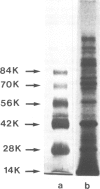
Abstract
Type IV procollagen was isolated from the culture medium of the teratocarcinoma cell line PYS-2 by affinity chromatography on heparin-Sepharose. Immunological studies showed that type IV procollagen is composed of pro-alpha 1(IV) and pro-alpha 2(IV) chains and contains two potential cross-linking sites which are located in the short triple-helical 7S domain and the globular domain NC1 . The 7S domain was also identified as the heparin binding site. Rotary shadowing visualized type IV procollagen as a single triple-helical rod (length 388 nm) with a globule at one end. Some of the procollagen in the medium, however, had formed aggregates by alignment of 2-4 molecules along their 7S domains. After deposition in the cell matrix, non-reducible cross-links between the 7S domains are formed while the globules of two procollagen molecules connect to each other. The latter may require a slight proteolytic processing of the globular domains NC1 . The shape of type IV procollagen and the initial steps in its assembly are compatible with a recently proposed network of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Since both type IV collagen and laminin bind to heparin, the formation of higher ordered structures by interaction of both proteins with heparan-sulfate proteoglycan may occur in situ.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Vaheri A., Krieg T., Timpl R. Biosynthesis of two subunits of type IV procollagen and of other basement membrane proteins by a human tumor cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch E., Sage H., Bornstein P. Structural basis for apparent heterogeneity of collagens in human basement membranes: type IV procollagen contains two distinct chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):745–749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rosso M., Cappelletti R., Viti M., Vannucchi S., Chiarugi V. Binding of the basement-membrane glycoprotein laminin to glycosaminoglycans. An affinity-chromatography study. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):699–704. doi: 10.1042/bj1990699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler J. H., Fessler L. I. Biosynthesis of procollagen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Timpl R., Fessler J. H. Assembly and processing of procollagen type III in chick embryo blood vessels. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2531–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heathcote G., Sear C. H., Grant M. E. Studies on the assembly of the rat lens capsule. Biosynthesis and partial characterization of the collagenous components. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):283–294. doi: 10.1042/bj1760283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Farquhar M. G. Presence of heparan sulfate in the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1303–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn K., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Risteli J., Dieringer H., Voss T., Glanville R. W. Macromolecular structure of basement membrane collagens. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 9;125(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. M., Speers W. C., Swartzendruber D. E., Pierce G. B. Neoplastic differentiation: characteristics of cell lines derived from a murine teratocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Aug;84(1):13–27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Alitalo K., Risteli L., Vaheri A., Timpl R., Wartiovaara J. Basal lamina glycoproteins laminin and type IV collagen are assembled into a fine-fibered matrix in cultures of a teratocarcinoma-derived endodermal cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jan;137(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Roll F. J., Furthmayr H., Foidart J. M. Ultrastructural localization of fibronectin and laminin in the basement membranes of the murine kidney. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):682–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor R. R., Clark C. C., Strause E. L., Koszalka T. R., Brent R. L., Kefalides N. A. Basement membrane procollagen is not converted to collagen in organ cultures of parietal yolk sac endoderm. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1789–1794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Odermatt E., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Protease resistance and conformation of laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Bächinger H. P., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. 7-S collagen: characterization of an unusual basement membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Rohde H., Timpl R. Sensitive radioimmunoassays for 7 S collagen and laminin: application to serum and tissue studies of basement membranes. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):372–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Schuppan D., Glanville R. W., Timpl R. Immunochemical distinction between two different chains of type IV collagen. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj1910517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Wick G., Timpl R. Immunological characterization of the 7-S domain of type IV collagens. Coll Relat Res. 1981 Sep;1(5):419–432. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(81)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakashita S., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. Basement membrane glycoprotein laminin binds to heparin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Veis A. Characterization of bovine anterior-lens-capsule basement-membrane collagen. 2. Segment-long-spacing precipitates: further evidence for large N-terminal and C-terminal extensions. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Kefalides N. A. Collagen crosslinks: occurrence in basement membrane collagens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):775–780. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rohrbach D. H., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment of PAM 212 (epithelial) cells to basement membrane collagen. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wiedemann H., van Delden V., Furthmayr H., Kühn K. A network model for the organization of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Robey P. G., Martin G. R. Biosynthesis of type IV procollagens. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1284–1289. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]