Abstract
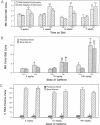
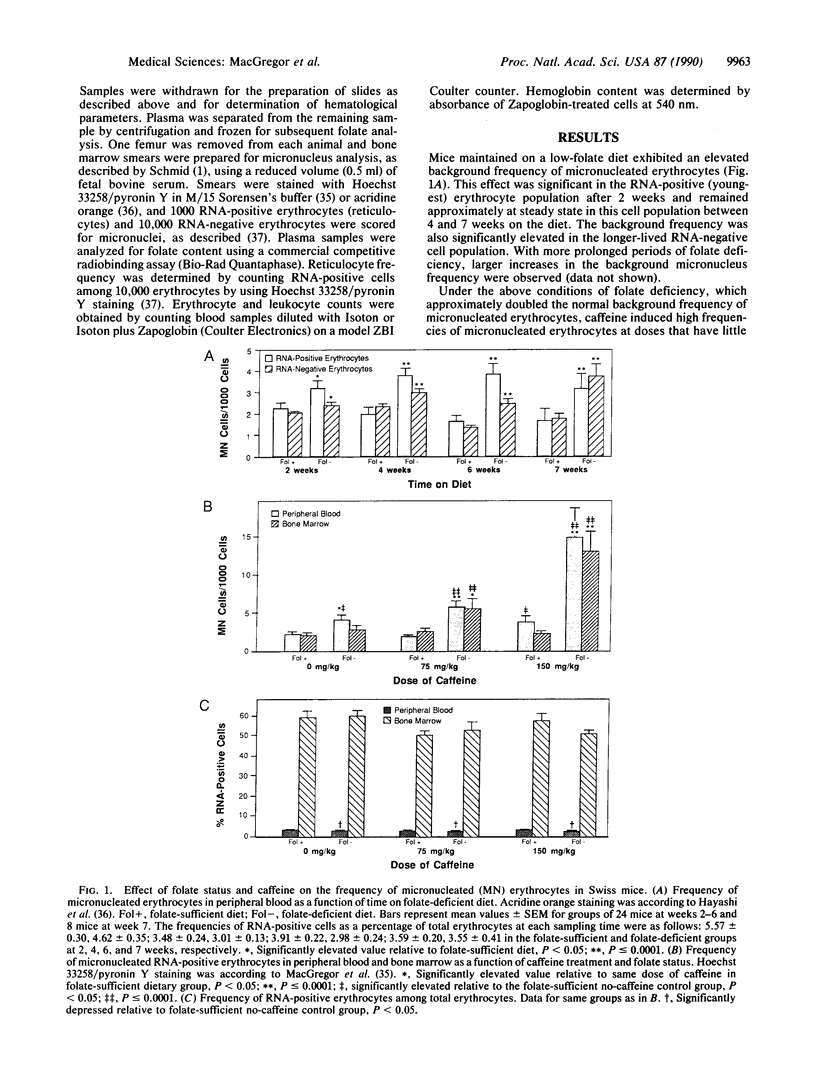
Folate deficiency in Swiss mice increased the incidence of micronuclei in peripheral blood erythrocytes, indicating increased chromosomal damage in nucleated erythrocyte precursors. Caffeine enhanced the incidence of micronuclei in blood and bone marrow by up to 5-fold in folate-deficient mice at doses that did not significantly alter the micronucleus frequency in the presence of adequate dietary folate. The lower dose of caffeine used in this study (75 mg/kg) approaches doses received by humans who consume large amounts of caffeinated beverages. Since folate deficiency and caffeine consumption are highly prevalent in the human population, the potential for a similar interaction in man should be evaluated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aeschbacher H. U., Meier H., Jaccaud E. The effect of caffeine in the in vivo SCE and micronucleus mutagenicity tests. Mutat Res. 1986 May;174(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey L. B., Wagner P. A., Christakis G. J., Araujo P. E., Appledorf H., Davis C. G., Masteryanni J., Dinning J. S. Folacin and iron status and hematological findings in predominately black elderly persons from urban low-income households. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Nov;32(11):2346–2353. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.11.2346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone J. J., Grice H. C. Sixth International Caffeine Workshop, Hong Kong, 7-10 August 1989. Food Chem Toxicol. 1990 Apr;28(4):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(90)90040-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branda R. F., McCormack J. J., Perlmutter C. A., Mathews L. A., Robison S. H. Effects of folate deficiency on the metastatic potential of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4529–4534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce W. R., Heddle J. A. The mutagenic activity of 61 agents as determined by the micronucleus, Salmonella, and sperm abnormality assays. Can J Genet Cytol. 1979 Sep;21(3):319–334. doi: 10.1139/g79-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg A. W. Physiological disposition of caffeine. Drug Metab Rev. 1975;4(2):199–228. doi: 10.3109/03602537508993756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth C. E., Jr, Hatch K. D., Gore H., Mueller H., Krumdieck C. L. Improvement in cervical dysplasia associated with folic acid therapy in users of oral contraceptives. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Jan;35(1):73–82. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/35.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. T., Reidy J. A., Annest J. L., Welty T. K., Zhou H. G. Increased chromosome fragility as a consequence of blood folate levels, smoking status, and coffee consumption. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(4):319–324. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson R. B., Wehr C. M., Erexson G. L., MacGregor J. T. Association of marginal folate depletion with increased human chromosomal damage in vivo: demonstration by analysis of micronucleated erythrocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Jun 1;80(7):525–529. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.7.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonatsch C. A simple method to demonstrate the fragile X chromosome in fibroblasts. Hum Genet. 1981;59(2):186–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00293076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freireich E. J., Gehan E. A., Rall D. P., Schmidt L. H., Skipper H. E. Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966 May;50(4):219–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W., Coyle-Morris J., Morgan R. Fragile sites: overview, occurrence in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia and effects of caffeine on expression. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Jan 1;19(1-2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Sofuni T., Ishidate M., Jr An application of Acridine Orange fluorescent staining to the micronucleus test. Mutat Res. 1983 Jun;120(4):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(83)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. W., Jr Cytogenetic observations in vitamin B12 and folate deficiency. Blood. 1966 Jun;27(6):800–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F. Fragile sites, cancer chromosome breakpoints, and oncogenes all cluster in light G bands. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Mar;31(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F. The fragile site hypothesis of cancer. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Mar;31(1):119–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddle J. A., Hite M., Kirkhart B., Mavournin K., MacGregor J. T., Newell G. W., Salamone M. F. The induction of micronuclei as a measure of genotoxicity. A report of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Gene-Tox Program. Mutat Res. 1983 Sep;123(1):61–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(83)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacky P. B., Beek B., Sutherland G. R. Fragile sites in chromosomes: possible model for the study of spontaneous chromosome breakage. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):69–70. doi: 10.1126/science.6828880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenssen D., Ramel C. Factors affecting the induction of micronuclei at low doses of X-rays, MMS and dimethylnitrosamine in mouse erythroblasts. Mutat Res. 1978 Sep;58(1):51–65. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(78)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIPSTEIN F. A. SUBNORMAL SERUM FOLATE AND MACROCYTOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH ANTICONVULSANT DRUG THERAPY. Blood. 1964 Jan;23:68–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz B. A. Mutagenesis and deoxyribonucleotide pool imbalance. Mutat Res. 1988 Jul-Aug;200(1-2):133–147. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird C. D. Proposed mechanism of inheritance and expression of the human fragile-X syndrome of mental retardation. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):587–599. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M. Chromosomal fragile sites and cancer-specific breakpoints--a moderating viewpoint. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Mar;31(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor J. T., Tucker J. D., Ziderman I. I., Wehr C. M., Wilson R. E., Friedman M. Non-clastogenicity in mouse bone marrow of fructose/lysine and other sugar/amino acid browning products with in vitro genotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989 Nov;27(11):715–721. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor J. T., Wehr C. M., Gould D. H. Clastogen-induced micronuclei in peripheral blood erythrocytes: the basis of an improved micronucleus test. Environ Mutagen. 1980;2(4):509–514. doi: 10.1002/em.2860020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor J. T., Wehr C. M., Langlois R. G. A simple fluorescent staining procedure for micronuclei and RNA in erythrocytes using Hoechst 33258 and pyronin Y. Mutat Res. 1983 Jun;120(4):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(83)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier P., Schmid W. Ten model mutagens evaluated by the micronucleus test. Mutat Res. 1976 Nov;40(4):325–337. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(76)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzies R. C., Crossen P. E., Fitzgerald P. H., Gunz F. W. Cytogenetic and cytochemical studies on marrow cells in B 12 and folate deficiency. Blood. 1966 Oct;28(4):581–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Jick H., Jick S. S., Bruell C. L., MacLaughlin D. S., Rothman K. J., Willett W. Multivitamin/folic acid supplementation in early pregnancy reduces the prevalence of neural tube defects. JAMA. 1989 Nov 24;262(20):2847–2852. doi: 10.1001/jama.262.20.2847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamone M., Heddle J., Stuart E., Katz M. Towards an improved micronucleus test: studies on 3 model agents, mitomycin C, cyclophosphamide and dimethylbenzanthracene. Mutat Res. 1980 Oct;74(5):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(80)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., MacGregor J. T., Everson R. B. Assessment of cytogenetic damage by quantitation of micronuclei in human peripheral blood erythrocytes. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3717–3721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Pardee A. B. Caffeine-induced uncoupling of mitosis from the completion of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2422760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Molecular mechanisms of DNA repair inhibition by caffeine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3522–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senti F. R., Pilch S. M. Analysis of folate data from the second National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES II). J Nutr. 1985 Nov;115(11):1398–1402. doi: 10.1093/jn/115.11.1398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., MacGregor J. T., Hiatt R. A., Hooper N. K., Wehr C. M., Peters B., Goldman L. R., Yuan L. A., Smith P. A., Becker C. E. Micronucleated erythrocytes as an index of cytogenetic damage in humans: demographic and dietary factors associated with micronucleated erythrocytes in splenectomized subjects. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):5049–5054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavric B. Methylxanthines: toxicity to humans. 2. Caffeine. Food Chem Toxicol. 1988 Jul;26(7):645–662. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(88)90236-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Simmers R. N. No statistical association between common fragile sites and nonrandom chromosome breakpoints in cancer cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Mar;31(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldren C. A., Patterson D. Effects of caffeine on purine metabolism and ultraviolet light-induced lethality in cultured mammalian cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):4975–4982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. I., Kikuchi Y. Studies on micronuclei time response and on the effects of multiple treatments of mutagens on induction of micronuclei. Mutat Res. 1981 Oct;90(2):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(81)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L. Constitutive fragile sites and cancer. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1199–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.6239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]