Abstract
The C-terminal hexapeptide of histone H3 of chicken erythrocytes (residues 130-135) corresponding to the sequence Ile-Arg-Gly-Glu-Arg-Ala ( IRGERA ) was prepared by solid-phase peptide synthesis and, after coupling to bovine serum albumin, was used to elicit antibodies in rabbits. The antigenic activity of the synthetic peptide IRGERA was found to be very similar to that of the natural CN3 fragment (residues 121-135), and it inhibited the H3-anti H3 reaction in complement fixation, solid-phase radioimmunoassay, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Antibodies induced by IRGERA were found to bind equally well to IRGERA coupled to hemocyanin, to the intact H3 molecule, and to chromatin subunits (nucleosomes and core particles). The results demonstrate that the C-terminal hexapeptide of histone H3 is located at the surface of chromatin subunits and agree with current models proposed for the spatial organization of the chromatin core particle.
Full text
PDF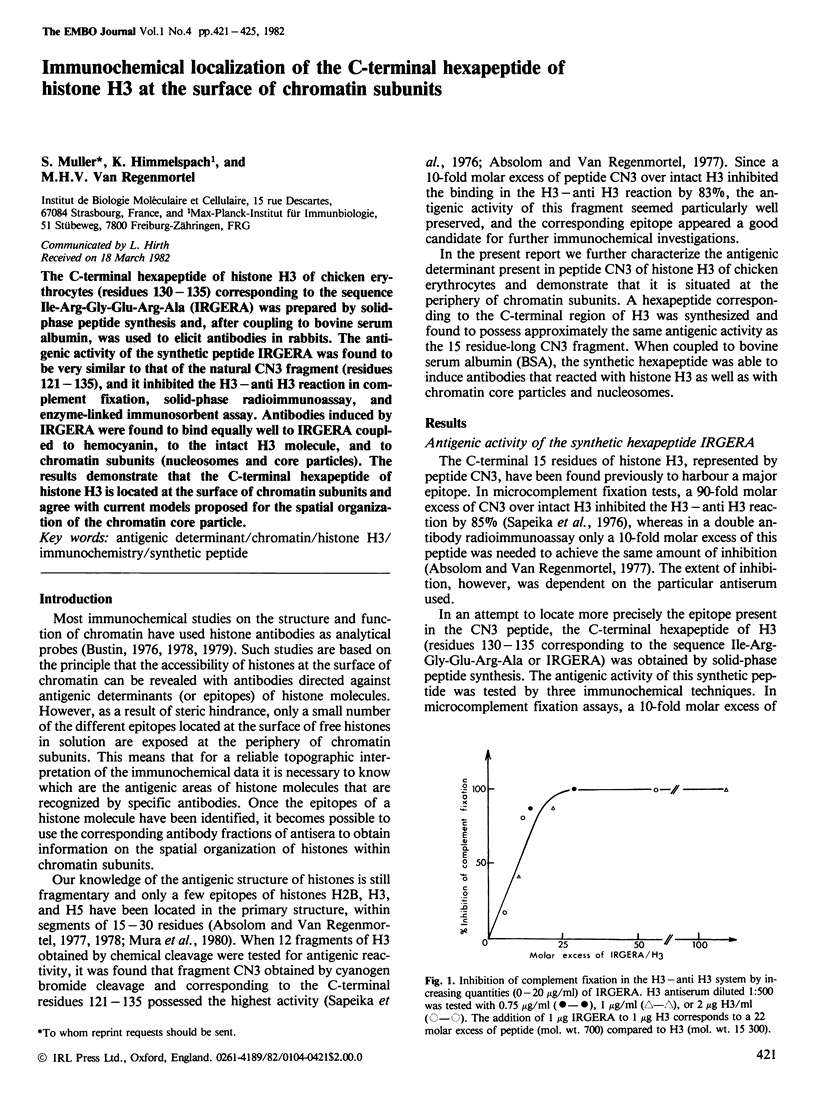


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERER F. A. Preparation and properties of an artificial antigen immunologically related to tobacco mosaic virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Apr 2;71:246–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absolom D., Van Regenmortel M. H. Nucleosome structure studied with purified antibodies to histones H2B, H3 and H4. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 20;85(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Absolom D., van Regenmortel M. H. Purification by immunoadsorption and immunochemical properties of histone H3. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atassi M. Z., Smith J. A. A proposal for the nomenclature of antigenic sites in peptides and proteins. Immunochemistry. 1978 Aug;15(8):609–610. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankstein L. A., Stollar B. D., Levy S. B. Immunochemical distinctions among histones and their variants in a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):168–172. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt W. F., von Holt C. Purification and characterization of the cysteine-containing F3 histone from chicken erythrocyte. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):338–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80295-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M. Arrangement of histones in chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 17;245(146):207–209. doi: 10.1038/newbio245207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M. Chromatin structure and specificity revealed by immunological techniques. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Goldblatt D., Sperling R. Chromatin structure visualization by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Stollar B. D. Immunological relatedness of thymus and liver F1 histone subfracions. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3506–3510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm L., Briand G., Sautière P., Crane-Robinson C. Proteolytic digestion studies of chromatin core-histone structure. Identification of the limit peptides of histones H3 and H4. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm L., Hayashi H., Cary P. D., Moss T., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. Sites of histone/histone interaction in the H3 - H4 complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Padua Mathieu D., Stollar B. D. Antibodies specific for histone H2b fragments 1-58 and 63-125 in antisera to H2b and to the fragments: probes for histone evolution. Biochemistry. 1980 May 13;19(10):2246–2252. doi: 10.1021/bi00551a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Brown R. S., Richmond T., Rushton B., Lutter L. C., Klug A. X-ray diffraction study of a new crystal form of the nucleosome core showing higher resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Bustin M. Exposure of histone antigenic determinants in chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1689–1695. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Bustin M., Sperling R. Heterogeneity in the interaction of chromatin subunits with anti-histone sera visulatized by immuno-electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 1;112(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman A., Sluyser M. Antigenic determinants on lysine-rich histones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 21;295(2):613–620. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Rhodes D., Smith J., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. A low resolution structure for the histone core of the nucleosome. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):509–516. doi: 10.1038/287509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M. Physical studies on the H3/H4 histone tetramer. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2261–2267. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mura C. V., Mazen A., Neelin J. M., Briand G., Sautiere P., Champagne M. Distribution of antigenicity in chicken erythrocyte histone H5. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):613–620. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch H. H. Structural complementarity in chromatin subunits. Naturwissenschaften. 1979 Apr;66(4):206–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00366027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romac J., Bouley J. P., Van Regenmortel M. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the study of histone antigens and nucleosome structure. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani M., Vidali G., Tahourdin C. S., Bustin M. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for chromosomal components. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapeika G., Absolom D., Van Regenmortel M. H. Three antigenic determinants in histone F3 from chicken erythrocytes. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jun;13(6):499–501. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Bustin M. Histone compostion of chromatin subunits studied by immunosedimentation. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4305–4312. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluyser M., Rümke P., Hekman A. Antigenicity of histones: comparative studies on histones with very high lysine content from various sources. Immunochemistry. 1969 May;6(3):494–498. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotirov N., Johns E. W. Rabbit precipitin antibody to chicken erythrocyte histone F2C. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):686–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Rezuke W. Separation of anti-histone antibodies from nonimmune histone-precipitating serum proteins, predominantly alpha2-macroglobulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Serological analyses of histones. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;18:105–122. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Ward M. Rabbit antibodies to histone fractions as specific reagents for preparative and comparative studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1261–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., Strickland M. S. More histone structures. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):201–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm F. X., Wilhelm M. L., Erard M., Duane M. P. Reconstitution of chromatin: assembly of the nucleosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):505–521. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., Carlson S. S., White T. J. Biochemical evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:573–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Mazen A., Erard M., Pouyet J., Champagne M. Isolation and physical characterization of a stable core particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):767–779. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Padua Mathieu D., Mura C. V., Frado L. L., Woodcock C. L., Stollar B. D. Differing accessibility in chromatin of the antigenic sites of regions 1-58 and 63-125 of histone H2B. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):135–141. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Westhuyzen D. R., von Holt C. A new procedure for the isolation and fractionation of histones. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


