Abstract
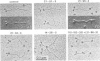
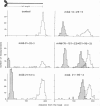
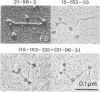
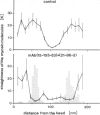
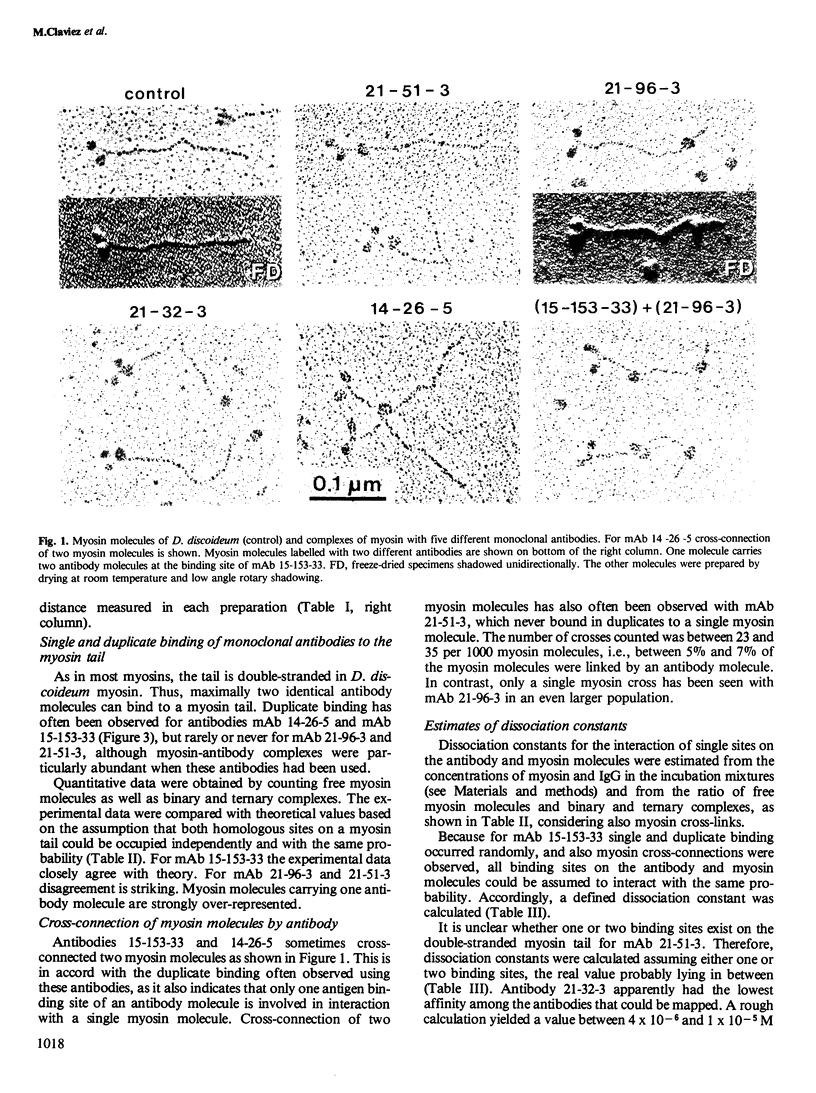
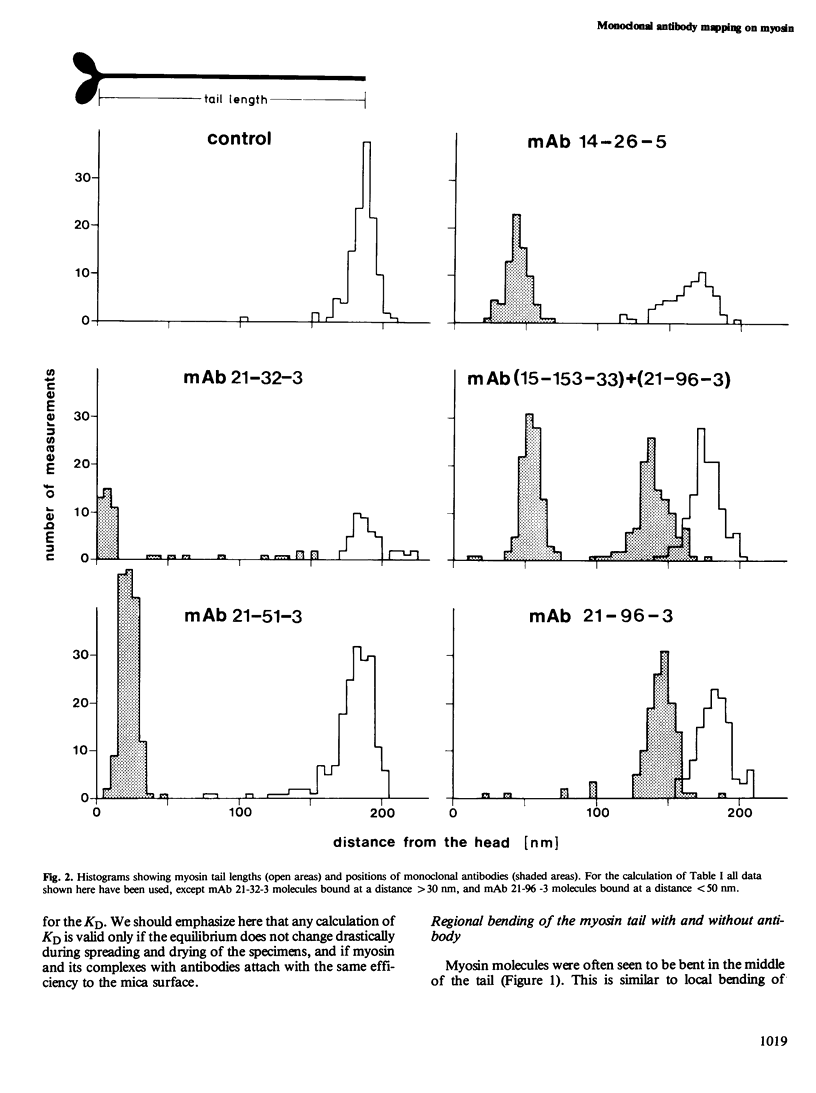
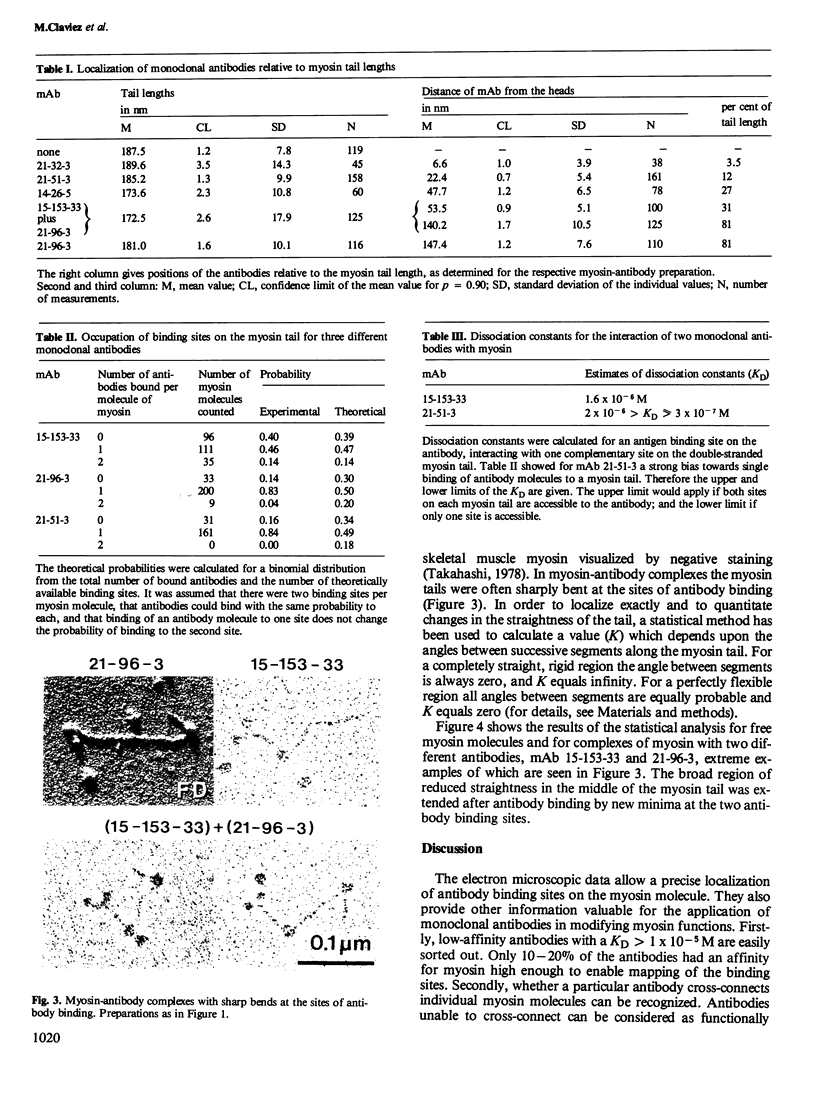
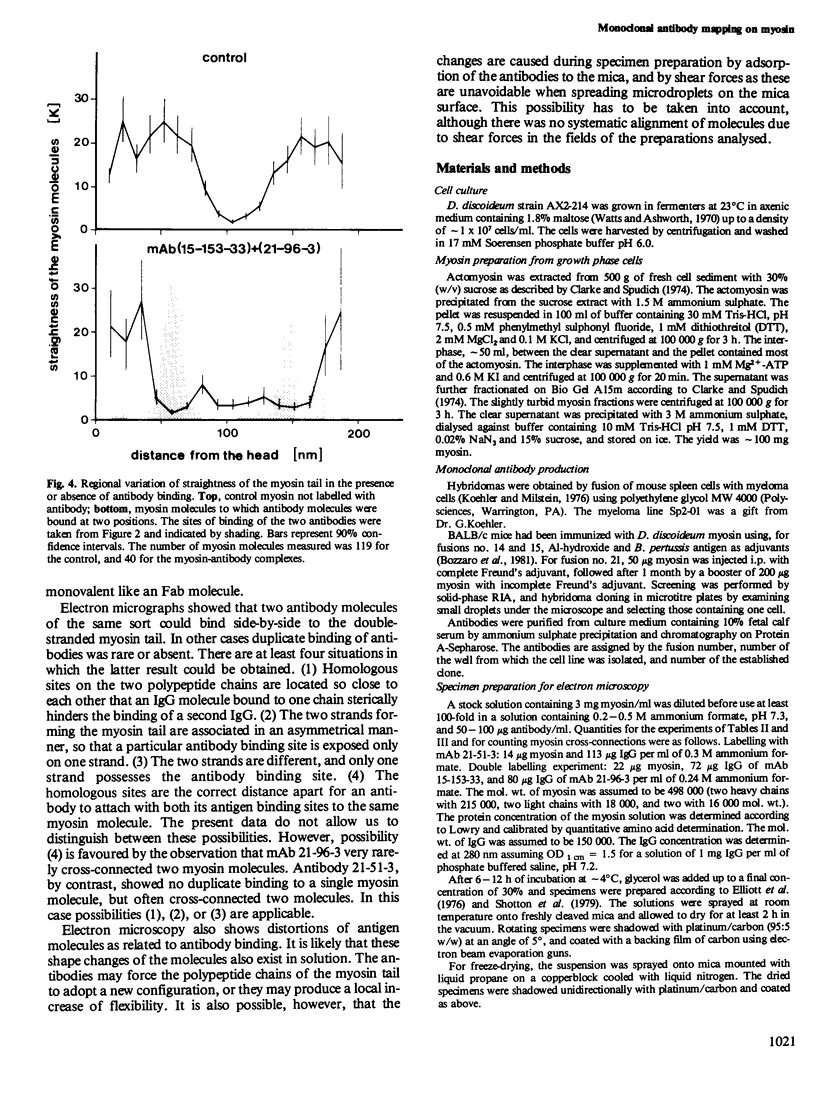
The binding sites of five monoclonal antibodies against myosin of Dictyostelium discoideum have been mapped. These antibodies bind to the tail region of the myosin molecule. By rotary shadowing, images of myosin-antibody complexes were obtained in which the mean distance of the midpoint of an antibody molecule from the myosin heads was localized with a precision better than 2 nm (90% confidence limit). Other quantitative data extracted from electron micrographs provided information on the stoichiometry of antibody-myosin interaction. Certain antibodies interacted with myosin molecules only at a ratio of 1:1. Other antibodies formed complexes of two molecules bound to homologous sites on a double-stranded myosin tail. Affinities were estimated and the abilities of different antibodies to cross-connect two myosin molecules were evaluated.
Keywords: myosin, monoclonal antibodies, dissociation constants of antigen-antibody complexes, Dictyostelium
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bozzaro S., Tsugita A., Janku M., Monok G., Opatz K., Gerisch G. Characterization of a purified cell surface glycoprotein as a contact site in Polysphondylium pallidum. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jul;134(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M., Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. Isolation and characterization of myosin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):209–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott A., Offer G., Burridge K. Electron microscopy of myosin molecules from muscle and non-muscle sources. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Mar 30;193(1110):45–53. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. R., Smith E., Williams K. L. An extracellular chemical signal controlling phototactic behavior by D. discoideum slugs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):799–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G. Chemotaxis in Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:535–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczmarski E. R., Spudich J. A. Regulation of myosin self-assembly: phosphorylation of Dictyostelium heavy chain inhibits formation of thick filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7292–7296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Böhme R., Rahmsdorf H. J. Regulation of phosphorylation of myosin heavy chain during the chemotactic response of Dictyostelium cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Stafford W. F., Porter M. E. Characterization of a second myosin from Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4798–4808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. Topography of the myosin molecule as visualized by an improved negative staining method. J Biochem. 1978 Mar;83(3):905–908. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts D. J., Ashworth J. M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1190171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick U., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Cyclic-AMP stimulated calcium influx into aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Jan;2(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. Signal transduction in the cellular slime molds. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Apr;26(1-2):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]