Abstract
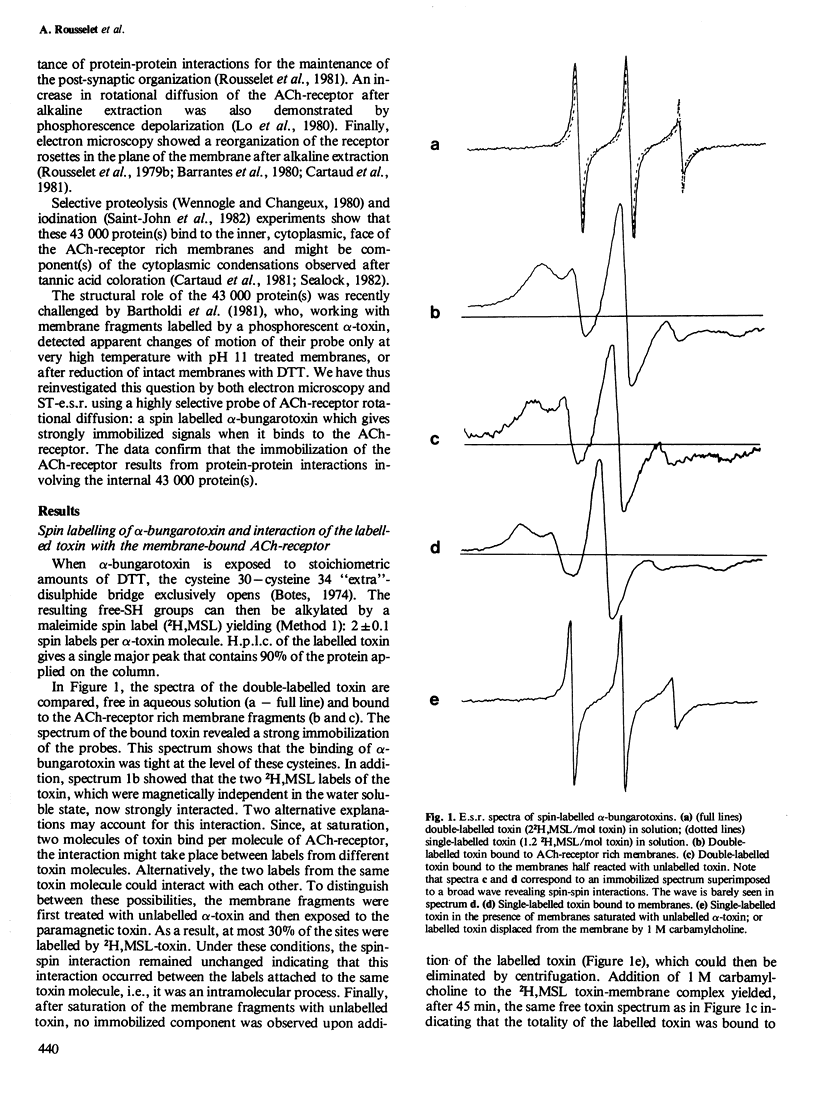
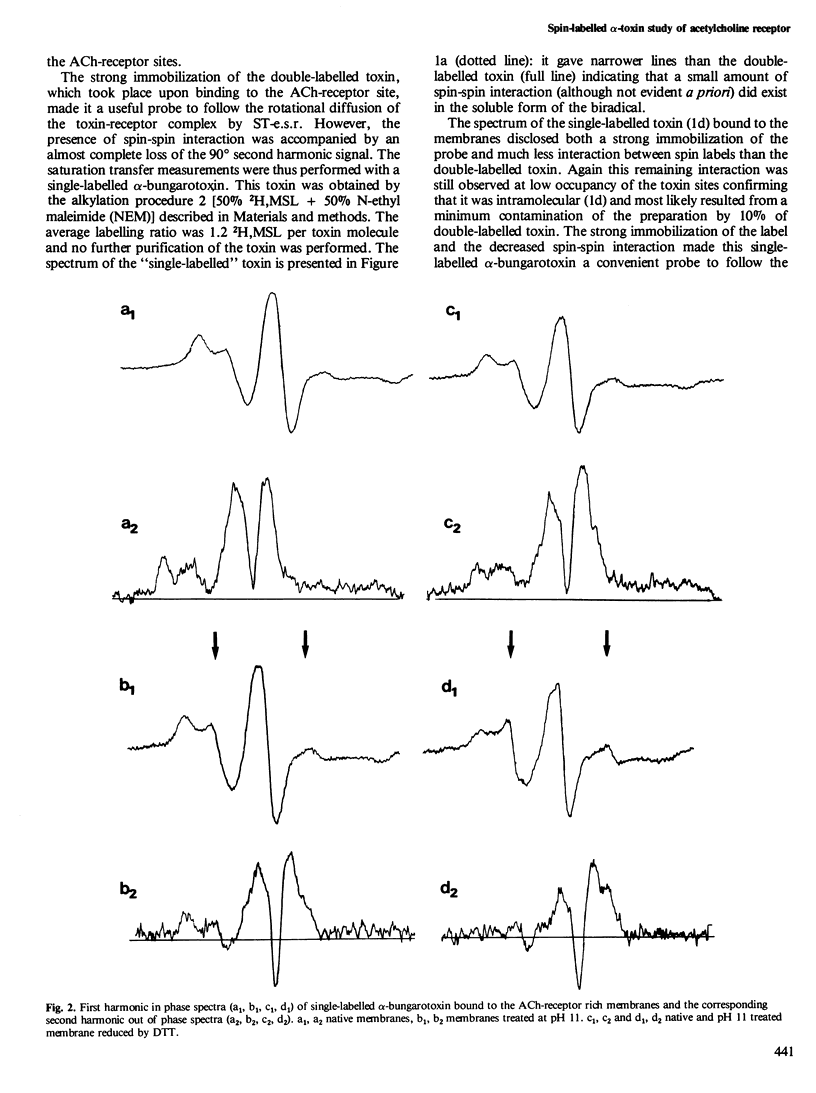
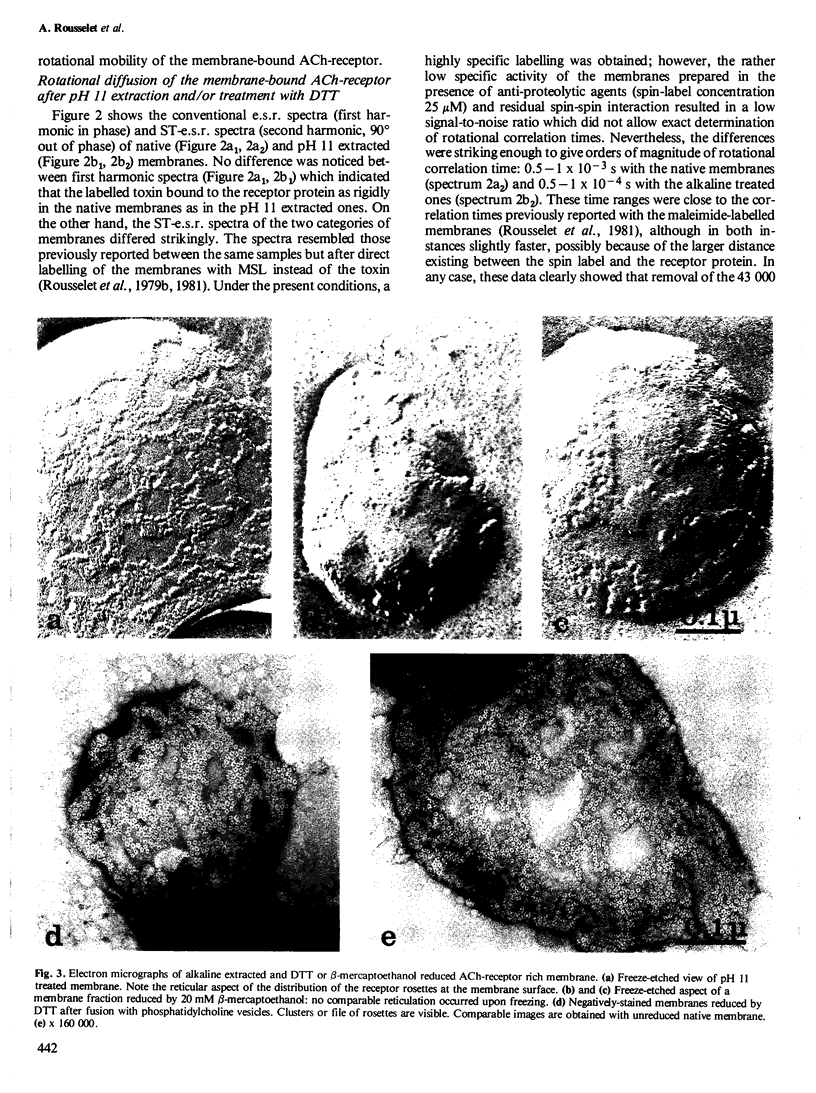
The rotational diffusion of the acetylcholine (ACh) receptor in subsynaptic membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata electric organ was investigated with a spin-labelled alpha-bungarotoxin. A toxin with two spin labels was first synthesized; the conventional electron spin resonance spectrum (e.s.r.) of this toxin bound to the receptor indicated: (1) a complete immobilization of the probes; and (2) a strong spin-spin interaction that was not, or barely, seen in solution. The modification of the degree of spin-spin interaction is taken as an indication of a toxin conformational change accompanying its binding to the ACh-receptor. To avoid spin-spin interaction a single-labelled toxin was made and used to follow the rotational diffusion of the receptor by saturation transfer e.s.r. (ST-e.s.r.). With native membranes a high immobilization of the ACh-receptor was noticed. Reduction of the membranes by dithiothreitol had little effect on this motion. Only extraction of the 43 000 protein(s) by pH 11 treatment was able to enhance the rotational diffusion of the ACh-receptor protein (rotational correlation time by ST-e.s.r. in the 0.5 - 1 X 10(-4) s range) and to allow its lateral diffusion in the plane of the membrane fragments (observed by electron microscopy after freeze-etching or negative staining).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D., Ravdin P. M., Podleski T. R. Control of acetylcholine receptor mobility and distribution in cultured muscle membranes. A fluorescence study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 20;511(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Ravdin P., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Webb W. W., Elson E. L., Podleski T. R. Lateral motion of fluorescently labeled acetylcholine receptors in membranes of developing muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4594–4598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Wight A., Webb W., Horwitz A. Influence of membrane lipids on acetylcholine receptor and lipid probe diffusion in cultured myotube membrane. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3604–3609. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrantes F. J., Neugebauer D. C., Zingsheim H. P. Peptide extraction by alkaline treatment is accompanied by rearrangement of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 24;112(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrantes F. J. Oligomeric forms of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor disclosed upon extraction of the Mr 43,000 nonreceptor peptide. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):60–68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholdi M., Barrantes F. J., Jovin T. M. Rotational molecular dynamics of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor revealed by phosphorescence spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):389–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienvenüe A., Rousselet A., Kato G., Devaux P. F. Fluidity of the lipids next to the acetylcholine receptor protein of torpedo membrane fragments. Use of amphiphilic reversible spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):841–848. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The reactivity of the disulphide bonds of Naja nivea toxin alpha. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois J. P., Popot J. L., Ryter A., Changeux J. P. Consequences of denervation on the distribution of the cholinergic (nicotinic) receptor sites from Electrophorus electricus revealed by high resolution autoradiography. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):557–563. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90722-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois J. P., Popot J. L., Ryter A., Changeux J. P. Quantitative studies on the localization of the cholinergic receptor protein in the normal and denervated electroplaque from Electrophorus electricus. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):200–216. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Sobel A., Rousselet A., Devaux P. F., Changeux J. P. Consequences of alkaline treatment for the ultrastructure of the acetylcholine-receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):418–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Vincent J. P., Kopeyan C., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. Structure-function relationship in the binding of snake neurotoxins to the torpedo membrane receptor. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2081–2091. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellena J. F., McNamee M. G. Interaction of spin-labeled Naja naja siamensis alpha-neurotoxin with acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank E., Gautvik K., Sommerschild H. Cholinergic receptors at denervated mammalian motor end-plates. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Sep;95(1):66–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gysin R., Wirth M., Flanagan S. D. Structural heterogeneity and subcellular distribution of nicotinic synapse-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11373–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Disulfide bond cross-linked dimer in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):692–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Damle V., Hamilton S., McLaughlin M., Valderamma R., Wise D. Acetylcholine receptors in and out of membranes. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979;3:183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Heuser J. E., Stroud R. M. Protease effects on the structure of acetylcholine receptor membranes from Torpedo californica. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):823–838. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. M., Garland P. B., Lamprecht J., Barnard E. A. Rotational mobility of the membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo electric organ measured by phosphorescence depolarisation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Barrantes F. J. Immobilized lipid in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4329–4333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Watts A., Barrantes F. J. Phospholipid chain immobilization and steroid rotational immobilization in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 6;645(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee M. G., Ellena J. F., Dalziel A. W. Lipid-protein interactions in membranes containing the acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):103–104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84622-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Krodel E. K., Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):690–694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Cartaud J., Devaux P. F. Effects of temperature, lipid modification and pH on the mobility of the major proteins of the receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmarata. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 6;648(2):169–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Devaux P. F. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance on membrane bound proteins. II-Absence of rotational diffusion of the cholinergic receptor protein in Torpedo marmorata membrane fragments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Devaux P. F., Wirtz K. W. Free fatty acids and esters can be immobilized by receptor rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata but not phospholipid acyl chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):871–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91908-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Changeux J. P. Phosphorylation in vitro of membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Effect on membrane solubilization by detergents. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;105(1):51–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Factors regulating the susceptibility of the acetylcholine receptor protein to heat inactivation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80595-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealock R. Cytoplasmic surface structure in postsynaptic membranes from electric tissue visualized by tannic-acid-mediated negative contrasting. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):514–522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Heidmann T., Hofler J., Changeux J. P. Distinct protein components from Torpedo marmorata membranes carry the acetylcholine receptor site and the binding site for local anesthetics and histrionicotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Weber M., Changeux J. P. Large-scale purification of the acetylcholine-receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-extracted forms from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):215–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John P. A., Froehner S. C., Goodenough D. A., Cohen J. B. Nicotinic postsynaptic membranes from Torpedo: sidedness, permeability to macromolecules, and topography of major polypeptides. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):333–342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Lazarides E., Raftery M. A. The characterization of actin associated with postsynaptic membranes from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90342-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsetlin V. I., Karlsson E., Arseniev A. S., Utkin Y. N., Surin A. M., Pashkov V. S., Pluzhnikov K. A., Ivanov V. T., Bystrov V. F., Ovchinnikov Y. A. EPR and fluorescence study of interaction of Naja naja oxiana neurotoxin II and its derivatives with acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80692-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Transmembrane orientation of proteins present in acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes from Torpedo marmorata studied by selective proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):381–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]