Abstract
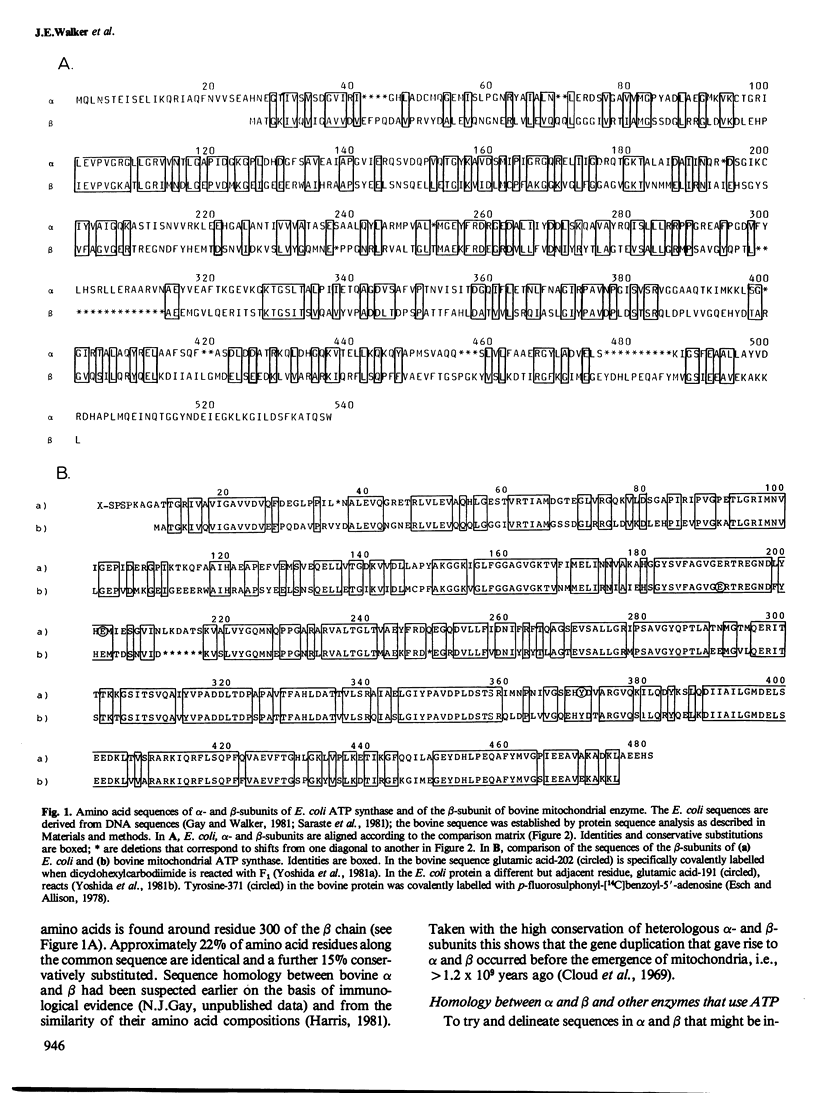
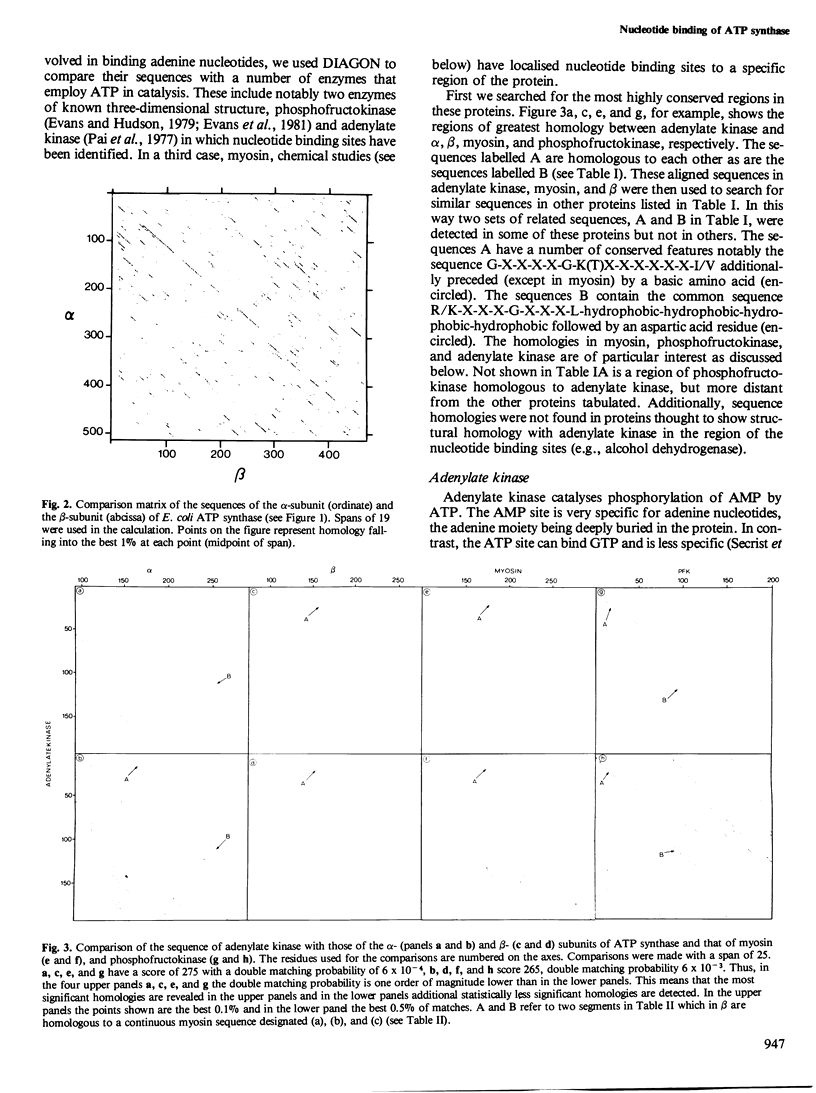
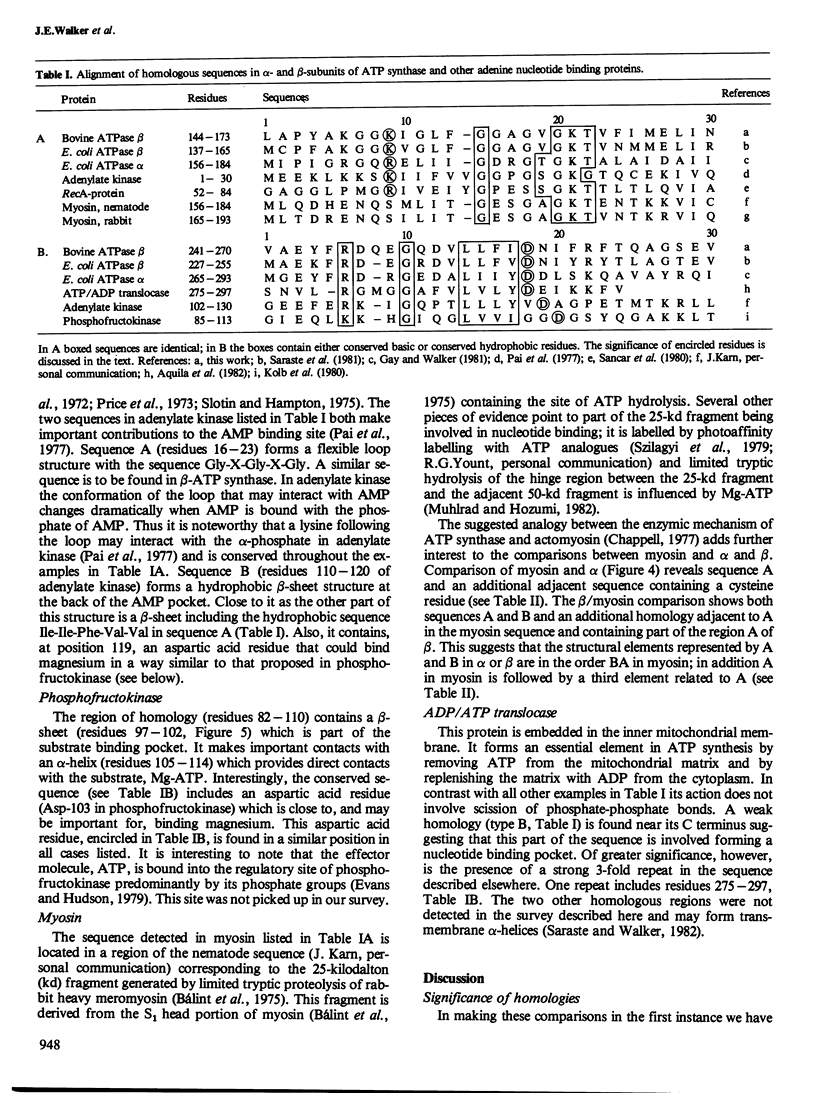
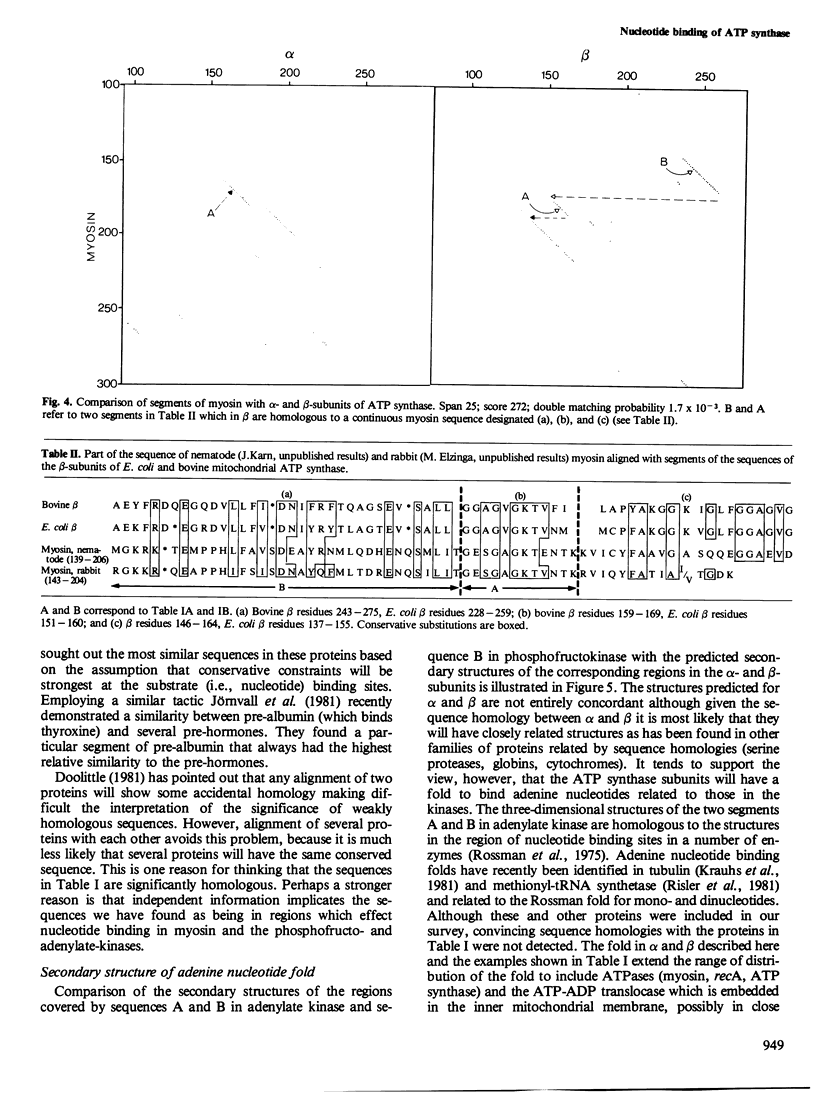
The alpha- and beta-subunits of membrane-bound ATP synthase complex bind ATP and ADP: beta contributes to catalytic sites, and alpha may be involved in regulation of ATP synthase activity. The sequences of beta-subunits are highly conserved in Escherichia coli and bovine mitochondria. Also alpha and beta are weakly homologous to each other throughout most of their amino acid sequences, suggesting that they have common functions in catalysis. Related sequences in both alpha and beta and in other enzymes that bind ATP or ADP in catalysis, notably myosin, phosphofructokinase, and adenylate kinase, help to identify regions contributing to an adenine nucleotide binding fold in both ATP synthase subunits.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aquila H., Misra D., Eulitz M., Klingenberg M. Complete amino acid sequence of the ADP/ATP carrier from beef heart mitochondria. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Mar;363(3):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beechey R. B., Hubbard S. A., Linnett P. E., Mitchell A. D., Munn E. A. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of adenosine triphosphatase from submitochondrial particles. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):533–537. doi: 10.1042/bj1480533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragg P. D., Hou C. Subunit composition, function, and spatial arrangement in the Ca2+-and Mg2+-activated adenosine triphosphatases of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock C. J., Walker J. E. Superoxide dismutase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Complete amino acid sequence of a manganese enzyme. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2873–2882. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Sréter F. A., Wolf I., Nagy B., Gergely J. The substructure of heavy meromyosin. The effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on the tryptic fragmentation of heavy meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6168–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Pedersen P. L. Adenosine triphosphatase from rat liver mitochondria. I. Purification, homogeneity, and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):4987–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloud P. E., Licari G. R., Wright L. A., Troxel B. W. Proterozoic eucaryotes from eastern california. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):623–630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Nalin C. M. Adenine nucleotide binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Evidence for three exchangeable sites that are distinct from three noncatalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2874–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L. The mechanism and regulation of ATP synthesis by F1-ATPases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:681–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Gibson F., Cox G. B. Membrane adenosine triphosphatases of prokaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:103–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutsa V. L., Kozlov I. A., Milgrom Y. M., Shabarova Z. A., Sokolova N. I. An active-site-directed adenosine triphosphate analogue binds to the beta-subunits of factor F1 mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase with its triphosphate moiety. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):617–619. doi: 10.1042/bj1820617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D. ATP causes a large change in the conformation of the isolated alpha subunit of Escherichia coli F1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11857–11860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Allison W. S. Identification of a tyrosine residue at a nucleotide binding site in the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATPase with p-fluorosulfonyl[14C]-benzoyl-5'-adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6100–6106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. R., Farrants G. W., Hudson P. J. Phosphofructokinase: structure and control. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):53–62. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans P. R., Hudson P. J. Structure and control of phosphofructokinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):500–504. doi: 10.1038/279500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., Lloyd W. J., Lyons M. H., Radda G. K. The mitochondrial ATPase. Evidence for a single essential tyrosine residue. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):117–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the genes for the membrane proteins, and the delta subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3919–3926. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the region encoding the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2187–2194. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S. Cooperatively between catalytic sites in the mechanism of action of beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3728–3734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton A., Slotin L. A. Inactivation of rabbit, pig, and carp adenylate kinases by N6-o- and p-fluorobenzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5438–5444. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A. The coupling ATPase complex: an evolutionary view. Biosystems. 1981;14(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(81)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A. The interactions of coupling ATPases with nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 10;463(3-4):245–273. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Carlström A., Pettersson T., Jacobsson B., Persson M., Mutt V. Structural homologies between prealbumin, gastrointestinal prohormones and other proteins. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):261–263. doi: 10.1038/291261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayalar C., Rosing J., Boyer P. D. An alternating site sequence for oxidative phosphorylation suggested by measurement of substrate binding patterns and exchange reaction inhibitions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2486–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Penefsky H. S. The subunit structure of beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Physical and chemical properties of isolated subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6624–6630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb E., Hudson P. J., Harris J. I. Phosphofructokinase: complete amino-acid sequence of the enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):587–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauhs E., Little M., Kempf T., Hofer-Warbinek R., Ade W., Ponstingl H. Complete amino acid sequence of beta-tubulin from porcine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4156–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebbers E. T., Larrinua I. M., McIntosh L., Bogorad L. The maize chloroplast genes for the beta and epsilon subunits of the photosynthetic coupling factor CF1 are fused. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4985–5002. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka I., Watanabe T., Tonomura Y. Reaction mechanism of the ATPase activity of mitochondrial F1 studied by using a fluorescent ATP analog, 2'-(5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1-sulfonyl) amino-2'-deoxyATP: its striking resemblance to that of myosin ATPase. J Biochem. 1981 Oct;90(4):967–989. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad A., Hozumi T. Tryptic digestion as a probe of myosin S-1 conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):958–962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Sachsenheimer W., Schirmer R. H., Schulz G. E. Substrate positions and induced-fit in crystalline adenylate kinase. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. C., Reed G. H., Cohn M. Magnetic resonance studies of substrate and inhibitor binding to porcine muscle adenylate kinase. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3322–3327. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risler J. L., Zelwer C., Brunie S. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase shows the nucleotide binding fold observed in dehydrogenases. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):384–386. doi: 10.1038/292384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Gay N. J., Eberle A., Runswick M. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the genes for the gamma, beta, and epsilon subunits of Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5287–5296. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Walker J. E. Internal sequence repeats and the path of polypeptide in mitochondrial ADP/ATP translocase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 2;144(2):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80648-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrist J. A., 3rd, Barrio J. R., Leonard N. J., Weber G. Fluorescent modification of adenosine-containing coenzymes. Biological activities and spectroscopic properties. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3499–3506. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C., Kemp A., van der Kraan I., Muller J. L., Roveri O. A., Verschoor G. J., Wagenvoord R. J., Wielders J. P. The ATP-and ADP-binding sites in mitochondrial coupling factor F1 and their possible role in oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 1;103(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi L., Balint M., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Photoaffinity labelling with an ATP analog of the N-terminal peptide of myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):936–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoord R. J., Kemp A., Slater E. C. The number and localisation of adenine nucleotide-binding sites in beef-heart mitochondrial ATPase (F1) determined by photolabelling with 8-azido-ATP and 8-azido-ADP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 3;593(2):204–211. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Auffret A. D., Carne A., Gurnett A., Hanisch P., Hill D., Saraste M. Solid-phase sequence analysis of polypeptides eluted from polyacrylamide gels. An aid to interpretation of DNA sequences exemplified by the Escherichia coli unc operon and bacteriophage lambda. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Poser J. W., Allison W. S., Esch F. S. Identification of an essential glutamic acid residue in the beta subunit of the adenosine triphosphatase from the thermophilic bacterium PS3. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


