Abstract
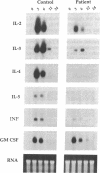
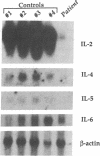
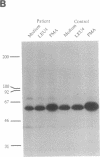
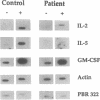
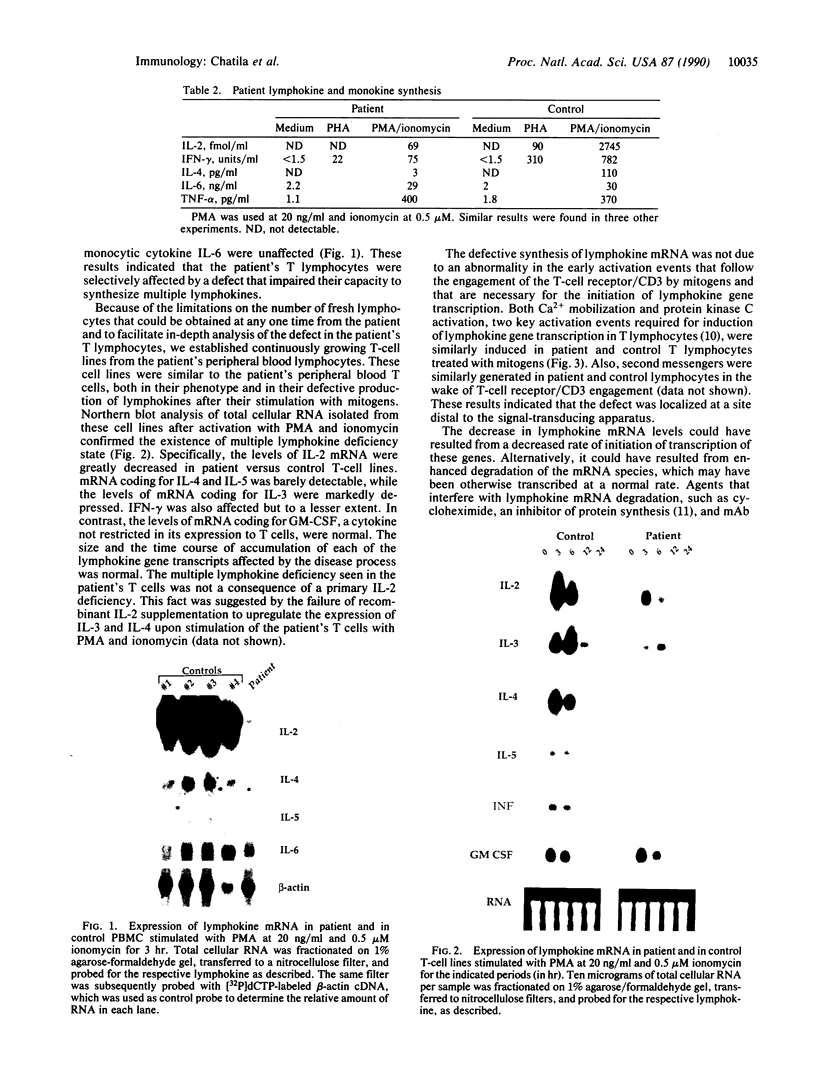
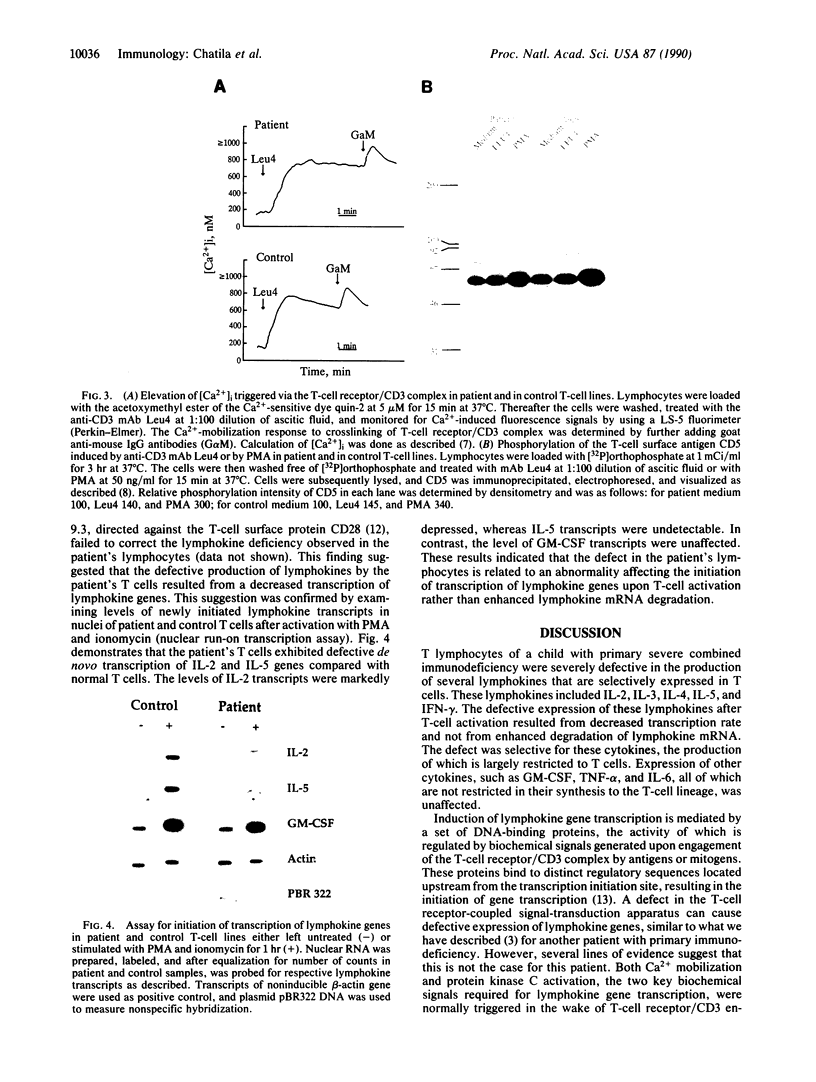
The circulating T lymphocytes of a female child with recurrent opportunistic infections were normal in number and phenotype but exhibited poor proliferation and decreased synthesis of the T-cell growth factor interleukin (IL) 2 in response to mitogens. Recombinant IL-2 fully restored the proliferative responses of her T cells, suggesting that her poor immune function was related to IL-2 deficiency. Northern blot analysis of total cellular RNA from the patient's T cells revealed markedly decreased levels of IL-2 mRNA of normal size. In addition, mRNA levels of other lymphokines selectively expressed by T cells, which include IL-3, IL-4, and IL-5, were either severely depressed or absent. The levels of interferon gamma mRNA were moderately decreased, while those of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, a lymphokine the production of which is not restricted to T cells, were unaffected. The decreased level of lymphokine mRNA in the patient's T lymphocytes was not from enhanced catabolism but resulted from a diminution in the transcription rate of the affected lymphokine genes. Normal transduction via the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex of biochemical signals necessary for the initiation of lymphokine gene transcription indicated that the defect was distal to the membrane signal-transducing apparatus. The defect is hypothesized to involve a T-cell-specific trans-acting regulatory factor required for transcription of the affected lymphokine genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatila T. A., Geha R. S. Phosphorylation of T cell membrane proteins by activators of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4308–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatila T., Wong R., Young M., Miller R., Terhorst C., Geha R. S. An immunodeficiency characterized by defective signal transduction in T lymphocytes. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 16;320(11):696–702. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903163201104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSanto J. P., Keever C. A., Small T. N., Nicols G. L., O'Reilly R. J., Flomenberg N. Absence of interleukin 2 production in a severe combined immunodeficiency disease syndrome with T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1697–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Lymphokines. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 8;317(15):940–945. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710083171506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmel E. A., Verweij C. L., Durand D. B., Higgins K. M., Lacy E., Crabtree G. R. Cyclosporin A specifically inhibits function of nuclear proteins involved in T cell activation. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1617–1620. doi: 10.1126/science.2595372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B. D. Cyclosporine. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1725–1738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstein T., June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Stella G., Thompson C. B. Regulation of lymphokine messenger RNA stability by a surface-mediated T cell activation pathway. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):339–343. doi: 10.1126/science.2540528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa R., Chatila T., Pahwa S., Paradise C., Day N. K., Geha R., Schwartz S. A., Slade H., Oyaizu N., Good R. A. Recombinant interleukin 2 therapy in severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Morgan D. A., Gallo R. C. Functional and morphologic characterization of human T cells continuously grown in vitro. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L. B., Wong R. C., Remold-O'Donnell E., Vercelli D., Sancho J., Terhorst C., Rosen F., Geha R., Chatila T. Mechanism of mononuclear cell activation by an anti-CD43 (sialophorin) agonistic antibody. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4194–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg K., Parkman R. Severe combined immunodeficiency due to a specific defect in the production of interleukin-2. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 14;322(24):1718–1723. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006143222406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]