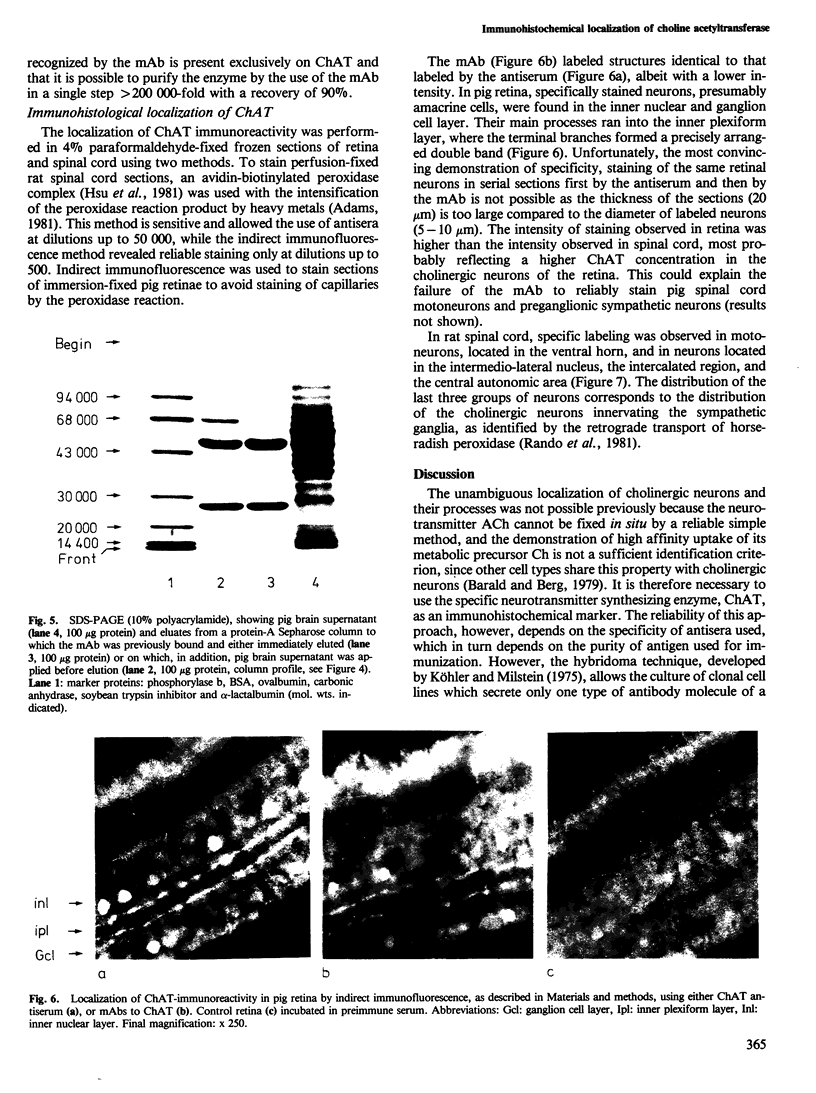
Abstract
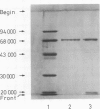
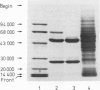
Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) has been purified from pig brain to greater than 95% homogeneity (purification factor: 646 000, specific activity of the purified enzyme: 128 mumol acetylcholine formed/min/mg). Gel electrophoresis of the purified enzyme in the presence of sodium dodecylsulphate and beta-mercaptoethanol revealed a single protein band at 68 000 daltons. Immunoprecipitation and double immunodiffusion tests showed that antisera raised against this protein specifically recognize ChAT. A monoclonal antibody prepared against the enzyme specifically binds a protein from crude pig brain supernatants which has a mol. wt. of 68 000 and a specific activity of 153 mumol/min/mg. This antibody shows no species cross-reactivity. The specificity of the immunohistochemical localization of ChAT has been established by comparing the labeling of pig retina using the antiserum with that obtained using the monoclonal antibody. Both probes specifically identify the same retinal structures: labeled cell bodies are found in the inner nuclear layer and the ganglion cell layer, while a double band is stained in the inner plexiform layer. In rat spinal cord, the antiserum labels the motoneurons and the preganglionic sympathetic neurons, located in the intermedio-lateral nucleus, the intercalated region, and the central autonomic area.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Jun;29(6):775–775. doi: 10.1177/29.6.7252134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barald K. F., Berg D. K. Autoradiographic labeling of spinal cord neurons with high affinity choline uptake in cell culture. Dev Biol. 1979 Sep;72(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughman R. W., Bader C. R. Biochemical characterization and cellular localization of the cholinergic system in the chicken retina. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 23;138(3):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzari C., Hartman B. K. Preparation of antibodies specific to choline acetyltransferase from bovine caudate nucleus and immunohistochemical localization of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7453–7457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenstein F., Barde Y. A., Thoenen H. Production of specific antibodies to choline acetyltransferase purified from pig brain. Neuroscience. 1981;6(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehinger B., Falck B. Autoradiography of some suspected neurotransmitter substances: GABA glycine, glutamic acid, histamine, dopamine, and L-dopa. Brain Res. 1971 Oct 8;33(1):157–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. A rapid radiochemical method for the determination of choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):407–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. Characterization and tissue localization of catecholamine synthesizing enzymes. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Jun;24(2):293–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Coe B., Casey L. A fluorometric assay for choline acetyltransferase and its use in the purification of the enzyme from human placenta. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1077–1085. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., McGeer P. L., Peng F., McGeer E. G. Choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons in rodent brain demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. Science. 1980 May 30;208(4447):1057–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.6990490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Aoki M., Fitch F. W., Wainer B. H. The production of monoclonal antibodies reactive with bovine choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng J. H., McGeer P. L., Kimura H., Sung S. C., McGeer E. G. Purification and immunochemical properties of choline acetyltransferase from human brain. Neurochem Res. 1980 Sep;5(9):943–962. doi: 10.1007/BF00966135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando T. A., Bowers C. W., Zigmond R. E. Localization of neurons in the rat spinal cord which project to the superior cervical ganglion. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Feb 10;196(1):73–83. doi: 10.1002/cne.901960107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Biophysical properties of rat brain choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):555–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Choline acetyltransferase: a review with special reference to its cellular and subcellular localization. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1977;20:283–337. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60656-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J. Serum monospecificity: a prerequisite for reliable immunohistochemical localization of neuronal markers including choline acetyltransferase. Neuroscience. 1981;6(6):989–991. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. L., McClure W. O. Purification of choline acetyltransferase from rat and cow brain. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5357–5365. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Staehelin T., Miggiano V., Schmidt J., Häring P. High frequencies of antigen-specific hybridomas: dependence on immunization parameters and prediction by spleen cell analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]