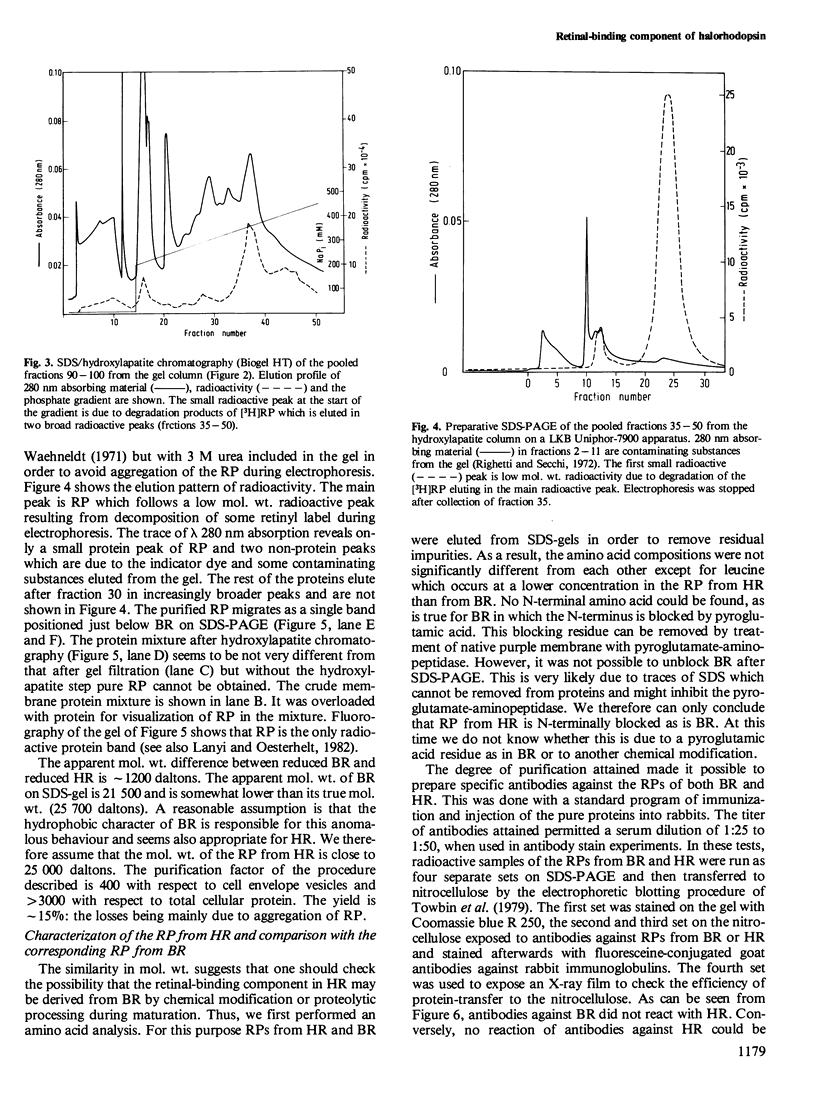
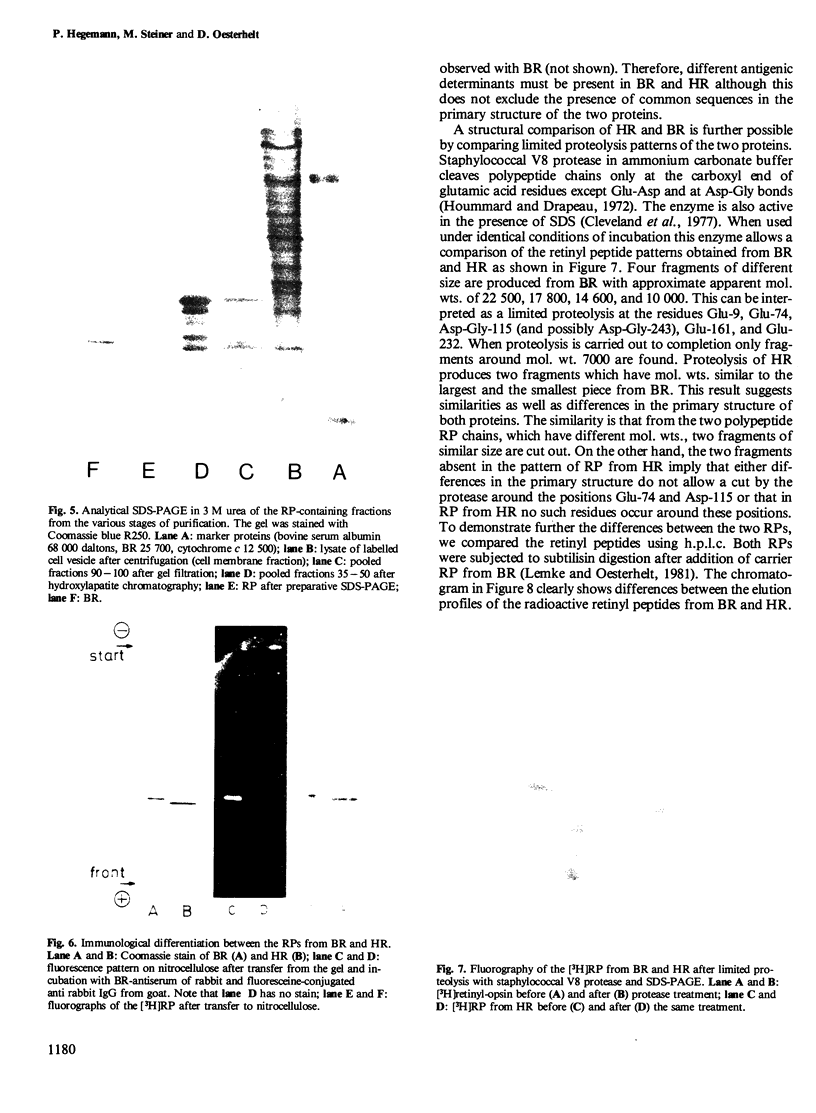
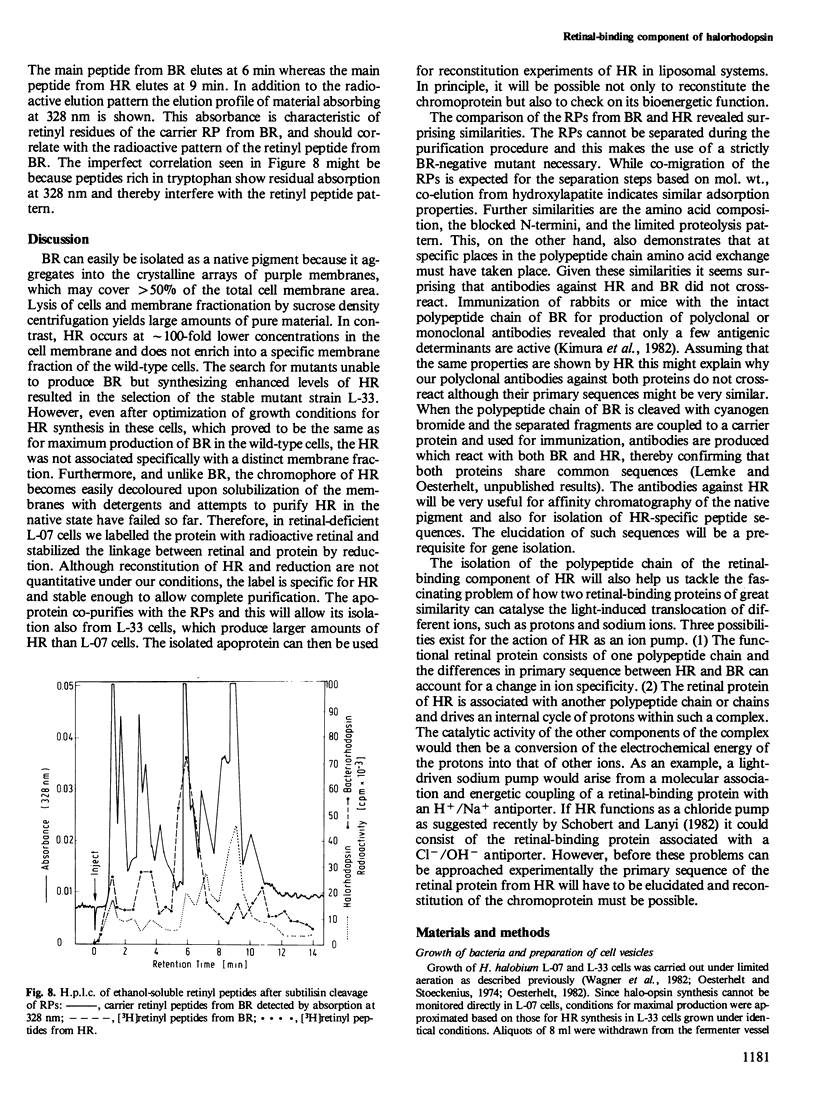
Abstract
Halorhodopsin (HR) was reconstituted in cell vesicles prepared from Halobacterium halobium strain L-07 by addition of tritium-labelled retinal and subsequently reduced with cyanoborohydride. Lysis of the labelled vesicles in water and dissolution of the cell membranes with 4% SDS allowed the purification of the retinyl protein (RP) by a 3-step procedure. Gel filtration on AcA-44 ultrogel was followed by chromatography on hydroxylapatite and preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. This procedure yielded material which migrated as a single band of an apparent mol. wt. of 25 000 on analytical SDS-polyacrylamide gels. The purification was ˜400-fold with an overall yield of ˜15%. Not only the mol. wts. but also the amino acid compositions of the RPs from bacteriorhodopsin (BR) and HR are very similar. Polyclonal antibodies against BR and HR did not, however, crossreact. When the two RPs were partially digested with staphylococcal V8 protease the proteolytic pattern of the retinyl peptides was similar, but not identical: two extra peptides are present in BR. The same kind of differences were found in the h.p.l.c. elution profiles of retinyl peptides produced by subtilisin digestion. Therefore, the two proteins must be different gene products and not modification products of one and the same protein.
Keywords: halorhodopsin, retinyl protein, light-driven ion pump, halobacteria, archaebacteria
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. V., Lanyi J. K. Proton movements in response to a light-driven electrogenic pump for sodium ions in Halobacterium halobium membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10986–10994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Konigsberg W. A micromethod for complete removal of dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Bayley H., Liao M. J., London E., Khorana H. G. Refolding of an integral membrane protein. Denaturation, renaturation, and reconstitution of intact bacteriorhodopsin and two proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3802–3809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Mason T. L., Khorana H. G. Immunological probes for bacteriorhodopsin. Identification of three distinct antigenic sites on the cytoplasmic surface. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2859–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Oesterhelt D. Identification of the retinal-binding protein in halorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2674–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Weber H. J. Spectrophotometric identification of the pigment associated with light-driven primary sodium translocation in Halobacterium halobium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke H. D., Oesterhelt D. Lysine 216 is a binding site of the retinyl moiety in bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):255–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley E. V., MacDonald R. E. A second mechanism for sodium extrusion in Halobacterium halobium: a light-driven sodium pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. E., Greene R. V., Clark R. D., Lindley E. V. Characterization of the light-driven sodium pump of Halobacterium halobium. Consequences of sodium efflux as the primary light-driven event. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11831–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno-Yagi A., Mukohata Y. ATP synthesis linked to light-dependent proton uptake in a rad mutant strain of Halobacterium lacking bacteriorhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jan;199(1):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno-Yagi A., Mukohata Y. Two possible roles of bacteriorhodopsin; a comparative study of strains of Halobacterium halobium differing in pigmentation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N. Hydroxylapatite chromatography of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. A new method for the separation of polypeptide subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5194–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Schuhmann L. Reconstitution of bacteriorhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):262–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobert B., Lanyi J. K. Halorhodopsin is a light-driven chloride pump. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10306–10313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waehneldt T. V. Preparative isolation of membrane proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of ionic detergent (SDS): proteins of rat brain myelin. Anal Biochem. 1971 Sep;43(1):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]