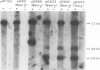
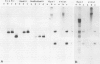
Abstract
An assay has been developed and used to locate an origin of DNA replication on the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) genome. Baby hamster kidney cells were transfected with circular plasmid molecules containing cloned copies of HSV-1 DNA fragments, and helper functions were provided by superinfection with wild-type HSV-1. The presence of an HSV-1 origin of replication within a plasmid enabled amplification of the vector DNA sequences, which was detected by the incorporation of [32P]orthophosphate. By screening various HSV-1 DNA fragments it was possible to identify a 995-bp fragment that maps entirely within the reiterated sequences flanking the short unique region of the viral genome and contains all the cis-acting signals necessary to function as an origin of viral DNA replication. The products of plasmid replication were shown to be high mol. wt. DNA molecules consisting of tandem duplications of the complete plasmid, suggesting that replication was occurring by a rolling-circle mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker Y., Dym H., Sarov I. Herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., McKenna G., Sharp P. A. Cleavage of mouse DNA by a restriction enzyme as a clue to the arrangement of genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:383–395. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Cortini R., Wilkie N. M. Analysis of herpesvirus DNA substructure by means of restriction endonucleases. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):243–256. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Nucleotide sequences of the joint between the L and S segments of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):315–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Clements J. B. A partial denaturation map of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA: evidence for inversions of the unique DNA regions. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denniston K. J., Madden M. J., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. Characterization of coliphage lambda hybrids carrying DNA fragments from Herpes simplex virus type 1 defective interfering particles. Gene. 1981 Dec;15(4):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Locker H., Vlazny D. A. Studies of defective herpes simplex viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:347–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkeĺ N., Locker H., Batterson W., Hayward G. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. VI. Defective DNA originates from the S component. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.527-531.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Shlomai J., Becker Y. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus DNA molecules isolated from infected cells by centrifugation in CsCl density gradients. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):507–522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstrom R. H., Alwine J. C., Steinhart W. L., Hill C. W., Hyman R. W. The terminal repetition of herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):144–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstrom R. H., Alwine J. C., Steinhart W. L., Hill C. W. Terminal repetitions in herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):679–681. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B. J., Bengali Z., Vande Woude G. F. Physical map of the origin of defective DNA in herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):878–887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.878-887.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Maichle I. B., Ott A., Schröder C. H. Origin of two different classes of defective HSV-1 Angelotti DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1467–1478. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Ott-Hartmann A., Schatten R., Schröder C. H., Gray C. P. Amplification of a short nucleotide sequence in the repeat units of defective herpes simplex virus type 1 Angelotti DNA. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.75-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N. Structure and origin of defective genomes contained in serially passaged herpes simplex virus type 1 (Justin). J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1065–1077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1065-1077.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Site-specific inversion sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome: domain and structural features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7047–7051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder C. H., Stegmann B., Lauppe H. F., Kaerner H. C. An unusual defective genotype derived from herpes simplex virus strain ANG. Intervirology. 1975;6(4-5):270–284. doi: 10.1159/000149481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M. J., Summers W. C. Structure of the joint region and the termini of the DNA of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):374–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.374-387.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Skare J., Summers W. C. Analysis of DNA of defective herpes simplex virus type 1 by restriction endonuclease cleavage and nucleic acid hybridization. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):683–686. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Davison A., Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C. Recombination in herpes simplex virus: mapping of mutations and analysis of intertypic recombinants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):827–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M. The synthesis and substructure of herpesvirus DNA: the distribution of alkali-labile single strand interruptions in HSV-1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1973 Dec;21(3):453–467. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]