133; human Wfdc2, Hs00899484; human Cdh2, Hs00983056; human; human Fosl1, Hs04187685; human, Tuba, Hs0102675; and human Gapdh, Hs03929097 were purchased from Life Technologies.
Co-immunoprecipitation binding studies
Cells expressing the epitope-tagged target proteins were lysed in 1X IP buffer (ThermoFisher Sci) with 150 mM NaCl, protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Lysates were incubated with anti-epitope antibody for 3 hrs at 4°C and immune complexes collected on ProteinA/G-agarose beads (Sigma). Immune complexes were washed five times with lysis buffer and eluted in Laemmli buffer containing 1% SDS. Cell extracts and immune complexes were separated by SDS–PAGE and immunoblot analysis done with anti-Flag, anti-Myc and anti-HA antibodies.
Native ß-catenin and ß-TrCP in HeLa cells were co-immunoprecipitated from cells treated for increasing times with TAT-Dkk3b. Anti-Dkk3b affinity DynaBeads® (7.2 μg/mg resin) and control rabbit IgG affinity DynaBeads® (8.4 μg/mg resin) were prepared by coupling affinity purified anti-Dkk3b IgG [46] and rabbit IgG, respectively, to Dynabeads M-270 (ThermoFisher) according to manufacturer’s instructions. HeLa cell lysates were prepared in 1X IP buffer (ThermoFisher) supplemented with 150 mM NaCl and 1X protease inhibitors. Cell lysates (200 μg protein) were incubated with 1 mg of anti-Dkk3b or Control affinity beads, in duplicate. Immune complexes were collected using a DynaMag™magnet. Acid eluates were then separated on 10% SDS-PAGE gels and target proteins identified by immunoblot. All native co-immunoprecipitation experiments were repeated three times.
TAT-fusion protein synthesis
Dkk3b cDNA was cloned into the pTAT-HA plasmid [47], a gift from Steven Dowdy (Addgene plasmid # 35612). TAT-Dkk3b expression was induced with isopropyl ß-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside in BL21(DE3) cells. TAT-Dkk3b present in inclusion bodies was solubilized by denaturation in PBS containing 6 M urea, purified by affinity chromatography on Ni-NTA resin, and eluted with 150 mM imidazole in 6M Urea. Urea was rapidly removed by G10 spin column gel filtration and TAT- Dkk3b was stored at -20°C at 1 mg/ml in PBS at pH 6.0.
Results
The Dkk3 gene encodes multiple transcripts
The unaltered ß-catenin signaling in the Dkk3 knockout mouse (Dkk3tm1Cni) [20] led us to re-examine the biological relevance of an intracellular ~30 kDa DKK3 isoform (D2p29) that showed dynamic, microfilament dependent intracellular trafficking in rat astrocytes [46, 48]. Amino acid sequence alignment showed that the secreted DKK3 and D2p29 (designated hereafter Dkk3b) shared all but the N-terminal 71 residues that comprise the signal peptide sequence and N-glycosylation sites.
The Dkk3tm1Cni mutant mouse was generated by replacement of the majority of exon 2 of the Dkk3 gene with an in-frame LacZ-stop cassette [20]. Exon 2 encodes the N-terminal 71 amino acids responsible for directing DKK3 to the secretory vesicle, and also harbors a biologically important CpG island (Fig 1A).
The first codon in exon 3 of the Dkk3 gene encodes the initiator methionine of Dkk3b from frogs to man, suggesting that Dkk3b is generated from a second Dkk3b transcript, possibly initiating within the 6 kb intron 2 (Fig 1A). Using exon specific qPCR to quantify Dkk3 locus transcripts containing exon 2 or exon 3 (Fig 1B, S1 Fig), we found that all Dkk3 transcripts present in mouse astrocyte mRNA had Dkk3 exon 3 codons, while only ~60% generated a PCR product with Dkk3 exon 2 specific PCR primers, suggesting that ~40% of the total Dkk3 mRNA lacked the exon 2 codon and could presumably encode Dkk3b (S1 Fig). The specificity of the exon-specific qPCR of these Dkk3 exons was validated using total RNA from Dkk3tm1Cni mutant mouse brain; no Dkk3 transcripts with exon 2 codons were detected and only Dkk3 transcripts with exon 3 codons were found (Fig 1B).
Promoter: luciferase reporter assays were used to search for transcriptional regulatory elements located in intron 2 of the rat Dkk3 gene. Robust promoter activity is found in the 750 nucleotides of intron 2 immediately upstream of exon 3 and progressive deletion from the 5’ end of this intron 2 fragment localized a functional promoter (TSS2) to the 250 nucleotides just upstream of the 5’ end of exon 3 (Fig 1C). The essential TATA box was located at -35 nucleotides upstream from the 5’ end of exon 3 of the Dkk3 gene (Fig 1C, see construct P259D); in mouse and human Dkk3 genes a TATA box is located ~90 nucleotides upstream of exon 3 and the transcriptional start site was determined to be at -92 nucleotides upstream of exon 3 by 5’RACE analysis of the Cfp mRNA surrogate of DKK3b (see S2 Fig). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of rat astrocyte gDNA revealed that the native TSS2 in the Dkk3 gene bound RNA pol II (Fig 1D) and the TATA Box Binding Protein (TBP) (Fig 1D) indicating that the TATA box at -35nt in intron 2 (see Fig 1C) is functional.
Dkk3b is a biologically active product of the Dkk3 gene in vivo
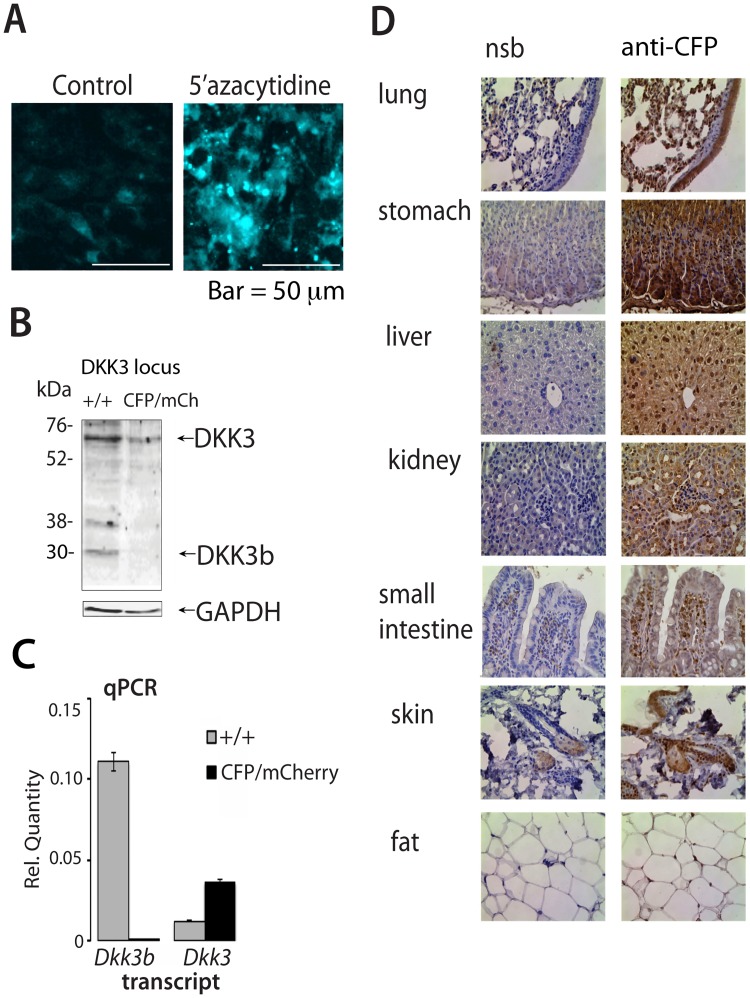
To explore the biological significance of Dkk3b, we used targeted homologous recombination (HR) driven by artificial nucleases to selectively disrupt this transcript within the mouse genome. A promoter trap knock-in strategy was devised using zinc finger nucleases [33] (ZFNs) to create a double stranded break (DSB) in intron 2 of the Dkk3 gene between TSS2 and exon 3 that would facilitate the HR mediated insertion of a floxed CFP-stop cassette. Splice junctions at exon 3 were preserved so that TSS1-driven transcripts encoding the secreted DKK3 could produce full-length, spliced mRNA (Fig 2A–2C). The CFP insert diverts TSS2-driven transcription to the CFP surrogate resulting in the selective, functional loss of Dkk3b transcripts in homozygous animals. Immortal C8D1A cells, isogenic to the C57Bl/6j mouse, Cel-I assays, and single stranded oligonucleotide directed HR repair were used to validate the targeting strategy and ZFN-facilitated donor DNA HR. ZFN-generated DSBs and HR repair in the presence of the donor DNA resulted in weak expression of CFP in C8D1A cells (Fig 3A). These modified cells retain an intact exon 2 CpG island(s) upstream of the edited Dkk3 locus [49–51]. Since CpG island methylation is common in immortalized cells [52] and presumably depresses expression of REIC (Reduced Expression in Immortal Cells)—a synonym for DKK3 [11]—we examined whether the methyltransferase inhibitor, azacytidine, would enhance expression of the TSS2-driven CFP decoy. Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase activity in the gene-edited C8D1Acfp/wt cells resulted in a >5-fold increase in CFP expression (Fig 3A).
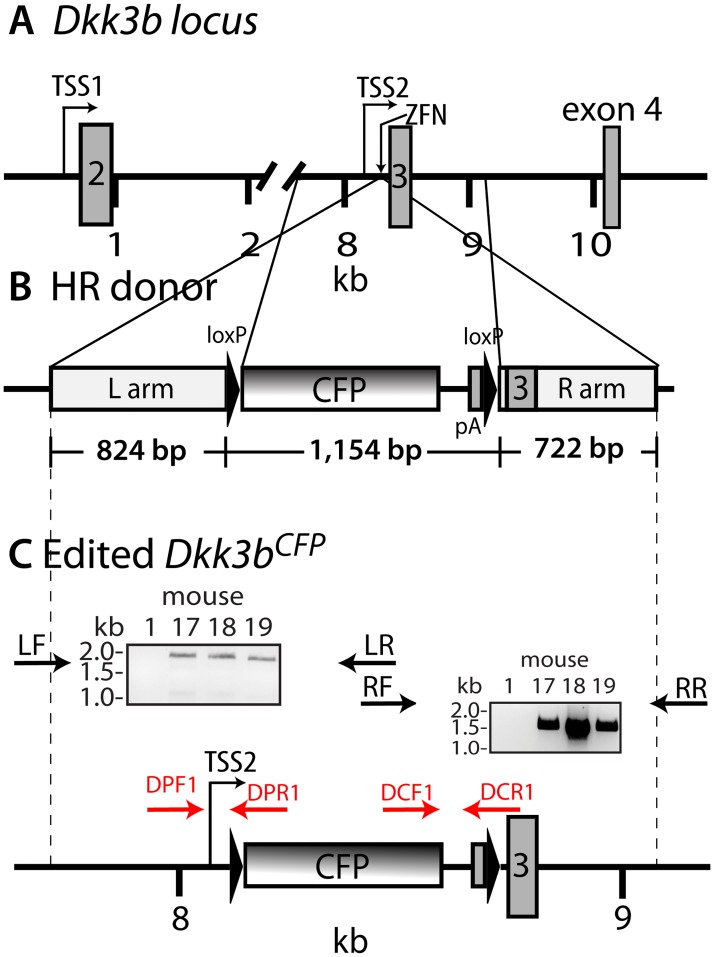
Fig 2. Targeting strategy for ZFN gene-editing of the Dkk3b locus in the mouse.
(A) Organization of exons 2–4 of the wild type Dkk3 locus. TSS1, transcriptional start site 1; TSS2, transcriptional start site 2 and ZFN targeting site. (B) Organization of the HR donor. C. Schematic diagram of the gene edited Dkk3bCFP locus. Target locus modification confirmed using PCR primers anchored outside of the HR region (LF and RR) and overlapping in the CFP cds (LR and RF). PCR products (LF:LR and RF:RR) were sequenced in both directions. Genotyping PCR primers indicated by arrows (see Table 1 for sequences).
Fig 3. Analysis of the biological role the TSS2 driven Dkk3b in the ZFN gene-edited Dkk3bCFP/+ mouse.
(A) Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase activity increases TSS2-driven CFP in Dkk3bCFP/+ cells. (B) DKK3 isoforms present in wild type and Dkk3bCFP/mCherry MEFs (anti-DKK3 (ab186409) (Abcam). (C) QPCR analysis of Dkk3 and Dkk3b transcripts in wild type and Dkk3bCFP/mCherry MEFs. Data reported as means ± se, n = 3. (D) TSS2-driven, immunoreactive CFP expression in representative tissues of the Dkk3bCFP/wt mouse. NSB, Normal rabbit serum, CFP, anti-CFP IgG(cat#632381) (TakaRa).
C57Bl6 mouse zygotes were then injected with ZFNDkk3b mRNAs and a linear HR donor DNA to create the Dkk3bCFP knock-in mouse. Thirty-five of 65 (54%) injected one cell embryos produced viable pups, and DNA sequencing of the target locus confirmed that 1 male (#17) and 2 females (#18 & #19) (8.6%) had HR mediated insertion of a floxed CFP decoy inserted 35 nucleotides upstream from exon 3 (see Fig 2C) with intact splice junctions. No off-target mutations were found for the 10 highest predicted candidate target sites in founder #19 (Table 2). F1 progeny from crosses of the Dkkb3CFP/+ male and a wild type female showed Mendelian inheritance patterns characteristic of a single segregating allele (Table 3). The tissue distribution of Dkk3b expression was evaluated using the ~26 kDa CFP surrogate in the Dkk3bCFP/+ mutant mouse. Immunoreactive CFP was found throughout the Dkk3bCFP/+ mouse (Fig 3D) illustrating the ubiquitous nature of TSS2 activity of the Dkk3 gene.
Table 2. Off-target analysis of ZFN gene edited Dkk3bCFP mouse (Founder #19).
Mouse C57bl6 genome GRCm38; mismatched bases are italicized and underlined.
| Gene | Chr | Str | gap (nt) | location (nt) | Target sequence | # clones | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left nuclease | Right nuclease | wt indels | ||||||
| Dkk3 | 7 | - | 7 | 112150811–12150781 | 5’-gaagg CAGCCCCTTTTC ttcacct CAGTTGTAACTG aaaga-3’ | 4 | 6 | |
| Dlst | 12 | + | 7 | 85127757–85127787 | 5’-gcccc CAGCCCCTTAGC actggct CAGCTTTAACTG tatcc-3’ | 12 | 0 | |
| Rnu6 | 19 | + | 7 | 14405226–14405196 | 5’-aagtc CAACCCCTTTTC tcatctc CAGTTGGCCCTG tggcg-3 | 10 | 0 | |
| Tcf7l2 | 19 | + | 7 | 55794079–55794109 | 5’-actga CACCCCCTTTTC caaatga ATGTTGTAACTG gcctt-3’ | 10 | 0 | |
| Akap9 | 5 | + | 7 | 3954573–3954603 | 5’-ccact CATCCCCTTTTT tctgtga CAGTTGTAACAG agtgc-3 | 10 | 0 | |
| Drb1 | 2 | + | 7 | 76502794–76502835 | 5’-gtttg CAGCCCTTTTTG tagaacc CAGTTGTAAAAG taact-3’ | 12 | 0 | |
| Aldoart1 | 4 | + | 7 | 73254288–73254328 | 5’-gaaat CACCTCCTTTTC tttgatc CATTTGAAACTG actaa-3’ | 10 | 0 | |
| Fam168b | 1 | - | 6 | 34825844–34825873 | 5’-ctctc CAGCCCCCTTTC ttaatg CAGTTGTAAATG GAGAG-3’ | 10 | 0 | |
| Mettl21e | 1 | + | 6 | 44440591–44440619 | 5’-gcaaa CAGTCCCTTTTA tactgt CAGGTGTACCTG actgt-3’ | 8 | 0 | |
| Rps6ka5 | 12 | + | 5 | 100605356–100605384 | 5’-tcact GAGCCAATTTTC tggcc CAGTTGTAACTG tttta-3’ | 10 | 0 | |
| Arhgef2 | 3 | - | 5 | 88647980–88647952 | 5’-agtga CAGCCCCTTTTC agaaa CCGTGGTCACTG cctgg-3’ | 10 | 0 | |
Table 3. Outcome of crosses of the Dkk3bCFP/wt, Cre-rescued DKK3bΔCFP/wt mutant and Dkk3bwt/wt mice.
| Genotype | Genotype | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | male | female | pups | Dkk3bwt/wt | Dkk3bCFP/wt | Dkk3bCFP/CFP | |||
| Exp. | Obs. | Exp. | Obs. | Exp. | Obs. | ||||
| C57Bl6j | Dkk3bCFP/wt | Dkk3bwt/wt | 159 | 80 | 84 | 80 | 75 | 0 | 0 |
| (50%) | (53%) | (50%) | (47%) | (0%) | (0%) | ||||
| Dkk3bCFP/wt | 135 | 33 | 46 | 68 | 89 | 33 | 0 | ||
| (25%) | (34%) | (50%) | (66%) | (25%) | (0%) | ||||
| CD1 | Dkk3bCFP/wt | Dkk3bwt/wt | 159 | 80 | 84 | 80 | 75 | 0 | 0 |
| (50%) | (53%) | (50%) | (47%) | (0%) | (0%) | ||||
| Dkk3bCFP/wt | 135 | 33 | 46 | 68 | 89 | 33 | 0 | ||
| (25%) | (34%) | (50%) | (66%) | (25%) | (0%) | ||||
| Dkk3bwt/wt | Dkk3bΔCFP/wt | Dkk3bΔCFP/CFP | |||||||
| Dkk3bCFP/wt | |||||||||
| CD1 | Dkk3bwt/wt | Dkk3bΔCFP/wt | 56 | 28 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 0 | 0 |
| (50%) | (48%) | (50%) | (52%) | (0%) | (0%) | ||||
| Dkk3bCFP/wt | Dkk3bΔCFP/wt | 63 | 16 | 18 | 32 | 32 | 15 | 13 | |
| (25%) | (29%) | (50%) | (51%) | (25%) | (21%) | ||||
The mRNA for the CFP surrogate of Dkk3b was then used to establish the TSS2-driven transcription initiation site by 5’RACE of polyadenylated mRNA isolated from the cerebral cortex of the mutant Dkk3CFP mouse. The Cfp mRNA began at nt8284 of the Dkk3 gene, ~90 nt upstream of the ATG start site of exon 3 of the Dkk3 gene (S2 Fig). The 5’UTR of the Cfp transcript also harbored the imbedded LoxP site used to excise the promoter trap reporter illustrating that the TSS2 is functional at this mouse gene locus.
No viable homozygous mutant offspring were found after mating of heterozygous Dkk3bCFP/wt mice (Table 3), and no homozygous mutant blastocyst implants were found as early as embryonic day 5.5 (n = 34 embryos) suggesting that DKK3b is essential for development at or near the time of embryo implantation. This outcome differs markedly from that of the Dkk3tm1Cni mouse and suggests that at least one wild type Dkk3b allele is required for survival. The penetrance of the lethal phenotype for the single segregating Dkk3bCFP allele was confirmed in out-crosses on the CD1 background (Table 3).
Excision of the floxed CFP cassette (ΔCFP) in the unfertilized mutant oocyte using a Sox2 promoter-driven Cre recombinase [53, 54] rescued the lethal phenotype of the Dkk3bCFP mutation and left behind a diagnostic single 34 bp loxP remnant at the target locus. Bi-allelic, gene-edited Dkk3bΔCFP/CFP offspring were recovered from crosses of Dkk3bΔCFP/+ to a Dkk3bCFP/+ mice (Table 3) and showed Mendelian inheritance confirming that embryonic lethality resulted from the interruption of Dkk3b transcription rather than any tightly linked cis gene defect(s).
Since embryonic lethality prevented the generation of homozygous mutants, ex vivo gene editing of heterozygous mutant MEFs was used to confirm the promoter trap knock-in strategy. Bi-allelic disruption of the Dkk3b locus was done in heterozygous mutant MEFs (Dkk3bCFP/+) using a second round of ZFN-initiated, HR repair to insert an mCherry reporter into the remaining wild type allele. Forty-eight hours after ex vivo gene editing, viable MEFs with bi-allelic mutations at the target locus expressing both fluorescent proteins were found attached to the dish, as well as free floating in the growth medium. Mutant Dkk3bCFP/mCherry MEFs, both attached and free floating, were pooled and sorted by FACS. Immunoblots of sorted cell lysates showed that the Dkk3bCFP/mCherry MEFs continued to express the ~65 kDa glycosylated DKK3 protein, while the 30 kDa DKK3b was absent (Fig 3B). Exon-specific qPCR confirmed preservation of the secreted Dkk3 transcript and the selective loss of the Dkk3b transcript in Dkk3bCFP/mCherry MEFs (Fig 3C). Attempts to propagate these mutant MEFs was prevented by the severe attachment defect associated with the DKK3b-deficient cells. These data suggest that DKK3b is necessary for cell-cell interactions, required for embryogenesis, and that TSS2-driven CFP is a surrogate for Dkk3b expression.
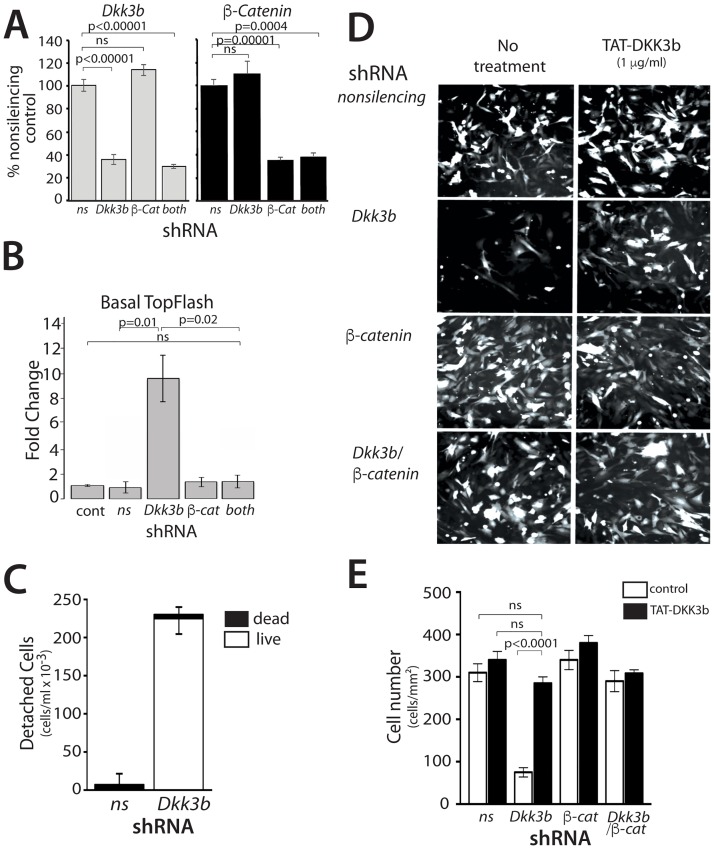
RNAi knock down was used to explore the role of DKK3b on MEF attachment, cell proliferation and its relationship to ß-catenin signaling. RNAi knockdown of the Dkk3/Dkk3b and/or ß-catenin transcripts in MEFs was confirmed by qPCR (Fig 4A). The effects of Dkk3b knockdown on ß-catenin dependent gene expression was examined using the ß-catenin responsive TOPflash luciferase reporter. Dkk3b KD MEFs showed a 10-fold increase in basal TOPflash activity compared that of the unaltered control and non-silencing KD cells (Fig 4B). Simultaneous knockdown of Dkk3/Dkk3b and ß-catenin expression completely blocked this increased signaling. Similar to the Dkk3b-null MEFs (see above), >70% of the viable Dkk3/Dkk3b KD cells were found free-floating after 3 days in culture (Fig 4C). Cell attachment and proliferation during this 3-day growth period was unaffected in cells expressing a non-silencing shRNA control or in ß-catenin KD cells (Fig 4D). The attachment defect in Dkk3/Dkk3b KD cells was completely reversed by simultaneous knockdown of ß-catenin mRNA (Fig 4D and 4E). Replacement of cellular DKK3b by addition of a cell penetrating TAT-DKK3b protein to the growth medium [55] completely restored cell attachment of the Dkk3/Dkk3b knockdown MEFs to that of the controls, but provided no additional benefit to either the ß-catenin KD cells or in ß-catenin KD:Dkk3/Dkk3b KD MEFs (Fig 4D and 4E).
Fig 4. Characterization of DKK3b loss of function in MEFs.
(A) QPCR analysis of shRNA knockdown of Dkk3 and ß-catenin in MEFs. Data reported as means ± se, n = 3. (B) Basal TOPflash activity in shRNA KD MEFs. Data reported as the means ± se, n = 6. (C) Quantification of unattached, viable cells after 72 h in Dkk3/Dkk3b KD MEFs. Viability determined by Trypan blue exclusion; data reported as means ± se, n = 3. (D) Representative photomicrographs of GFP-expressing, shRNA KD MEFs. TAT-DKK3b (1 μg/ml) was added to the growth medium as indicated. GFP positive KD cells in 10 random fields were counted for each KD condition and the data reported as the means ± SD. (E) Quantitative analysis of the attached cells in part D. A total of 100 cells counted and the data expressed as cells/mm2. Data represent the means ± se, n = 6 wells for each condition. Taken together, these data show that our promoter-trap knock-in gene-editing strategy: i) selectively eliminated expression of the intracellular DKK3b; and ii) preserved expression of the secreted DKK3. Loss of DKK3b in MEFs led to elevated nuclear ß-catenin levels, increased ß-catenin signaling, and defective cell attachment to the substratum.
DKK3b modulates cell proliferation and ß-catenin signaling
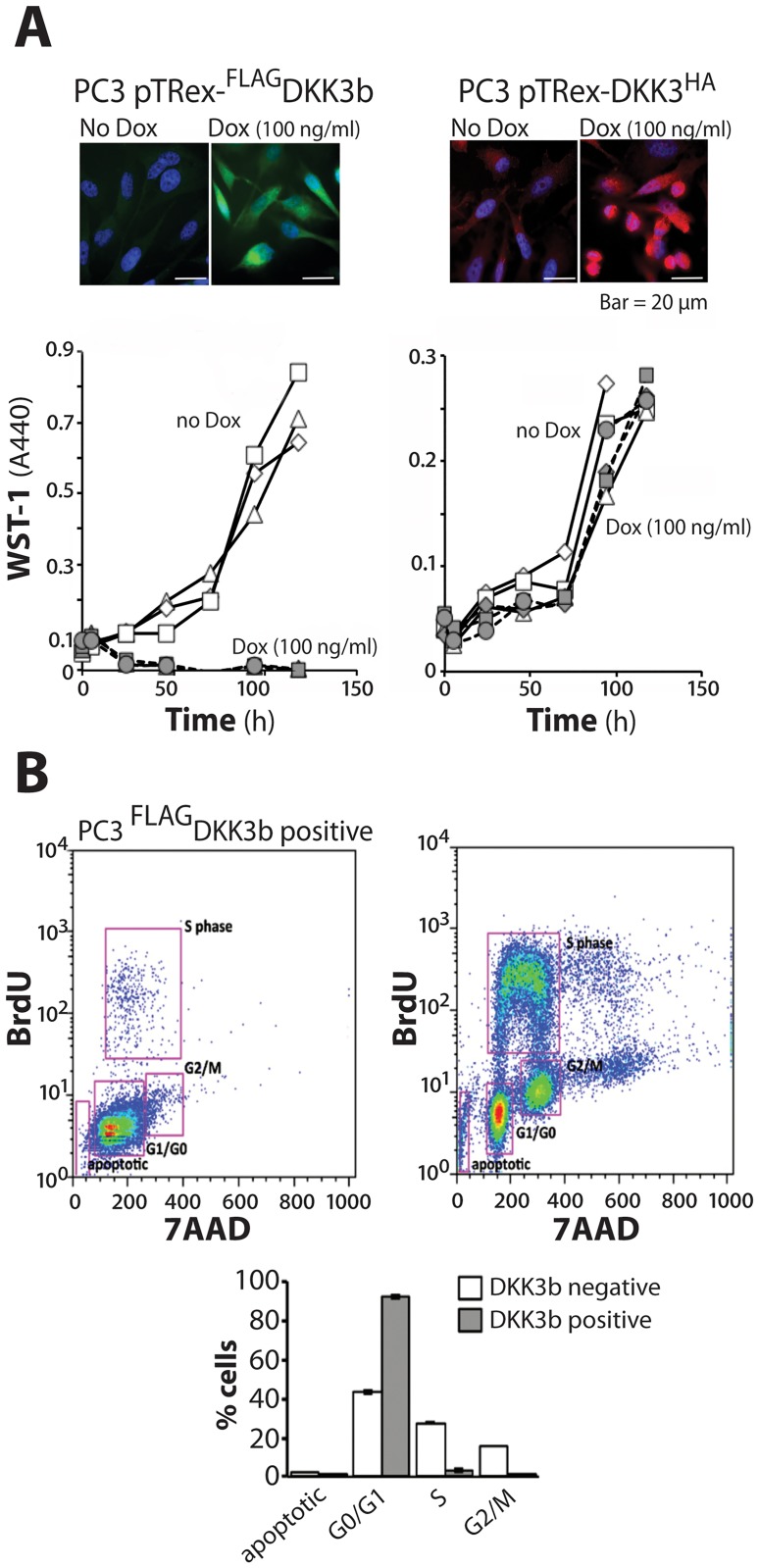
The relationship between DKK3b and the ß-catenin signaling pathway was further defined by cell proliferation, promoter-driven reporter assays, and cell migration analysis in prostate and breast cancer cells. Tet-inducible constructs of the intracellular DKK3b and the secreted DKK3 were used to provide fine control over exogenous expression levels and to avoid the untoward effects of over-expression. In the DKK3/DKK3b-deficient, PC3 prostate cancer line, expression of DKK3b arrested cell proliferation of the (Fig 5A) at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle (Fig 5B) and led to the loss of DKK3b expressing cells by 24–36 h of induction (Fig 5A). Unlike prior over-expression studies [11, 19, 56, 57], induction of equivalent levels of secreted DKK3 did not alter PC3 cell proliferation (Fig 5A and 5B).
Fig 5. DKK3b regulation of cell proliferation.
(A) Comparison of the effects of DKK3b and DKK3 on PC3 cell proliferation. Representative photomicrographs of immune-reactive, Dox-induced DKK3b and DKK3 expression in PC3 cells. Cell proliferation over 5 days (open symbols, no Dox; solid symbols, Dox; each symbol a separate experiment; time points determined in triplicate for each experiment). (B) DKK3b arrests cell proliferation at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle (Error bars represent the SE of three independent experiments.
These data show that DKK3b has the anti-proliferative activity in cancer cells that were previously associated with gene product(s) from the Dkk3 locus [11, 56].
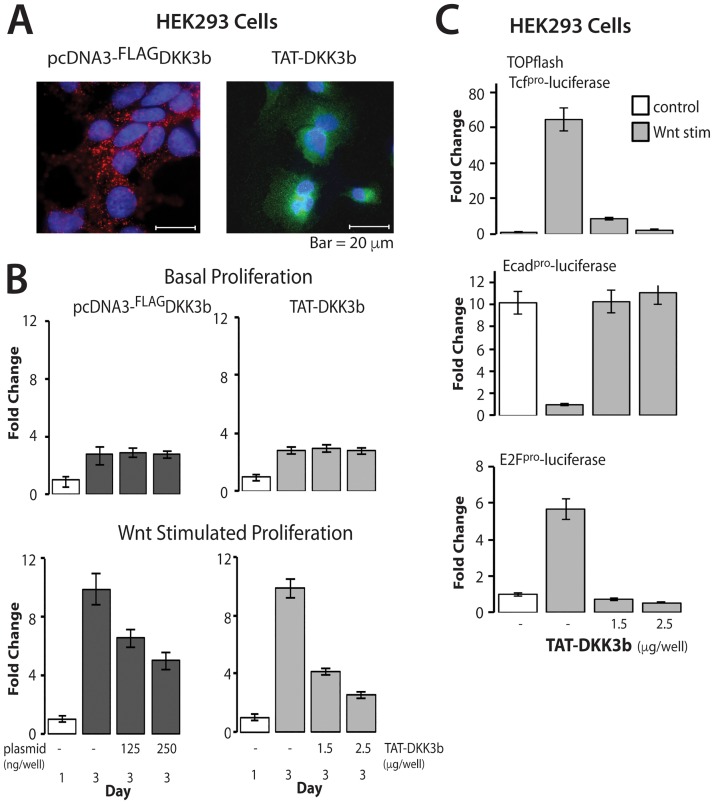
The relationship between DKK3b and ß-catenin signaling was defined by cell proliferation and promoter-driven reporter assays in HEK293 cells with reduced endogenous DKK3b. Basal cell proliferation was unaffected by ectopic DKK3b produced either by transient transfection and by addition of the TAT-DKK3b (Fig 6A and 6B). On the other hand, Wnt-stimulated cell proliferation was progressively slowed, but not arrested in cells treated with DKK3 by either transient transfection or by TAT-Dkk3b (Fig 6B). The more robust decrease in proliferation observed with TAT-DKK3b treatment is likely due to the more uniform delivery of the tumor suppressor to the cell monolayer. Concentrations of TAT-DKK3b ≥2.5 μg/ml completely silenced Wnt-stimulated cell proliferation without altering basal cell proliferation (Fig 6B, compare basal and Wnt stimulated proliferation at 2.5 μg/ml TAT-DKK3b).
Fig 6. DKK3b effects on Wnt1-stimulated ß-catenin signaling.
(A) Representative photomicrographs of the cellular distribution of transiently transfected DKK3b and TAT-DKK3b in HEK293 cells. DKK3b identified with anti-Flag IgG and anti-DKK3 IgG, respectively. (B) DKK3b blocks Wnt1-stimulated cell proliferation without altering basal cell proliferation. Data reported as means ± se of 4 independent experiments; n = 3 in individual experiments. Open bar—day 1; shared bars—day 3. (C) TAT-DKK3b antagonizes Wnt1-stimulated TOPflash activity and secondary ß-catenin dependent gene expression. Data reported as means ± se of 3 independent experiments; triplicate determinations done in individual experiments.
Primary and downstream promoter-luciferase reporter assays determined the effects of DKK3b on ß-catenin-driven gene expression. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with Wnt1 and promoter-driven firefly luciferase constructs paired with a control CMV-driven renilla luciferase cDNA, and then treated with TAT-DKK3b for 24 h. Wnt1 stimulated cells showed a 65-fold increase in TOPflash activity and TAT-DKK3b completely arrested expression of this canonical ß-catenin reporter (Fig 6C). DKK3b also modulated downstream ß-catenin regulated pathways that reduce cell adhesion (ECad promoter [58]) and promote cell cycle progression (E2F promoter [59]). Wnt1 silenced E-Cad promoter activity by 90%, but the presence of TAT-DKK3b restored promoter activity to basal levels (Fig 6C). Similarly, Wnt1 increased E2F-promoter activity 6-fold, but the presence of TAT-DKK3B maintained E2F-promoter activity at baseline levels (Fig 6C). Taken together, these data show that DKK3b modulates multiple aspects of ß-catenin signaling.
DKK3b blocks nuclear translocation of ß-catenin
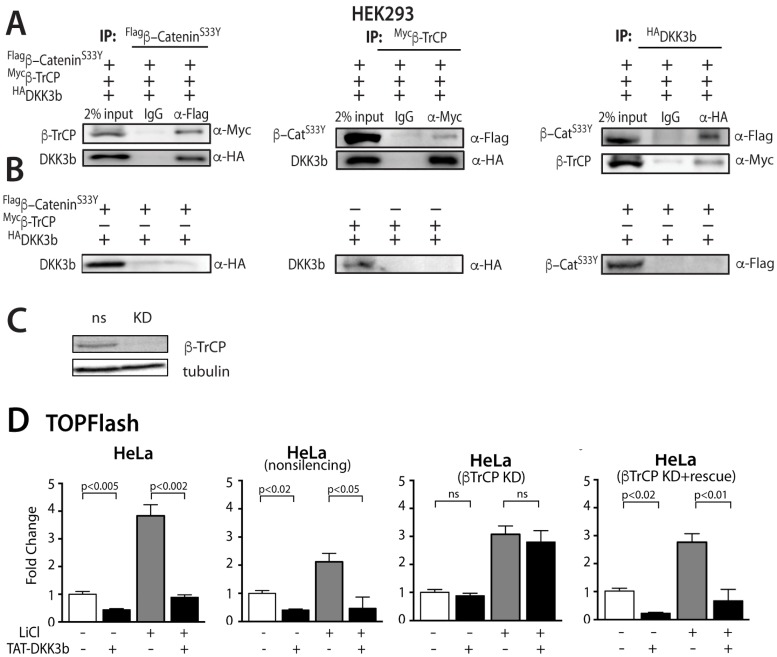
Yeast two hybrid screens showed that DKK3 interacted with the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, ß-TrCP, and that this complex captured cytoplasmic dephosphorylated ß-catenin [17], although the source of the essential intracellular effector produced by the Dkk3 gene was not identified [17, 18]. DKK3b provides just such an intracellular effector.
Co-IP studies were done with lysates of HEK293 cells constitutively expressing epitope-tagged DKK3b, ß-TrCP and the constitutively active S33Y mutant of ß-catenin that evades the destruction complex. When all three proteins were present, immune precipitates of Flag-S33Yß-catenin also contained both ß-TrCP and DKK3b, while control IgG precipitates failed to capture any epitope tagged targets (Fig 7A). Similarly, immune precipitates of myc-ß-TrCP contained both S33Yß-catenin and DKK3b; immune precipitates of HA-DKK3b contained both S33Yß-catenin, and ß-TrCP (Fig 7A). Co-IP studies of cell lysates expressing only two of the three binding partners (Myc-ß-TrCP and HA-DKK3b) or (FLAG-S33Yß-catenin and HA-DKK3b) failed to show any interaction between these epitope-tagged binding partners (Fig 7B). These data suggest that DKK3b captures unphosphorylated ß-catenin in a complex with ß-TrCP and that all three partners are required to assemble this complex.
Fig 7. Characterization of the DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin complex and its effects of ß-catenin nuclear translocation/signaling.
(A) Co-IP of DKK3b, ß-TrCP and ß-S33Ycatenin from HEK293 cell lysates. Epitope tagged targets were expressed by transient transfection in HEK293 cells, immune precipitates collected by Protein A/G Sepharose, and co-precipitating partners were analyzed by immunoblot with epitope specific antibodies. (B) Co-IP of HEK293 cell lysates lacking one binding partner. (C) shRNA knockdown of ß-TrCP in HeLa cells. Immunoblots done with anti-TrCP IgG. (D) Effects of ß-TrCP KD and ß-TrCP rescue on TAT-DKK3b dependent inhibition of TOPflash activity in HeLa cells. Unaltered, non-silencing control, ß-TrCP KD cells, and rescued ß-TrCP KD cells expressing a mouse ß-TrCP rescue plasmid were stimulated with ±LiCl for 16h in the absence or presence of TAT-DKK3b (5 μg/ml). TOPflash activity reported as fold change from resting HeLa cells. Data are reported as the means ± se (n = 4); each experiment was repeated 3 times.
The role of ß-TrCP in the DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin complexes on nuclear trafficking and gene expression was examined in ß-TrCP KD HeLa cells. Immunoblot analysis confirmed shRNA dependent loss of the ß-TrCP transcript in KD cells (Fig 7C). To maximize nuclear localization of ß-catenin, control and ß-TrCP KD cells were treated with LiCl, a chemical mimic of Wnt that stabilizes cytosolic ß-catenin by inhibiting its phosphorylation by GSK-3 in the destruction complex [60]. The effects of the DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin complex on ß-catenin-driven gene expression in ß-TrCP KD HeLa cells was then evaluated using the TOPflash assay. In both resting and LiCl-stimulated control and non-silencing KD cells, addition of TAT-DKK3b silenced TOPflash activity (Fig 7D). In ß-TrCP KD cells, TAT-DKK3b had no effect on TOPflash activity, whereas rescue of the ß-TrCP KD by transfection with mouse ß-TrCP cDNA restored the ability of TAT-DKK3b to arrest TOPflash activity in both resting and LiCl-stimulated cells. These data show that the DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin complex alters the ability of the ß-catenin to enter the cell nucleus and blocks ß-catenin-driven gene expression.
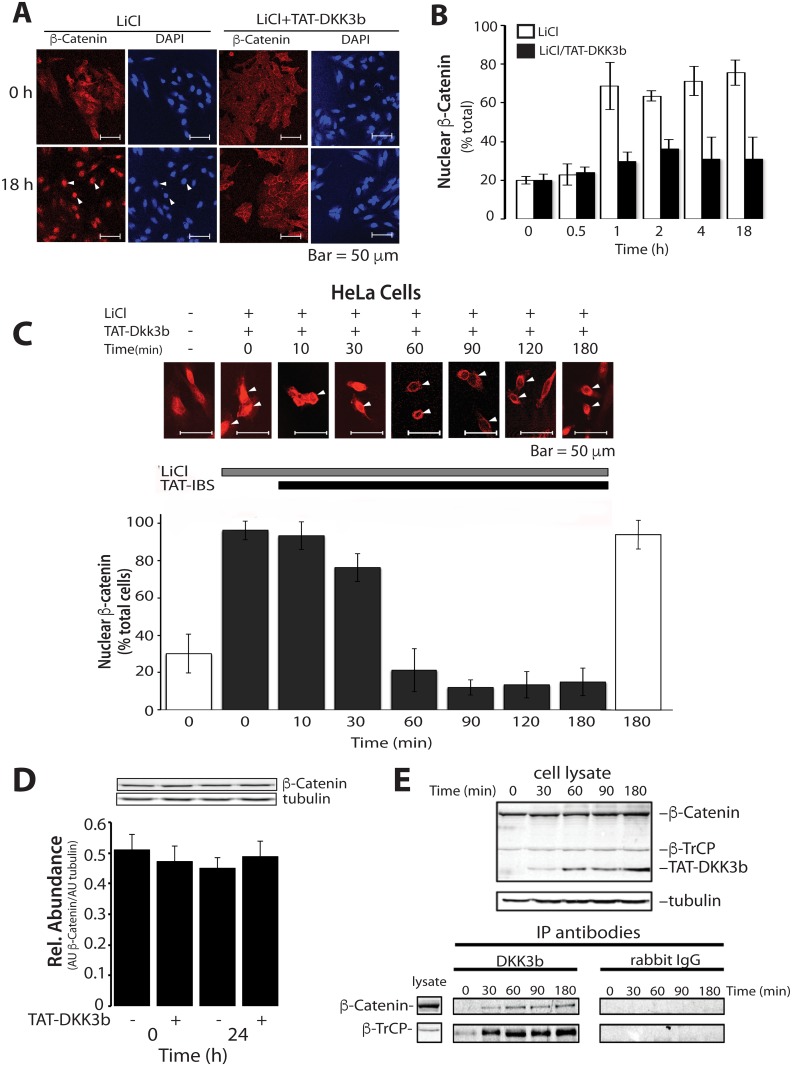
The effects of DKK3b on the dynamics ß-catenin nuclear trafficking was determined in LiCl stimulated HeLa cells. HeLa cells lack native Dkk3/Dkk3b expression and show accelerated ß-catenin-driven cell proliferation [61]. As expected, HeLa cell ß-catenin was distributed throughout the cell interior with marginal localization at the cell periphery (Fig 8A). In the absence of DKK3b, LiCl led to the rapid accumulation of ß-catenin in the nucleus reaching maximal levels after 60 min in >70% of the treated cells, and this remained constant for 18 h when LiCl was present (Fig 8A and 8B). Addition of TAT-DKK3b along with LiCl completely blocked the accumulation of nuclear ß-catenin for up to 18 h.
Fig 8. Effects of TAT-DKK3b on the dynamics of ß-catenin nuclear translocation.
(A) Representative photomicrographs of the distribution of ß-catenin in control (unstimulated) and LiCl-stimulated HeLa cells ± TAT-DKK3b (arrows—cell nucleus). (B) Time course of LiCl-induced nuclear translocation of ß-catenin in HeLa ± TAT-DKK3b (5 μg/ml). At least 200 cells were counted in 20 random fields from 3 individual slides; data reported as means ± SD. (C) Time course of the effects of TAT-DKK3b on steady-state nuclear ß-catenin in LiCl-stimulated HeLa cells. Nuclear ß-catenin positive cells were scored as in B, and the data reported as means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. (D) Immunoblot of the effects of TAT-DKK3b on ß-catenin levels in HeLa cell lysates. Data reported as means ± se, n = 3. (E) Time dependent assembly of the TAT-DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin complex in LiCl-stimulated HeLa cells. Cell lysates were incubated with anti-DKK3b-IgG or NRS-conjugated DynaBeads, and co-precipitating proteins determined by immunoblot with anti-target antibodies.
The time dependent efflux of nuclear ß-catenin due to TAT-DKK3b was determined in HeLa cells stimulated with LiCl for 18 hrs. Addition of TAT-DKK3b to these maximally stimulated cells resulted in the rapid loss of nuclear ß-catenin, beginning within 30 min and reaching maximal suppression by 60 min (Fig 8C). TAT-DKK3b-suppressed nuclear ß-catenin below levels in untreated HeLa cells for at least 3 h. Total HeLa cell ß-catenin levels were unaffected by TAT-DKK3b (Fig 8D) indicating that the loss of ß-catenin from the nucleus in TAT-DKK3b treated cells was due to cellular redistribution rather than enhanced ß-catenin degradation. Anti-DKK3b-IgG-affinity beads were used to capture DKK3b associated native proteins in the LiCl-stimulated HeLa cell lysates (Fig 8E). The loss of nuclear ß-catenin in LiCl-stimulated cells was accompanied by the time-dependent accumulation of both ß-catenin and ß-TrCP in a complex with the TAT-DKK3b (Fig 8E). Total cellular levels of both ß-catenin and ß-TrCP were unaltered during the 3 h TAT-DKK3b treatment period, while intracellular DKK3b showed a time-dependent accumulation in the complex that paralleled the loss of ß-catenin from the cell nucleus (Fig 8E). Thus, the DKK3b:ß-TrCP:ß-catenin inhibitory complex is formed rapidly, interrupts the dynamics of nuclear import/export, and defines the molecular basis for the silencing of ß-catenin signaling by DKK3b.
Since DKK3b silenced both TOPflash activity and captured the native transfactor in an inhibitory complex with DKK3b:ß-TrCP, we determined the effects of TAT-DKK3b on native gene expression in resting and LiCl-stimulated HeLa cells. Like the TOPflash assay, addition of TAT-DKK3b to unstimulated HeLa cells led to a 40–60% decrease in both native CyclinD1 and c-Myc transcripts after 16 h (S3A Fig). Similarly, in both resting and LiCl-stimulated cells, the expression of 5 representative ß-catenin dependent genes Cdh2, Axin2, Cox2, Wfdc2 and Fosl1 all showed DKK3b dependent silencing (S3B Fig), while expression of the ß-catenin independent Gapdh used for normalizaiton, and alpha tubulin (Tuba) transcripts were unaffected. These data show that both reporter and intrinsic gene expression are modulated by ability of DKK3b to control ß-catenin translocation to the cell nucleus, and that this action depends on the the ability of DKK3b to capture the native transactivator in an extranuclear complex with ß-TrCP.
Discussion
DKK3 is the enigmatic member of an ancient family of secreted glycoproteins that regulate the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway by interrupting the assembly of a functional Wnt liganded receptor [4, 11]. It is the only unambiguous tumor suppressor in the family, and a diverse literature links DKK3 and tumor suppression to the ß-catenin pathway [11]. Unfortunately, the inability of DKK3 to block Wnt receptor assembly due to steric hindrance [4, 12] poses a significant challenge to our understanding of its tumor suppressor function. Yeast two-hybrid screens [17] showed that DKK3 formed a complex with ß-TrCP, and dephosphorylated ß-catenin that prevented transfactor nuclear translocation [17], but Lee and co-workers did not identify the authentic intracellular DKK3 isoform responsible for this biology.
The recognition that the Dkk3 gene encodes a second gene product, DKK3b—a vital intracellular protein that regulates ß-catenin trafficking—provides the missing component that connects the Dkk3 gene to its regulation of the ß-catenin signaling pathway. DKK3b acts on the ß-catenin signaling pathway independent of the Wnt modulated destruction complex and modulates a diverse array of cellular functions, such as cell proliferation, cell attachment, embryogenesis and gene expression. Positioned downstream of the Wnt regulated degradation complex, DKK3b modulates ß-catenin trafficking to the nucleus. In astrocytes, DKK3b rapidly shuttles between the perinuclear space and the plasma membrane using myosin motors and actin fibers [48, 62], suggesting that it may carry ß-catenin back the cell periphery for reuse in the adherens complex remodeling. The ability of DKK3b to repair the attachment defect observed in DKK3b-null MEFs suggests that DKK3b plays a key role in the delivery of ß-catenin to its plasma membrane reservoir.
The Dkk3 gene joins a growing list of mammalian genes that use multiple alternate promoters to achieve functional diversity [63, 64]. Our identification of a second TSS element in the Dkk3 gene and the demonstration that it generates a second transcript encoding a vital intracellular isoform was unexpected. Using targeted gene editing to abolish Dkk3b expression, while preserving expression of its sister (Dkk3), we found that DKK3b was essential for early embryonic development at or near implantation, dramatically different from the Dkk3tm1Cni mutant mouse where secreted Dkk3 expression was inactivated [20]. Despite the presence of the entire Wnt/ß-catenin pathway from oocyte to the late blastocyst stage [65, 66], active canonical Wnt signaling is not observed in pre-implantation blastocysts [67], and is first observed post-implantation at E6.5 [68]. Using a Wnt reporter mouse expressing a functional mutant of ß-catenin that evades the destruction complex, Kemler et al [69] found the stabilized ß-catenin in the cytoplasm of pre-implantation embryos, but that it did not traffic to the nucleus and no Wnt reporter expression was observed. They suggested that cellular mechanism(s) other than the canonical destruction complex [69] were responsible for keeping the stabilized ß-catenin out of the cell nucleus before implantation. Since DKK3b is an important gatekeeper of ß-catenin nuclear translocation, its loss in the zygote is likely to unleash ß-catenin signaling that has detrimental consequences on the developing embryo both before implantation and at this critical developmental event.
DKK3b-deficient MEFs showed both elevated ß-catenin signaling and cell attachment defect(s); two events likely to interrupt orderly development of the embryo. These disruptions in the signaling pathway were rescued by replacement with ectopic DKK3b or by simultaneous knockdown of ß-catenin. These data illustrate that the loss of DKK3b directly leads to aberrant ß-catenin signaling and disrupts cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions.
Unlike its ubiquitous expression in somatic cells, silencing of the Dkk3 gene is common in cancer and ectopic over-expression of DKK3 arrests tumor cell growth [16–19]. Analysis of intracellular product of the Dkk3 gene, revealed that DKK3b arrests Wnt stimulated cell proliferation and selectively silences ß-catenin dependent gene expression in both immortal and cancer cells. The ability a purified cell-penetrating DKK3b protein to fully restore control of ß-catenin signaling by partnering with ß-TrCP to capture the transfactor in an extra nuclear complex offers a promising new therapeutic target for ß-catenin driven hyper-proliferative disease(s) like cancer.
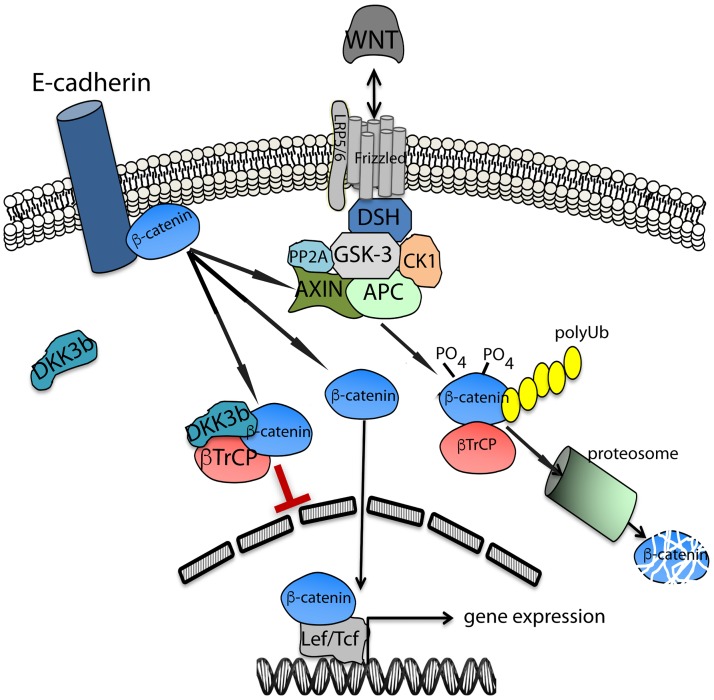
An essential partner in the molecular mechanism of DKK3b action is ß-TrCP, an F-box protein with WD40 repeats that captures a broad range of protein targets through a consensus dephosphorylated 6 amino acid long degron domain in the target protein(s) that is located 10 to 20 residues downstream of the lysine used for ubiquitin conjugation [70]. DKK3b captured dephosphorylated ß-catenin in a complex with ß-TrCP, prolonged the biological half-life of the transfactor, and prevented its translocation to the nucleus (Fig 9). Direct analysis of the dynamics of ß-catenin nuclear entry and exit showed that the tripartite complex trapped the transfactor outside the nucleus providing a clear molecular mechanism for the DKK3b-dependent regulation of this pathway. Since the N-terminal localized degron of ß-catenin docks with ß-TrCP, the ability of DKK3b stabilize transient interaction(s) between the dephos-degron of ß-catenin and ß-TrCP during “kiss-and-run” interaction(s) [71], suggests that other ß-TrCP ligands that similarly engage this E3 ligase are potential regulatory targets. These include members of most of the kinase signaling cascades that impact cell growth, motility, and apoptosis [71–74]. Further studies are required to determine if DKK3b captures other ß-TrCP interacting proteins and impacts their signaling pathways.
Fig 9. Schematic diagram of the novel regulatory role of DKK3b in the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway.
DSH, Disheveled; GSK-3, Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; CK1, Casein kinase 1; PP2A, Protein Phosphatase 2A; APC, Adenomatous Polyposis Coli; ß-TrCP, ß-Transducin Repeat-Containing Protein; Ub, ubiquitin.
DKK3b is a novel and essential component of the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway that plays a key role in both development and cancer. It serves as a gatekeeper for ß-catenin nuclear entry, directly modulates this pro-proliferative signaling molecule, and provides an important new point of control that impacts the regulatory pathways responsible for differentiation, lineage specification, pluripotency and oncogenesis.
Supporting information
(A) The position of the PCR primer pairs used for amplification of exon 2 and exon 3 shown on the Dkk3 cds. (B) Validation of the Dkk3 exon 2 and exon 3 primer sets using increasing concentrations of 1st strand cDNA primed total RNA isolated from two independent mouse astrocyte preparations. Each data point determined in triplicate. (C) Dkk3 mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH mRNA. Data shown as (mean ± SE) from 3 independent experiments.
(TIF)
(A) Map of the insertion of the CFP promoter trap in gene-edited intron 2 of the Dkk3 gene. TSS2 is positioned upstream of the forward LoxP site (black box) of the gene and the downstream LoxP site (in black) is positions 35 nt upstream of exon 3. Position of the CFP234 5’RACE primer indicated by arrow. (B) Sequence of the 5’UTR of the Cfp mRNA captured by 5’RACE highlighted in yellow.
(TIF)
(A) Basal CyclinD1 and Myc expression in HeLa cells ±TAT-DKK3b for 16 h. (B) Native ß-catenin dependent gene expression in HeLa cells. Cells were stimulated with ±LiCl in the absence or presence of TAT-DKK3b for 16 h. QPCR data are reported as % of unstimulated controls for each target transcript and expressed as means ± se, n = 9. Gene products probed: Cdh2, N-cadherin; Axin2, Axin2; Cox2, cyclooxygenase-2; Wfdc2, WAP Four-disulfide Core Domain 2; Fosl1, FOS Like Antigen 1; Tuba, alpha tubulin.
(TIF)
Acknowledgments
We thank the UMMS Transgenic Animal Modeling Core for their help with zygote injections and embryo implantation and the UMMS FACS Core for isolation of gene-edited MEFS.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health NIDDK: DK38772 and DK060051 to J.L.L., Pancreatic Cancer Alliance Fund (www.pancreaticalliance.org) 2014j to J.L.L., Hyundai Hope on Wheels Scholar Program (www.hyundaihopeonwheels.org) 80389MA to J.L.L. PinkRevolution www.PinkRevolution.org K.J.S.
References
- 1.Kawano Y, Kypta R. Secreted antagonists of the Wnt signalling pathway. Journal of cell science. 2003;116(Pt 13):2627–34. Epub 2003/05/31. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00623 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Guder C, Pinho S, Nacak TG, Schmidt HA, Hobmayer B, Niehrs C, et al. An ancient Wnt-Dickkopf antagonism in Hydra. Development. 2006;133(5):901–11. Epub 2006/02/03. doi: 10.1242/dev.02265 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Monaghan AP, Kioschis P, Wu W, Zuniga A, Bock D, Poustka A, et al. Dickkopf genes are co-ordinately expressed in mesodermal lineages. Mech Dev. 1999;87(1–2):45–56. Epub 1999/09/24. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Niehrs C. Function and biological roles of the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene. 2006;25(57):7469–81. Epub 2006/12/05. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210054 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2002;417(6889):664–7. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zorn AM. Wnt signalling: antagonistic Dickkopfs. Current biology: CB. 2001;11(15):R592–5. Epub 2001/08/23. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ahn VE, Chu ML, Choi HJ, Tran D, Abo A, Weis WI. Structural basis of Wnt signaling inhibition by Dickkopf binding to LRP5/6. Developmental cell. 2011;21(5):862–73. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.09.003 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cheng Z, Biechele T, Wei Z, Morrone S, Moon RT, Wang L, et al. Crystal structures of the extracellular domain of LRP6 and its complex with DKK1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2011;18(11):1204–10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2139 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fedders H, Augustin R, Bosch TC. A Dickkopf- 3-related gene is expressed in differentiating nematocytes in the basal metazoan Hydra. Development genes and evolution. 2004;214(2):72–80. doi: 10.1007/s00427-003-0378-9 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Krupnik VE, Sharp JD, Jiang C, Robison K, Chickering TW, Amaravadi L, et al. Functional and structural diversity of the human Dickkopf gene family. Gene. 1999;238(2):301–13. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Veeck J, Dahl E. Targeting the Wnt pathway in cancer: The emerging role of Dickkopf-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1825(1):18–28. Epub 2011/10/11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2011.09.003 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fujii Y, Hoshino T, Kumon H. Molecular simulation analysis of the structure complex of C2 domains of DKK family members and beta-propeller domains of LRP5/6: explaining why DKK3 does not bind to LRP5/6. Acta Med Okayama. 2014;68(2):63–78. doi: 10.18926/AMO/52403 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gotze S, Wolter M, Reifenberger G, Muller O, Sievers S. Frequent promoter hypermethylation of Wnt pathway inhibitor genes in malignant astrocytic gliomas. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(11):2584–93. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24981 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Veeck J, Bektas N, Hartmann A, Kristiansen G, Heindrichs U, Knuchel R, et al. Wnt signalling in human breast cancer: expression of the putative Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) is frequently suppressed by promoter hypermethylation in mammary tumours. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(5):R82 doi: 10.1186/bcr2151 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Agirre X, Castillejo JA, Navarro G, Barrios M, et al. Transcriptional silencing of the Dickkopfs-3 (Dkk-3) gene by CpG hypermethylation in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(4):707–13. . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gu YM, Ma YH, Zhao WG, Chen J. Dickkopf3 overexpression inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(33):3810–7. Epub 2011/10/12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3810 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee EJ, Jo M, Rho SB, Park K, Yoo YN, Park J, et al. Dkk3, downregulated in cervical cancer, functions as a negative regulator of beta-catenin. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(2):287–97. Epub 2008/11/13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23913 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yue W, Sun Q, Dacic S, Landreneau RJ, Siegfried JM, Yu J, et al. Downregulation of Dkk3 activates beta-catenin/TCF-4 signaling in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(1):84–92. Epub 2007/12/01. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm267 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hsieh SY, Hsieh PS, Chiu CT, Chen WY. Dickkopf-3/REIC functions as a suppressor gene of tumor growth. Oncogene. 2004;23(57):9183–9. Epub 2004/11/02. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208138 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Barrantes Idel B, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Guadano-Ferraz A, Obregon MJ, Martinez de Mena R, Gailus-Durner V, et al. Generation and characterization of dickkopf3 mutant mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(6):2317–26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2317-2326.2006 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lewis SL, Khoo PL, De Young RA, Steiner K, Wilcock C, Mukhopadhyay M, et al. Dkk1 and Wnt3 interact to control head morphogenesis in the mouse. Development. 2008;135(10):1791–801. doi: 10.1242/dev.018853 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pietila I, Ellwanger K, Railo A, Jokela T, Barrantes Idel B, Shan J, et al. Secreted Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 controls kidney papilla development coordinated by Wnt-7b signalling. Dev Biol. 2011;353(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.02.019 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seib DR, Corsini NS, Ellwanger K, Plaas C, Mateos A, Pitzer C, et al. Loss of Dickkopf-1 restores neurogenesis in old age and counteracts cognitive decline. Cell stem cell. 2013;12(2):204–14. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.11.010 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mukhopadhyay M, Gorivodsky M, Shtrom S, Grinberg A, Niehrs C, Morasso MI, et al. Dkk2 plays an essential role in the corneal fate of the ocular surface epithelium. Development. 2006;133(11):2149–54. doi: 10.1242/dev.02381 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Li X, Liu P, Liu W, Maye P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, et al. Dkk2 has a role in terminal osteoblast differentiation and mineralized matrix formation. Nature genetics. 2005;37(9):945–52. doi: 10.1038/ng1614 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kerkela R, Kockeritz L, Macaulay K, Zhou J, Doble BW, Beahm C, et al. Deletion of GSK-3beta in mice leads to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy secondary to cardiomyoblast hyperproliferation. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2008;118(11):3609–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI36245 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xie R, Jiang R, Chen D. Generation of Axin1 conditional mutant mice. Genesis. 2011;49(2):98–102. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20703 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sieber OM, Howarth KM, Thirlwell C, Rowan A, Mandir N, Goodlad RA, et al. Myh deficiency enhances intestinal tumorigenesis in multiple intestinal neoplasia (ApcMin/+) mice. Cancer Res. 2004;64(24):8876–81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2958 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chia IV, Kim MJ, Itoh K, Sokol SY, Costantini F. Both the RGS domain and the six C-terminal amino acids of mouse Axin are required for normal embryogenesis. Genetics. 2009;181(4):1359–68. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.101055 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guardavaccaro D, Kudo Y, Boulaire J, Barchi M, Busino L, Donzelli M, et al. Control of meiotic and mitotic progression by the F box protein beta-Trcp1 in vivo. Developmental cell. 2003;4(6):799–812. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nakayama K, Hatakeyama S, Maruyama S, Kikuchi A, Onoe K, Good RA, et al. Impaired degradation of inhibitory subunit of NF-kappa B (I kappa B) and beta-catenin as a result of targeted disruption of the beta-TrCP1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(15):8752–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1133216100 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Biechele S, Cox BJ, Rossant J. Porcupine homolog is required for canonical Wnt signaling and gastrulation in mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 2011;355(2):275–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.04.029 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gupta A, Christensen RG, Rayla AL, Lakshmanan A, Stormo GD, Wolfe SA. An optimized two-finger archive for ZFN-mediated gene targeting. Nature methods. 2012;9(6):588–90. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1994 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhu C, Gupta A, Hall VL, Rayla AL, Christensen RG, Dake B, et al. Using defined finger-finger interfaces as units of assembly for constructing zinc-finger nucleases. Nucleic acids research. 2013;41(4):2455–65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1357 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Meng X, Noyes MB, Zhu LJ, Lawson ND, Wolfe SA. Targeted gene inactivation in zebrafish using engineered zinc-finger nucleases. Nature biotechnology. 2008;26(6):695–701. doi: 10.1038/nbt1398 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Otto EA, Helou J, Allen SJ, O'Toole JF, Wise EL, Ashraf S, et al. Mutation analysis in nephronophthisis using a combined approach of homozygosity mapping, CEL I endonuclease cleavage, and direct sequencing. Human mutation. 2008;29(3):418–26. doi: 10.1002/humu.20669 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen F, Pruett-Miller SM, Huang Y, Gjoka M, Duda K, Taunton J, et al. High-frequency genome editing using ssDNA oligonucleotides with zinc-finger nucleases. Nature methods. 2011;8(9):753–5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1653 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fine EJ, Cradick TJ, Zhao CL, Lin Y, Bao G. An online bioinformatics tool predicts zinc finger and TALE nuclease off-target cleavage. Nucleic acids research. 2014;42(6):e42 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1326 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Farwell AP, Leonard JL. Identification of a 27-kDa protein with the properties of type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase in dibutyryl cyclic AMP-stimulated glial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(34):20561–7. Epub 1989/12/05. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Conner DA. Mouse embryo fibroblast (MEF) feeder cell preparation. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2001;Chapter 23:Unit 23 2 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Veeman MT, Slusarski DC, Kaykas A, Louie SH, Moon RT. Zebrafish prickle, a modulator of noncanonical Wnt/Fz signaling, regulates gastrulation movements. Current biology: CB. 2003;13(8):680–5. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hajra KM, Ji X, Fearon ER. Extinction of E-cadherin expression in breast cancer via a dominant repression pathway acting on proximal promoter elements. Oncogene. 1999;18(51):7274–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203336 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hiraiwa A, Kiyono T, Suzuki S, Ohashi M, Ishibashi M. E7 proteins of four groups of human papillomaviruses, irrespective of their tissue tropism or cancer association, possess the ability to transactivate transcriptional promoters E2F site dependently. Virus genes. 1996;12(1):27–35. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Najdi R, Proffitt K, Sprowl S, Kaur S, Yu J, Covey TM, et al. A uniform human Wnt expression library reveals a shared secretory pathway and unique signaling activities. Differentiation. 2012;84(2):203–13. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2012.06.004 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Soutoglou E, Talianidis I. Coordination of PIC assembly and chromatin remodeling during differentiation-induced gene activation. Science. 2002;295(5561):1901–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1068356 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Leonard DM, Stachelek SJ, Safran M, Farwell AP, Kowalik TF, Leonard JL. Cloning, expression, and functional characterization of the substrate binding subunit of rat type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(33):25194–201. Epub 2000/06/01. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002036200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nagahara H, Vocero-Akbani AM, Snyder EL, Ho A, Latham DG, Lissy NA, et al. Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27Kip1 induces cell migration. Nature medicine. 1998;4(12):1449–52. doi: 10.1038/4042 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stachelek SJ, Tuft RA, Lifschitz LM, Leonard DM, Farwell AP, Leonard JL. Real-time visualization of processive myosin 5a-mediated vesicle movement in living astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(38):35652–9. Epub 2001/07/27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103331200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsuji T, Miyazaki M, Sakaguchi M, Inoue Y, Namba M. A REIC gene shows down-regulation in human immortalized cells and human tumor-derived cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;268(1):20–4. Epub 2000/02/01. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.2067 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kobayashi K, Ouchida M, Tsuji T, Hanafusa H, Miyazaki M, Namba M, et al. Reduced expression of the REIC/Dkk-3 gene by promoter-hypermethylation in human tumor cells. Gene. 2002;282(1–2):151–8. Epub 2002/01/30. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xiang T, Li L, Yin X, Zhong L, Peng W, Qiu Z, et al. Epigenetic silencing of the WNT antagonist Dickkopf 3 disrupts normal Wnt/beta-catenin signalling and apoptosis regulation in breast cancer cells. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine. 2013;17(10):1236–46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12099 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vertino PM, Issa JP, Pereira-Smith OM, Baylin SB. Stabilization of DNA methyltransferase levels and CpG island hypermethylation precede SV40-induced immortalization of human fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1994;5(12):1395–402. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hayashi S, Lewis P, Pevny L, McMahon AP. Efficient gene modulation in mouse epiblast using a Sox2Cre transgenic mouse strain. Gene Expr Patterns. 2002;2(1–2):93–7. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hayashi S, Tenzen T, McMahon AP. Maternal inheritance of Cre activity in a Sox2Cre deleter strain. Genesis. 2003;37(2):51–3. doi: 10.1002/gene.10225 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Becker-Hapak M, Dowdy SF. Protein transduction: generation of full-length transducible proteins using the TAT system. Current protocols in cell biology / editorial board, Bonifacino Juan S [et al. ]. 2003;Chapter 20:Unit 20 2 Epub 2008/01/30. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb2002s18 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Abarzua F, Sakaguchi M, Takaishi M, Nasu Y, Kurose K, Ebara S, et al. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of REIC/Dkk-3 selectively induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through activation of c-Jun-NH2-kinase. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9617–22. Epub 2005/11/04. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0829 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Edamura K, Nasu Y, Takaishi M, Kobayashi T, Abarzua F, Sakaguchi M, et al. Adenovirus-mediated REIC/Dkk-3 gene transfer inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in an orthotopic prostate cancer model. Cancer Gene Ther. 2007;14(9):765–72. Epub 2007/06/30. doi: 10.1038/sj.cgt.7701071 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Jamora C, DasGupta R, Kocieniewski P, Fuchs E. Links between signal transduction, transcription and adhesion in epithelial bud development. Nature. 2003;422(6929):317–22. doi: 10.1038/nature01458 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li Q, Dashwood WM, Zhong X, Nakagama H, Dashwood RH. Bcl-2 overexpression in PhIP-induced colon tumors: cloning of the rat Bcl-2 promoter and characterization of a pathway involving beta-catenin, c-Myc and E2F1. Oncogene. 2007;26(42):6194–202. . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.van Noort M, Meeldijk J, van der Zee R, Destree O, Clevers H. Wnt signaling controls the phosphorylation status of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(20):17901–5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111635200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Huang M, Wang Y, Sun D, Zhu H, Yin Y, Zhang W, et al. Identification of genes regulated by Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and involved in apoptosis via microarray analysis. BMC Cancer. 2006;6:221 doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-221 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stachelek SJ, Kowalik TF, Farwell AP, Leonard JL. Myosin V plays an essential role in the thyroid hormone-dependent endocytosis of type II iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(41):31701–7. Epub 2000/07/07. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004221200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yamashita R, Sathira NP, Kanai A, Tanimoto K, Arauchi T, Tanaka Y, et al. Genome-wide characterization of transcriptional start sites in humans by integrative transcriptome analysis. Genome research. 2011;21(5):775–89. doi: 10.1101/gr.110254.110 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Davuluri RV, Suzuki Y, Sugano S, Plass C, Huang TH. The functional consequences of alternative promoter use in mammalian genomes. Trends in genetics: TIG. 2008;24(4):167–77. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.01.008 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kemp C, Willems E, Abdo S, Lambiv L, Leyns L. Expression of all Wnt genes and their secreted antagonists during mouse blastocyst and postimplantation development. Dev Dyn. 2005;233(3):1064–75. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20408 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wang QT, Piotrowska K, Ciemerych MA, Milenkovic L, Scott MP, Davis RW, et al. A genome-wide study of gene activity reveals developmental signaling pathways in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Developmental cell. 2004;6(1):133–44. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mohamed OA, Clarke HJ, Dufort D. Beta-catenin signaling marks the prospective site of primitive streak formation in the mouse embryo. Dev Dyn. 2004;231(2):416–24. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20135 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Maretto S, Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Braghetta P, Broccoli V, Hassan AB, et al. Mapping Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during mouse development and in colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(6):3299–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0434590100 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kemler R, Hierholzer A, Kanzler B, Kuppig S, Hansen K, Taketo MM, et al. Stabilization of beta-catenin in the mouse zygote leads to premature epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the epiblast. Development. 2004;131(23):5817–24. doi: 10.1242/dev.01458 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Skaar JR, Pagan JK, Pagano M. Mechanisms and function of substrate recruitment by F-box proteins. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2013;14(6):369–81. doi: 10.1038/nrm3582 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Low TY, Peng M, Magliozzi R, Mohammed S, Guardavaccaro D, Heck AJ. A systems-wide screen identifies substrates of the SCFbetaTrCP ubiquitin ligase. Science signaling. 2014;7(356):rs8 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005882 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Dehan E, Bassermann F, Guardavaccaro D, Vasiliver-Shamis G, Cohen M, Lowes KN, et al. betaTrCP- and Rsk1/2-mediated degradation of BimEL inhibits apoptosis. Mol Cell. 2009;33(1):109–16. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.020 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hayakawa M, Matsushima M, Hagiwara H, Oshima T, Fujino T, Ando K, et al. Novel insights into FGD3, a putative GEF for Cdc42, that undergoes SCF(FWD1/beta-TrCP)-mediated proteasomal degradation analogous to that of its homologue FGD1 but regulates cell morphology and motility differently from FGD1. Genes to cells: devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms. 2008;13(4):329–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01168.x . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Winston JT, Strack P, Beer-Romero P, Chu CY, Elledge SJ, Harper JW. The SCFbeta-TRCP-ubiquitin ligase complex associates specifically with phosphorylated destruction motifs in IkappaBalpha and beta-catenin and stimulates IkappaBalpha ubiquitination in vitro. Genes Dev. 1999;13(3):270–83. . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(A) The position of the PCR primer pairs used for amplification of exon 2 and exon 3 shown on the Dkk3 cds. (B) Validation of the Dkk3 exon 2 and exon 3 primer sets using increasing concentrations of 1st strand cDNA primed total RNA isolated from two independent mouse astrocyte preparations. Each data point determined in triplicate. (C) Dkk3 mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH mRNA. Data shown as (mean ± SE) from 3 independent experiments.
(TIF)
(A) Map of the insertion of the CFP promoter trap in gene-edited intron 2 of the Dkk3 gene. TSS2 is positioned upstream of the forward LoxP site (black box) of the gene and the downstream LoxP site (in black) is positions 35 nt upstream of exon 3. Position of the CFP234 5’RACE primer indicated by arrow. (B) Sequence of the 5’UTR of the Cfp mRNA captured by 5’RACE highlighted in yellow.
(TIF)
(A) Basal CyclinD1 and Myc expression in HeLa cells ±TAT-DKK3b for 16 h. (B) Native ß-catenin dependent gene expression in HeLa cells. Cells were stimulated with ±LiCl in the absence or presence of TAT-DKK3b for 16 h. QPCR data are reported as % of unstimulated controls for each target transcript and expressed as means ± se, n = 9. Gene products probed: Cdh2, N-cadherin; Axin2, Axin2; Cox2, cyclooxygenase-2; Wfdc2, WAP Four-disulfide Core Domain 2; Fosl1, FOS Like Antigen 1; Tuba, alpha tubulin.
(TIF)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.