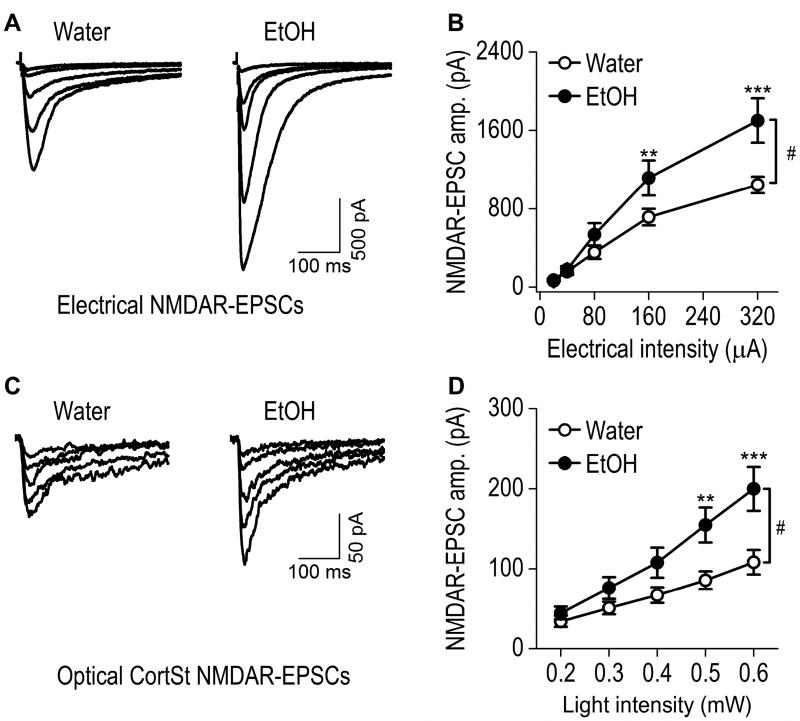
Fig. 3. Excessive alcohol intake increases corticostriatal NMDAR-mediated EPSCs within the rat DMS.
(A) Representative traces of NMDAR-EPSCs evoked by the indicated electrical stimulation intensities in slices from alcohol-drinking rats and water controls. (B) Input-output curves of electrical NMDAR-EPSCs in DMS neurons from the indicated study groups. #p < 0.05; Two-way RM-ANOVA. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs. Water at the same stimulation intensity, post hoc SNK tests. n = 15 neurons from 7 rats for Water and 13 neurons from 7 rats for EtOH. (C) Sample traces of CortSt NMDAR-EPSCs evoked by the indicated optical stimulation intensities in slices from water controls and alcohol-drinking rats. (D) Input-output curves of CortSt NMDAR-EPSCs in DMS neurons from the indicated study groups. #p < 0.05; Two-way RM-ANOVA. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 versus Water at the same stimulation intensity; post hoc SNK tests. n = 11 neurons from 7 rats for Water and 10 neurons from 6 rats for EtOH.