Abstract
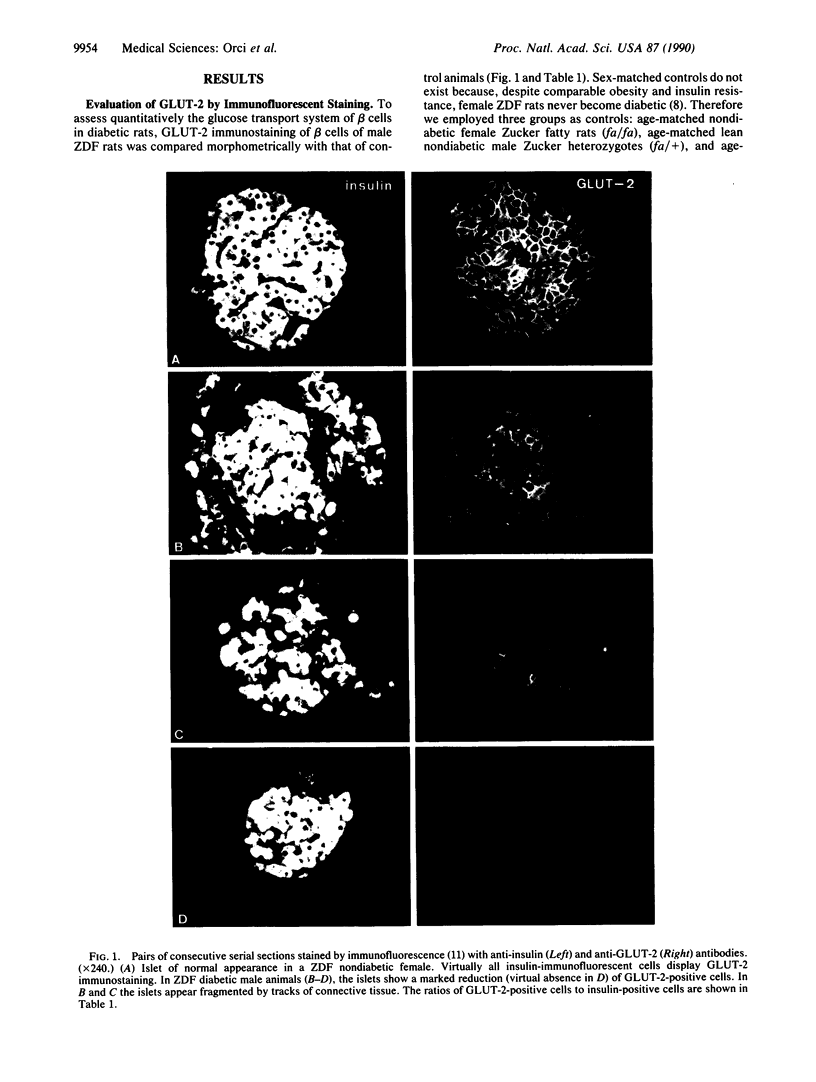
Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) is attributed to a failure of pancreatic beta cells to maintain insulin secretion at a level sufficient to compensate for underlying insulin resistance. In the ZDF rat, a model of NIDDM that closely resembles the human syndrome, we have previously reported profound underexpression of GLUT-2, the high-Km facilitative glucose transporter expressed by beta cells of normal animals. Here we report that islets of diabetic rats exhibit a marked decrease in the volume of GLUT-2-positive beta cells and a reduction at the electron-microscopic level in the number of GLUT-2-immunoreactive sites per unit of beta-cell plasma membrane. The deficiency of GLUT-2 cannot be induced in normal beta cells by in vivo or in vitro exposure to high levels of glucose nor can it be prevented in beta cells of prediabetic ZDF rats by elimination of hyperglycemia. We conclude that this dearth of immunodetectable GLUT-2 in NIDDM is not secondary to hyperglycemia and therefore that it may well play a causal role in the development of hyperglycemia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armbruster B. L., Carlemalm E., Chiovetti R., Garavito R. M., Hobot J. A., Kellenberger E., Villiger W. Specimen preparation for electron microscopy using low temperature embedding resins. J Microsc. 1982 Apr;126(Pt 1):77–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Stefan Y., Ravazzola M., Malaisse-Lagae F., Coleman D. L., Orci L. Alteration of islet cell populations in spontaneously diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):1–7. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H., LEDUC E. H., CONNOLLY J. M. Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med. 1955 Jul 1;102(1):49–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendic S. Decreased sensitivity of the pancreatic beta cells to glucose in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. A glucose dose-response study. Diabetes. 1972 Apr;21(4):224–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Alam T., Johnson J. H., Hughes S., Newgard C. B., Unger R. H. Regulation of beta-cell glucose transporter gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4088–4092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. B., Palmer C. J., Shaw W. N. The diabetic Zucker fatty rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 May;173(1):68–75. doi: 10.3181/00379727-173-41611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clissold S. P., Edwards C. Acarbose. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential. Drugs. 1988 Mar;35(3):214–243. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198835030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroix M. H., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. D-glucose transport and concentration in tumoral insulin-producing cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C847–C851. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Herberg L. Glucose- and arginine-induced insulin and glucagon responses from the isolated perfused pancreas of the BB-Wistar diabetic rat. Evidence for selective impairment of glucose regulation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1983 Apr;102(4):561–566. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1020561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Shino A., Matsuo T., Iwatsuka H., Suzuoki Z. A new genetically obese-hyperglycemic rat (Wistar fatty). Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1045–1050. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Newgard C. B., Milburn J. L., Lodish H. F., Thorens B. The high Km glucose transporter of islets of Langerhans is functionally similar to the low affinity transporter of liver and has an identical primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6548–6551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Ogawa A., Chen L., Orci L., Newgard C. B., Alam T., Unger R. H. Underexpression of beta cell high Km glucose transporters in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.2237405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya I., Baetens D., Kuwajima M., Orci L., Unger R. H. Compensatory capabilities of islets of BB/Wor rats exposed to sustained hyperglycemia. Metabolism. 1990 Jun;39(6):614–618. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90028-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Strangeways L., Vyakarnam A., Evan G. Raising antibodies by coupling peptides to PPD and immunizing BCG-sensitized animals. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;119:25–57. doi: 10.1002/9780470513286.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Matschinsky F. M. Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):163–214. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Like A. A., Amherdt M., Blondel B., Kanazawa Y., Marliss E. B., Lambert A. E., Wollheim C. B., Renold A. E. Monolayer cell culture of neonatal rat pancreas: an ultrastructural and biochemical study of functioning endocrine cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 May;43(3):270–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Thorens B., Ravazzola M., Lodish H. F. Localization of the pancreatic beta cell glucose transporter to specific plasma membrane domains. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.2665080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Benson J. W., Walter R. M., Ensinck J. W. Arginine-stimulated acute phase of insulin and glucagon secretion in diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):565–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI108502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz G. A., Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B., Blondel B., Strauss A. J., Renold A. E. Regulation of immunoreactive-insulin release from a rat cell line (RINm5F). Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):345–352. doi: 10.1042/bj2100345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikanta S., Ganda O. P., Eisenbarth G. S., Soeldner J. S. Islet-cell antibodies and beta-cell function in monozygotic triplets and twins initially discordant for Type I diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 10;308(6):322–325. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302103080607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga M., Komiya I., Johnson J. H., Inman L., Alam T., Moltz J., Crider B., Stefan Y., Baetens D., McCorkle K. Loss of insulin response to glucose but not arginine during the development of autoimmune diabetes in BB/W rats: relationships to islet volume and glucose transport rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9749–9753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]