Abstract
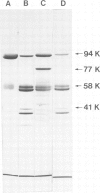
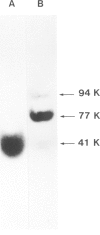
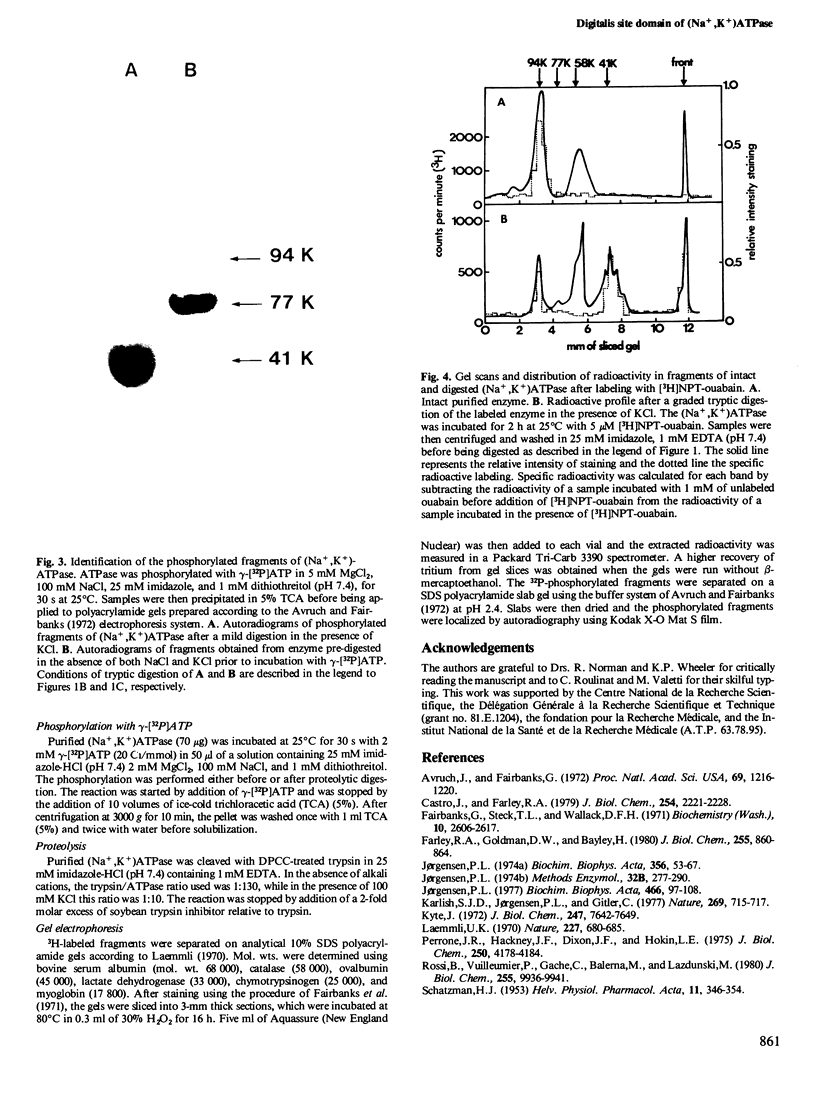
Digitalis compounds that are extensively used in the treatment of cardiovascular disorders are known to bind specifically at the extracellular side of (Na+,K+)ATPase. We have recently reported the synthesis of [3H]p- nitrophenyltriazene -ouabain, a derivative of ouabain, which specifically alkylates the catalytic chain of the (Na+,K+)ATPase at a defined region of the sequence. The peptidic segment involved in the binding of digitalis to (Na+,K+)ATPase has been located after mild trypsin treatment of the labeled enzyme. In the presence of 100 mM KCl, tryptic fragmentation results in two peptide fragments of mol. wt. 58 000 and 41 000, respectively. The radioactive probe labeled only the 41 000 fragment indicating that the digitalis binding site is located on the 41 000 domain situated at the N-terminal part of the sequence of the alpha-subunit.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Fairbanks G. Demonstration of a phosphopeptide intermediate in the Mg ++ -dependent, Na + - and K + -stimulated adenosine triphosphatase reaction of the erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1216–1220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro J., Farley R. A. Proteolytic fragmentation of the catalytic subunit of the sodium and potassium adenosine triphosphatase. Alignment of tryptic and chymotryptic fragments and location of sites labeled with ATP and iodoacetate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2221–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley R. A., Goldman D. W., Bayley H. Identification of regions of the catalytic subunit of (Na-K)-ATPase embedded within the cell membrane. Photochemical labeling with [3H]adamantane diazirine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):860–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. VI. Differential tryptic modification of catalytic functions of the purified enzyme in presence of NaCl and KCl. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen P. L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+ )-ATPase. IV. Estimation of the purity and of the molecular weight and polypeptide content per enzyme unit in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Jorgensen P. L., Gitler C. Identification of a membrane-embedded segment of the large polypeptide chain of (Na+, K+)ATPase. Nature. 1977 Oct 20;269(5630):715–717. doi: 10.1038/269715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Properties of the two polypeptides of sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7642–7649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone J. R., Hackney J. F., Dixon J. F., Hokin L. E. Molecular properties of purified (sodium + potassium)-activated adenosine triphosphatases and their subunits from the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias and the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4178–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi B., Vuilleumier P., Gache C., Balerna M., Lazdunski M. Affinity labeling of the digitalis receptor with p-nitrophenyltriazene-ouabain, a highly specific alkylating agent. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9936–9941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium- und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(4):346–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]