Abstract
A mouse monoclonal antibody, designated NF1, was obtained from a cloned hybridoma isolated from a fusion of mouse myeloma Sp2 cells with spleen cells from a BALB/c mouse immunized with a crude neurofilament preparation from porcine spinal cord. NF1 is an IgG1 and recognizes, in immune blotting procedures, only the 200 K neurofilament triplet component. Its neurofilament-specific nature is further revealed by immunofluorescence microscopy studies on frozen tissue sections and various cultured cells. Immunoelectron microscopy studies on cytoskeletons of cultured neurones emphasize the discontinuous display along each neurofilament previously observed with polyclonal antibodies specific for the 200 K component after appropriate but rather cumbersome cross-absorption steps. Use of NF1 on various neuronal cells strongly supports the previous proposal of the existence of certain subpopulations of neurofilament-free neurones and the observation that certain neuronal arrangements, (e.g., those in dendrites of pyramidal cells of the hippocampus), although rich in neurofilaments, probably lack the normal 200 K triplet component. Since NF1 shows a broad cross-species reactivity and is able to react on formaldehyde-fixed tissue, it should be a useful reagent to study differential neurofilament expression and organization in embryonic, adult and pathological tissues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Schauer A., Weber K. Antibodies to different intermediate filament proteins. Cell type-specific markers on paraffin-embedded human tissues. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderton B. H., Thorpe R., Cohen J., Selvendran S., Woodhams P. Specific neuronal localization by immunofluorescence of 10 nm filament polypeptides. J Neurocytol. 1980 Dec;9(6):835–844. doi: 10.1007/BF01205022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Korey B., Norton W. T. Intermediate filaments from bovine, rat, and human CNS: mapping analysis of the major proteins. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D. Study on the immunological crossreactivity of neurofilament polypeptides in axonal preparations of bovine brain. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80781-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Filliatreau G., Boutteau F., Biserte G., Schrevel J. Study of the 10-nm-filament fraction isolated during the standard microtubule preparation. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):543–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1910543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duce I. R., Keen P. An ultrastructural classification of the neuronal cell bodies of the rat dorsal root ganglion using zinc iodide-osmium impregnation. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Dec 13;185(2):263–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00220670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Yen S. H., Salomon G. D., Shelanski M. L. Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Komiya Y., Kurokawa M. Slowly migrating axonal polypeptides. Inequalities in their rate and amount of transport between two branches of bifurcating axons. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):174–184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Freeman L. A. Neurofilament proteins of rat peripheral nerve and spinal cord. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):653–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Franke W. W., Schachner M. Immunocytochemical demonstration of vimentin in astrocytes and ependymal cells of developing and adult mouse nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):435–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
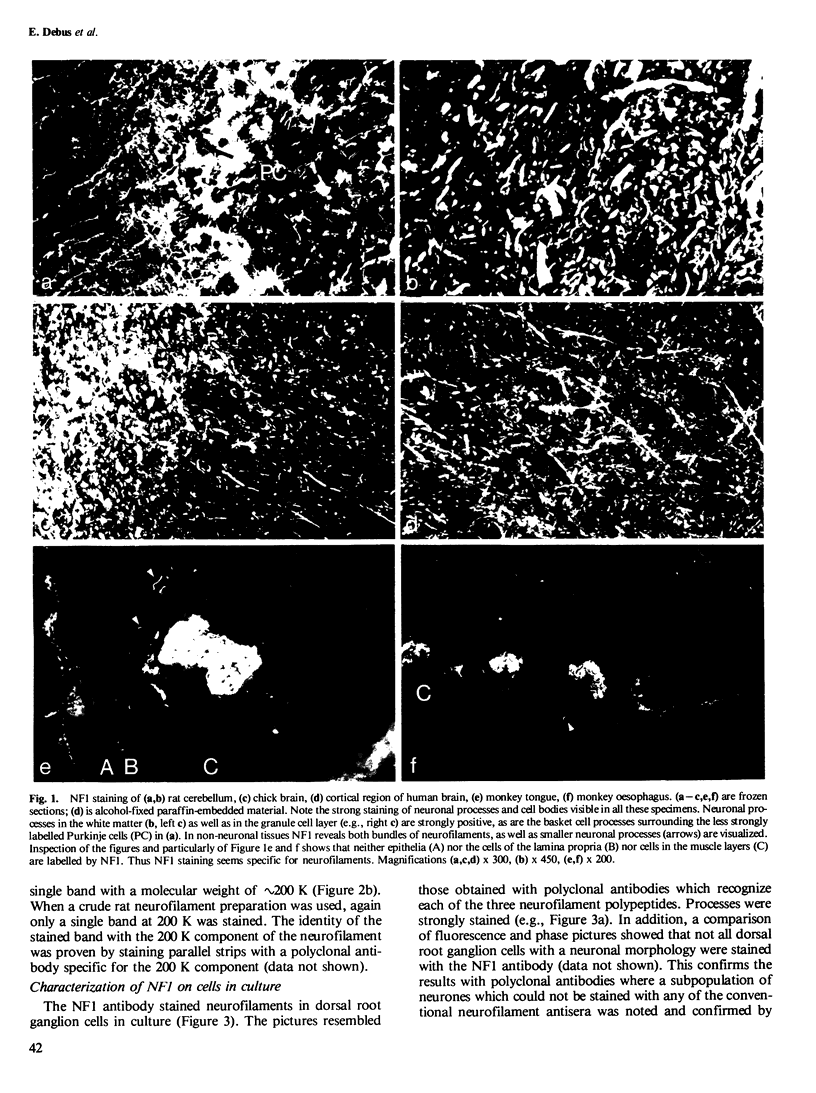
- Shaw G., Osborn M., Weber K. An immunofluorescence microscopical study of the neurofilament triplet proteins, vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein within the adult rat brain. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):68–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
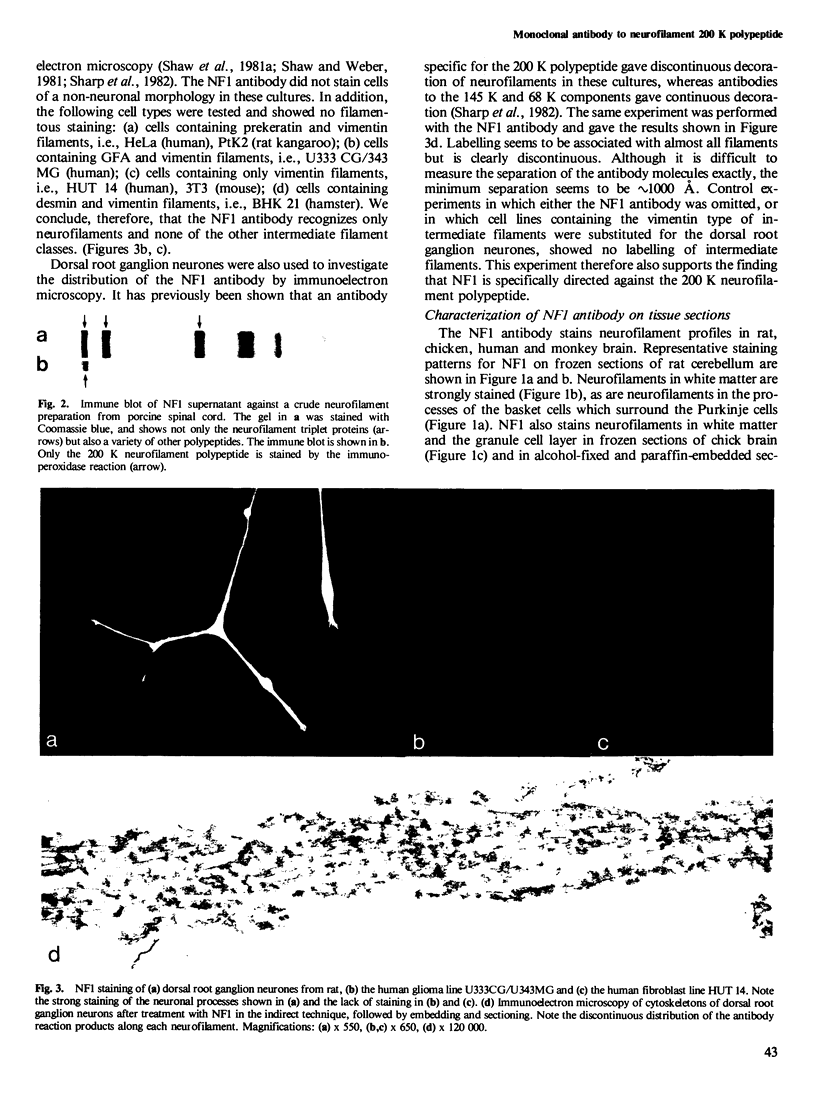
- Shaw G., Osborn M., Weber K. Arrangement of neurofilaments, microtubules and microfilament-associated proteins in cultured dorsal root ganglia cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Weber K. The distribution of the neurofilament triplet proteins within individual neurones. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Nov;136(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Antibody decoration of neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):198–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Anderton B. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mammalian neurofilaments. Biosci Rep. 1981 Mar;1(3):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01114913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Fields K. L. Antibodies to neurofilament, glial filament, and fibroblast intermediate filament proteins bind to different cell types of the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):115–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]