Abstract
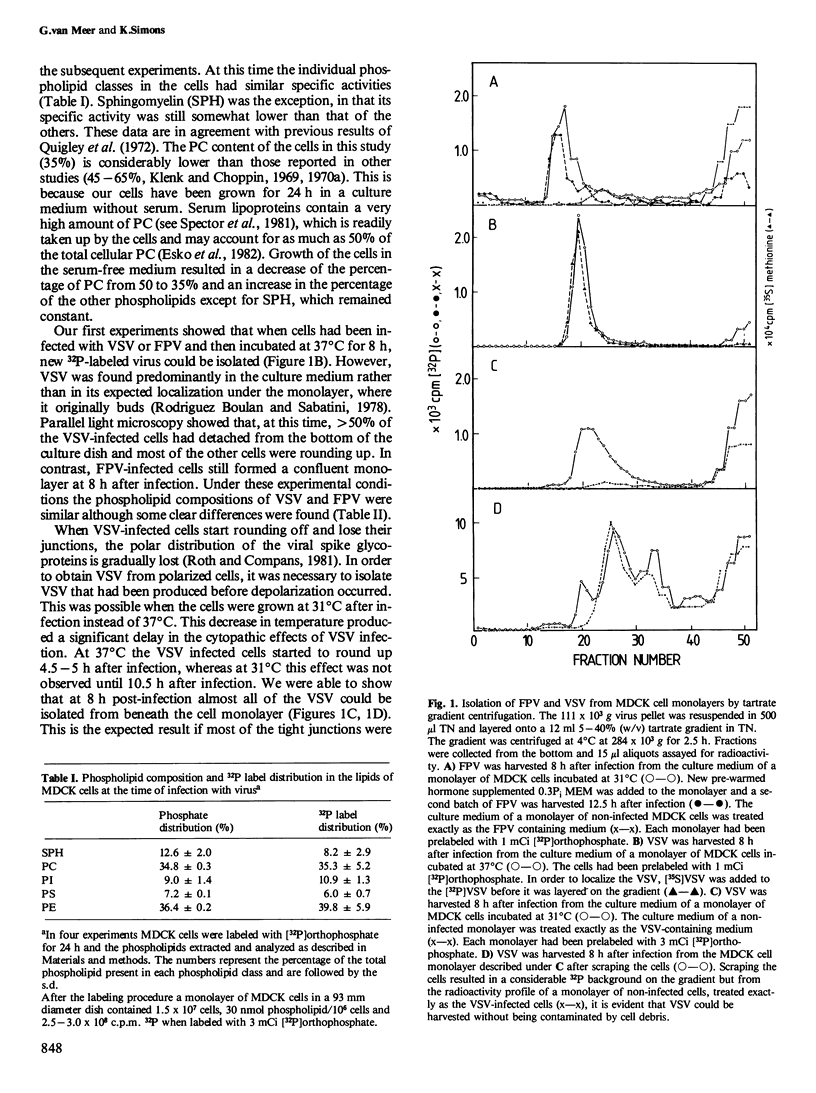
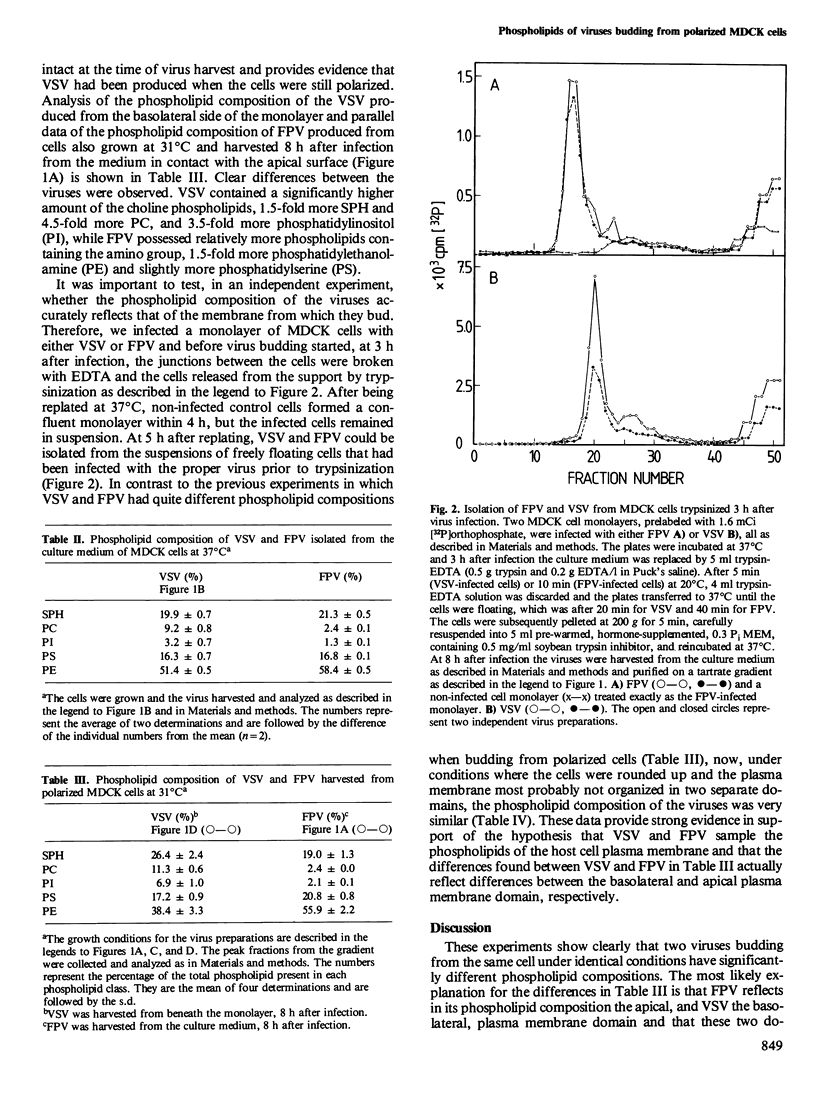
Influenza virus and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) obtain their lipid envelope by budding through the plasma membrane of infected cells. When monolayers of Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells, a polarized epithelial cell line, are infected with fowl plague virus (FPV), an avian influenza virus, or with VSV, new FPV buds through the apical plasma membrane whereas VSV progeny is formed by budding through the basolateral plasma membrane. FPV and VSV were isolated from MDCK host cells prelabeled with [32P]orthophosphate and their phospholipid compositions were compared. Infection was carried out at 31 degrees C to delay cytopathic effects of the virus infection, which lead to depolarization of the cell surface. 32P-labeled FPV was isolated from the culture medium, whereas 32P-labeled VSV was released from below the cell monolayer by scraping the cells from the culture dish 8 h after infection. At this time little VSV was found in the culture medium, indicating that the cells were still polarized. The phospholipid composition of the two viruses was distinctly different. FPV was enriched in phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine and VSV in phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and phosphatidylinositol. When MDCK cells were trypsinized after infection and replated, non-infected control cells attached to reform a confluent monolayer within 4 h, whereas infected cells remained in suspension. FPV and VSV could be isolated from the cells in suspension and under these conditions the phospholipid composition of the two viruses was very similar. We conclude that the two viruses obtain their lipids from the plasma membrane in the same way and that the different phospholipid compositions of the viruses from polarized cells reflect differences in the phospholipid composition of the two plasma membrane domains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Schachter D. Lipid dynamics and lipid-protein interactions in rat enterocyte basolateral and microvillus membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2763–2769. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas A. P., Kerley R., Isselbacher K. J. Preparation and characterization of the lateral and basal plasma membranes of the rat intestinal epithelial cell. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1329–1338. doi: 10.1042/bj1281329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esko J. D., Nishijima M., Raetz C. R. Animal cells dependent on exogenous phosphatidylcholine for membrane biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1698–1702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J. Lipid composition of the isolated rat intestinal microvillus membrane. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;109(1):51–59. doi: 10.1042/bj1090051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoi Sang U., Saier M. H., Jr, Ellisman M. H. Tight junction formation is closely linked to the polar redistribution of intramembranous particles in aggregating MDCK epithelia. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Sep;122(2):384–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachar B., Reese T. S. Evidence for the lipidic nature of tight junction strands. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):464–466. doi: 10.1038/296464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai K., Fujita M., Nakao M. Lipid components of two different regions of an intestinal epithelial cell membrane of mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 18;369(2):222–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycosphingolipids of plasma membranes of cultured cells and an enveloped virus (SV5) grown in these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):57–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Lipids of plasma membranes of monkey and hamster kidney cells and of parainfluenza virions grown in these cells. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):255–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90367-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Plasma membrane lipids and parainfluenza virus assembly. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt D. S., Hamamoto S. T., Pitelka D. R. Transepithelial transport in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Wagner R. R., Dubovi E. J. Viral membranes: model systems for studying biological membranes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1979;6(2):165–217. doi: 10.3109/10409237909102563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Glaser M. Budding of Rous sarcoma virus and vesicular stomatitis virus from localized lipid regions in the plasma membrane of chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9044–9050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Kachar B. On tight-junction structure. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisam M., Ripoche P. Redistribution of surface macromolecules in dissociated epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):907–920. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Einhorn M. H. Determination of phospholipid composition of RNA tumor viruses by 32 P labeling of infected cell cultures. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):614–619. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P., Rifkin D. B., Reich E. Phospholipid composition of Rous sarcoma virus, host cell membranes and other enveloped RNA viruses. Virology. 1971 Oct;46(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkonen O., Gahmberg C. G., Simons K., Käriäinen L. The lipids of the plasma membranes and endoplasmic reticulum from cultured baby hamster kidney cells (BHK21). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):66–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. C., Simmons N. L. Demonstration of protein asymmetries in the plasma membrane of cultured renal (MDCK) epithelial cells by lactoperoxidase-mediated iodination. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Compans R. W. Delayed appearance of pseudotypes between vesicular stomatitis virus influenza virus during mixed infection of MDCK cells. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):848–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.848-860.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Fkeischer S., Yamamoto A. Two dimensional then layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1970 May;5(5):494–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02531316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Mathur S. N., Kaduce T. L., Hyman B. T. Lipid nutrition and metabolism of cultured mammalian cells. Prog Lipid Res. 1980;19(3-4):155–186. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(80)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub M., Chuman L., Saier M. H., Jr, Sato G. Growth of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell (MDCK) line in hormone-supplemented, serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziomek C. A., Schulman S., Edidin M. Redistribution of membrane proteins in isolated mouse intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):849–857. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


