Abstract
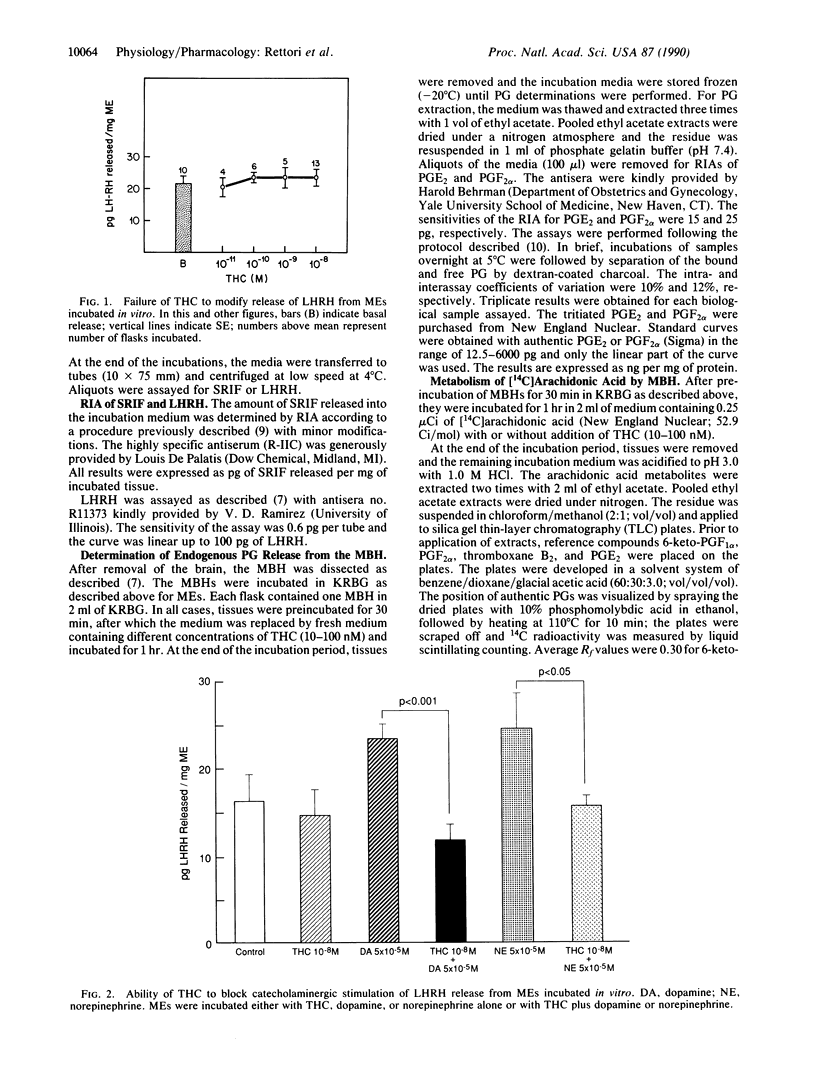
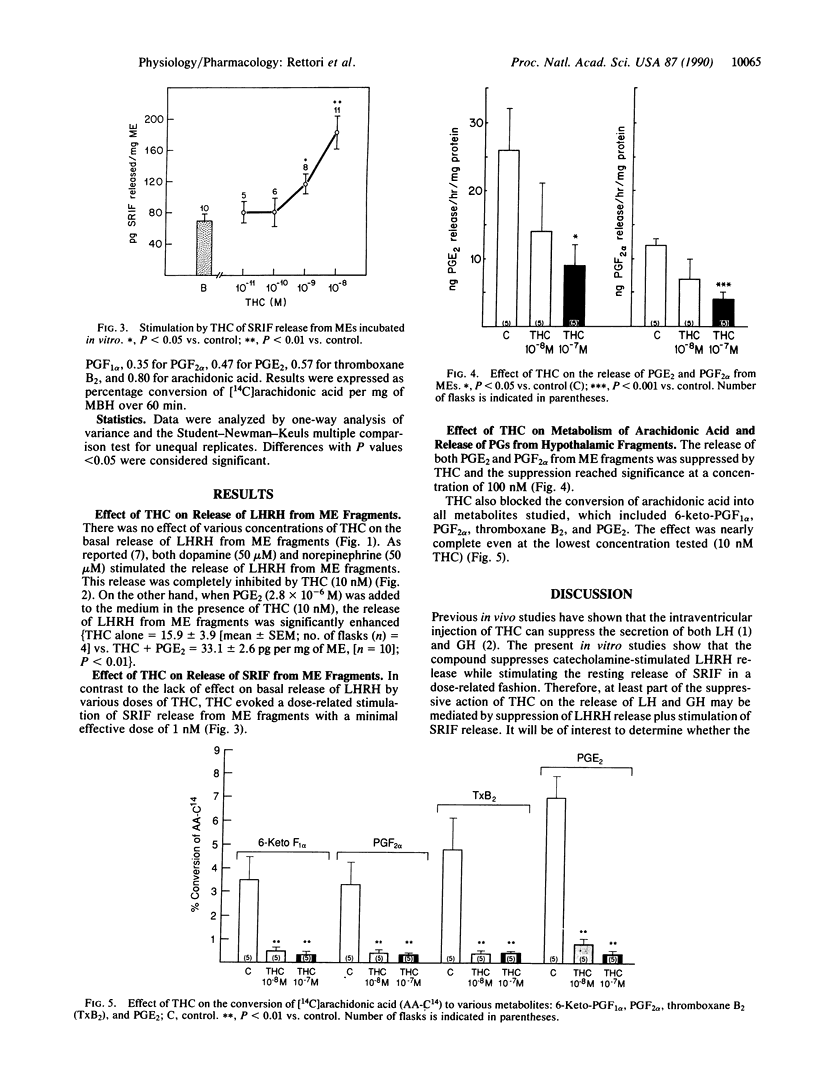
Previous in vivo studies have shown that delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal active ingredient in marijuana, can suppress both luteinizing hormone (LH) and growth hormone (GH) secretion after its injection into the third ventricle of conscious male rats. The present studies were designed to determine the mechanism of these effects. Various doses of THC were incubated with either stalk median eminence fragments (MEs) or mediobasal hypothalamic (MBH) fragments in vitro. Although THC (10 nM) did not alter basal release of LH-releasing hormone (LHRH) from MEs in vitro, it completely blocked the stimulatory action of dopamine or norepinephrine on LHRH release. The effective doses to block LHRH release were associated with a blockade of synthesis and release of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) from MBH in vitro. In contrast to the suppressive effect of THC on LHRH release, somatostatin release from MEs was enhanced in a dose-related manner with a minimal effective dose of 1 nM. Since PGE2 suppresses somatostatin release, this enhancement may also be related to the suppressive effect of THC on PGE2 synthesis and release. We speculate that these actions are mediated by the recently discovered THC receptors in the tissue. The results indicate that the suppressive effect of THC on LH release is mediated by a blockade of LHRH release, whereas the suppressive effect of the compound on growth hormone release is mediated, at least in part, by a stimulation of somatostatin release.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguila M. C., McCann S. M. Stimulation of somatostatin release from median eminence tissue incubated in vitro by taurine and related amino acids. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1158–1162. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupar I. M., Taylor D. A. Alteration in the level of endogenous hypothalamic prostaglandins induced by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):115–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devane W. A., Dysarz F. A., 3rd, Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Howlett A. C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):605–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eskay R. L., Warberg J., Mical R. S., Porter J. C. Prostaglandin E2-induced release of LHRH into hypophysial portal blood(1). Endocrinology. 1975 Oct;97(4):816–824. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-4-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno M. F., Chaud M., Borda E. S., Lazzari M., Gimeno A. L. Does hypoxia selectively stimulate the generation of prostaglandin E1 by the isolated rat uterus? Prostaglandins Med. 1981 Nov;7(5):375–388. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(81)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Lynn A. B., Little M. D., Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., de Costa B. R., Rice K. C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Harms P. G., McCann S. M. Effect of third ventricular injections of prostaglandins (PG's) on gonadotropin release in conscious free moving male rats. Prostaglandins. 1974 Dec 25;8(6):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Negro-Vilar A., Arimura A., McCann S. M. On the hypothalamic mechanism by which prostaglandin E2 stimulates growth hormone release. In vivo and in vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology. 1980 Jul;31(1):1–7. doi: 10.1159/000123042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Negro-Vilar A., McCann S. M. Release of prostaglandin Es by hypothalamic tissue: evidence for their involvement in catecholamine-induced luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release. Endocrinology. 1979 Mar;104(3):617–624. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-3-617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Wheaton J. E., McCann S. M. Prostaglandin E2-induced release of luteinizing hormone-releasing factor (LRF). Neuroendocrinology. 1975;17(3):283–287. doi: 10.1159/000122364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettori V., Wenger T., Snyder G., Dalterio S., McCann S. M. Hypothalamic action of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol to inhibit the release of prolactin and growth hormone in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Jun;47(6):498–503. doi: 10.1159/000124961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steger R. W., DePaolo L., Asch R. H., Silverman A. Y. Interactions of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with hypothalamic neurotransmitters controlling luteinizing hormone and prolactin release. Neuroendocrinology. 1983 Nov;37(5):361–370. doi: 10.1159/000123576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viggiano M., Franchi A. M., Zicari J. L., Rettori V., Gimeno M. A., Kozlowski G. P., Gimeno A. L. The involvement of oxytocin in ovulation and in the outputs of cyclo-oxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase products from isolated rat ovaries. Prostaglandins. 1989 Mar;37(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(89)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger T., Rettori V., Snyder G. D., Dalterio S., McCann S. M. Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the hypothalamic-pituitary control of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Dec;46(6):488–493. doi: 10.1159/000124870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



