Abstract
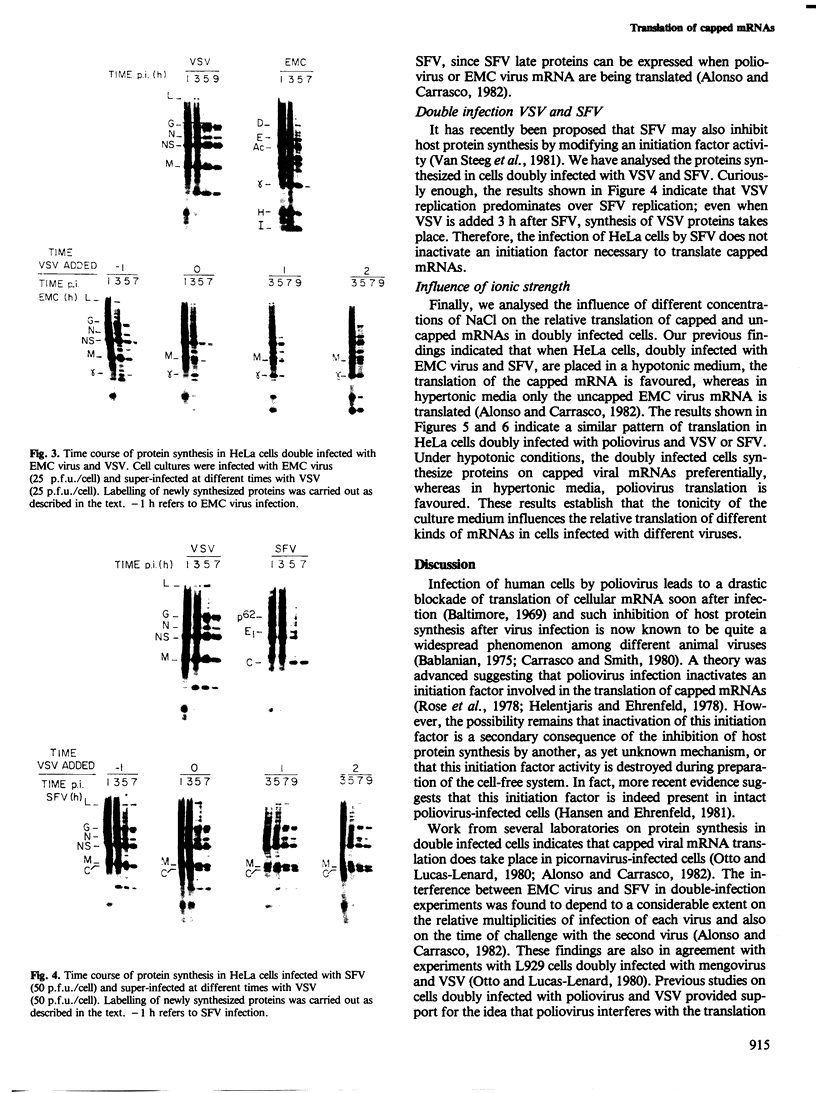
HeLa cells doubly infected with Semliki Forest virus (SFV) and poliovirus synthesize either more poliovirus proteins or more SFV late proteins depending on the time of super-infection with poliovirus. Under some conditions, the infected cells translate uncapped poliovirus mRNA and capped 26S mRNA from SFV simultaneously, even though host protein synthesis has been shut down. Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) protein synthesis is depressed drastically when VSV-infected cells are super-infected with poliovirus. In cells doubly infected with VSV and encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus or with VSV and SFV, dominance of one of the viruses depends on the time of addition of the challenge virus. The influence of external conditions on the relative translation of capped or uncapped viral mRNA in doubly infected cells has also been analysed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso M. A., Carrasco L. Protein synthesis in HeLa cells double-infected with encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):15–24. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balanian R. Structural and functional alterations in cultured cells infected with cytocidal viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:40–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Smith A. E. Molecular biology of animal virus infection. Pharmacol Ther. 1980;9(3):311–355. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W., Holmes K. V. Replication of SV5 RNA and the effects of superinfection with poliovirus. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):442–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M., Holland J. J. Virus-induced interference in heterologously infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):22–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.22-28.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Lund H. Untranslated vesicular stomatitis virus messenger RNA after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Control of protein synthesis in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. I. mRNA discrimination by crude initiation factors. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):510–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.510-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. J., Lucas-Lenard J. the influence of the host cell on the inhibition of virus protein synthesis in cells double infected with vesicular stomatitis virus and mengovirus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Oct;50(2):293–307. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Sonenberg N., Shatkin A. J., Rose J. K., Leong K., Bergmann J. E., Gordon J., Baltimore D. Purification of a factor that restores translation of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA in extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):770–774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg H., Thomas A., Verbeek S., Kasperaitis M., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Shutoff of neuroblastoma cell protein synthesis by Semliki Forest virus: loss of ability of crude initiation factors to recognize early Semliki Forest virus and host mRNA's. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):728–736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.728-736.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]