Abstract
Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) is a serine/threonine protein kinase ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells. It was first identified in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome as a tumor suppressor gene. Whether endothelial LKB1 regulates angiogenesis and tumor growth is unknown. In this study, we generated endothelial cell-specific LKB1-knockout (LKB1endo−/−) mice by crossbreeding vascular endothelial-cadherin-Cre mice with LKB1flox/flox mice. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) level was highly co-stained in endothelial cells but not macrophages in LKB1endo−/− mice. Consistently, LKB1endo−/− mouse tissues including the lung, skin, kidney, and liver showed increased vascular permeability. Tumors implanted in LKB1endo−/− mice but not macrophage-specific LKB1-knockout mice grew faster and showed enhanced vascular permeability and increased angiogenesis as compared with those implanted in wild-type mice. Injection of VEGF-neutralizing antibody but not the isotype-matched control antibody decreased endothelial-cell angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, LKB1 deletion enhanced mouse retinal and cell angiogenesis, and knockdown of VEGF by small-interfering RNA decreased endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Re-expression of LKB1 or knockdown of VEGF receptor 2 decreased the over-proliferation and -migration observed in LKB1endo−/− cells. Mechanistically, LKB1 could bind to the VEGF transcription factor, specificity protein 1 (Sp1), which then inhibited the binding of Sp1 to the VEGF promoter to reduce VEGF expression. Endothelial LKB1 may regulate endothelial angiogenesis and tumor growth by modulating Sp1-mediated VEGF expression.
Keywords: LKB1, VEGF, Sp1, angiogenesis, tumor growth
INTRODUCTION
Angiogenesis is the physiological process whereby new blood vessels are formed from preexisting vessels. It is crucial for growth, development, and postnatal organ repair. Angiogenesis also contributes to several pathological conditions, including cancer, by supplying nutrients and oxygen to maintain aggressive growth.1
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling plays an essential role in physiological and pathological angiogenesis.2 The VEGF family consists of VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D and placenta growth factor. VEGF-A, first described as a vascular permeability factor,3 binds to its cell-surface receptors including VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR2 and neuropilin-1/2 on endothelial cells (ECs). This binding dimerizes and authophosphorylates the receptor and starts the signaling cascades required for EC proliferation and migration.4 VEGF-A plays a critical role in angiogenesis; VEGF-A–knockout mice are lethal embryonically because of abnormal vascular development.5 Although VEGF-A (hereafter VEGF) is well known to regulate angiogenesis, how it is regulated remains poorly understood.
VEGF expression is regulated at many levels including transcription, translation and mRNA stability.6,7 Under various conditions, VEGF is upregulated by transcriptional factors such as specificity protein 1 (Sp1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1.8 Sp1 has 785 amino acids and regulates VEGF expression by binding to GC-rich motifs within the promoter.9 Sp1 downregulation reduces tumor vascularization,8 so it may play an anti-tumor role. Given the important roles of VEGF in angiogenesis, a complete understanding of its regulation is significant to elucidate the process of angiogenesis.
Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) is a serine/threonine protein kinase and ubiquitously expressed in mammalian cells. It was first identified in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome as a tumor suppressor.10,11 LKB1 can phosphorylate the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) family of proteins, including 14 members, and play an important role in energy metabolism and cell polarity.12,13 Many LKB1-knockout mouse models have been generated to further elucidate the in vivo roles.14 We previously showed that LKB1 overexpression inhibits endothelial tube formation,15 which suggests that LKB1 is anti-angiogenic. However, the detailed mechanism for this formation is unknown. In this study, we used endothelium-specific LKB1-knockout mice (LKB1endo−/−)16 to show that LKB1 deletion in ECs promoted tumor growth by increasing tumor angiogenesis.
RESULTS
Increased VEGF levels and permeability after LKB1 deletion
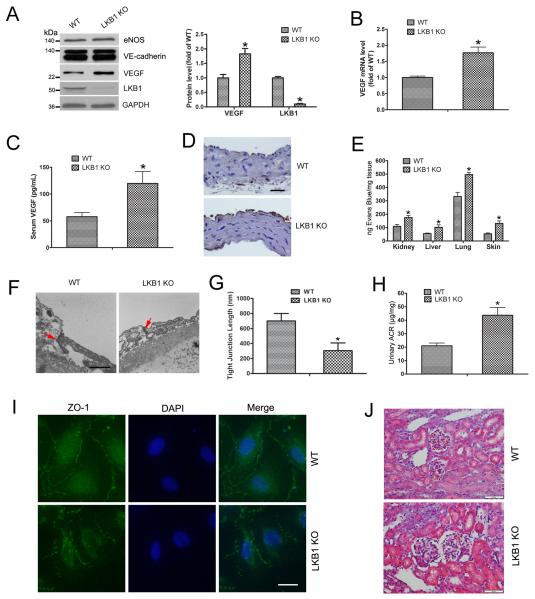
Because LKB1-deficient mice exhibit abnormal VEGF expression,17 we determined whether LKB1 deletion in the endothelium would affect VEGF levels. Primary lung ECs from WT and LKB1endo−/− mice were isolated and cultured. Levels of two important endothelial markers, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and vascular endothelial-cadherin (VE-cadherin), were checked, with no change between WT and LKB1endo−/− cells (Fig. 1A), which suggests no phenotypic changes in cells. VEGF protein and mRNA levels were increased in LKB1endo−/− ECs (Fig. 1A and 1B). Furthermore, serum VEGF levels were increased in LKB1endo−/− mice (Fig. 1C) and the mice showed more VEGF-positive staining in endothelium on immunohistochemistry (Fig. 1D). Hence, endothelial LKB1 deletion increased VEGF levels in ECs.
Figure 1. Increased VEGF levels and endothelial permeability after LKB1 deletion.
A, Western blot analysis of detect VEGF, eNOS and VE-cadherin expression. Quantification of VEGF and LKB1 levels in wild-type (WT) and LKB1endo−/− (LKB1 KO) endothelial cells (ECs) (n = 5). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT. B, RT-PCR analysis of VEGF mRNA levels in lung ECs. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). C, ELISA of serum VEGF levels in ECs. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). D, Immunohistochemical staining for VEGF in aortas. Bar = 50 μm. E, Evans blue dye leakage in mouse organs. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). F, Electron micrographs of the tight junctions between ECs from mouse aortas. Arrows point to the tight junctions. Bar = 500 nm. G, Tight junction lengths in ECs (n=10 junctions each from WT and LKB1endo−/− ECs). *, P < 0.05, compared with WT. H, ELISA of urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR). *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). I, Mouse ECs were stained with ZO-1 to analyze permeability. Bar = 20 μm. J, H&E staining in mouse kidneys. Bar = 50 μm. Data are mean ± SE.
VEGF is also a vascular permeability factor,18 so we evaluated the effect of LKB1 deletion on vascular permeability. To quantify vascular leakage, mice were injected with Evans blue. The amount of dye leaked was greater in tissues including the kidney, liver, lung, and skin from LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 1E), which suggests that endothelial LKB1 deletion results in increased vascular permeability. As well, aortas from WT and LKB1endo−/− mice were examined to identify possible ultrastructural changes. Tight junctions between LKB1endo−/− ECs were significantly smaller and wider than those between WT cells (Fig. 1F). The mean length of tight junctions in ECs from LKB1endo−/− mice was 52% of that from WT mice (Fig. 1G), which further confirmed the phenotype of hyperpermeability in LKB1endo−/− mice.
Microalbuminuria is a marker of endothelial hyperpermeability and dysfunction,19 and it can be determined by measuring the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR). Urinary ACR was significantly higher in LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 1H), so LKB1endo−/− mice exhibit microalbuminuria and hyperpermeability. To show the architecture of cell–cell contact, we used ZO-1 immunostaining of WT and LKB1endo−/− ECs. LKB1endo−/− cells showed increased permeability (Fig. 1I). The morphological structure of glomerulus from WT and LKB1endo−/− mice analyzed by H&E staining showed LKB1endo−/− mice with glomerular enlargement in the kidney (Fig. 1J and Supplementary Fig. 1). Taken together, LKB1 deletion increases VEGF level and permeability.
Tumors implanted in LKB1endo−/− mice grew fast and showed microvascular permeability
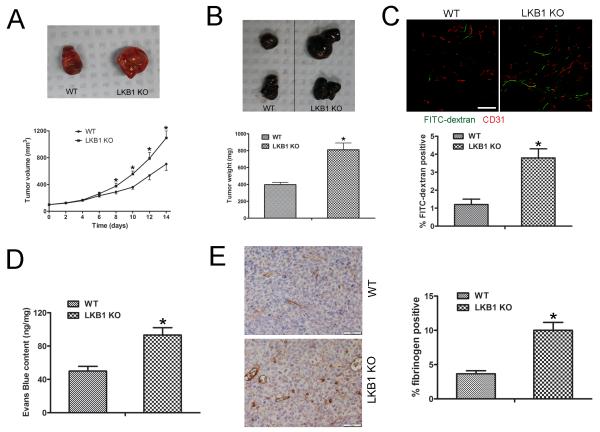
To address whether the loss of endothelial LKB1 affects tumor growth and vascular permeability, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) or B16F10 melanoma cells were implanted in the backs of WT and LKB1endo−/− mice, then tumor growth was monitored for 14 days, and tumors were excised; LLC tumors grew faster in LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 2A). Similarly, B16F10 melanoma tumors grew faster in LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 2B). To detect the vascular permeability in LLC tumors, FITC-labeled dextran was injected: the area of extravasated dextran was increased in LLC tumors from LKB1endo−/− mice (Fig. 2C). In addition, Evans blue was injected into mice, and samples were quantified spectrophotometrically. Evans-blue content was greater for LLC tumors from LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 2D). Tumor permeability can be quantified by using macromolecular tracers, such as fibrin/fibrinogen staining.20 Fibrinogen staining was greater for LLC tumors from LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 2E). Hence, tumors implanted in LKB1endo−/− mice feature increased growth and microvascular permeability.
Figure 2. Tumors implanted into LKB1endo−/− mice show increased growth and microvascular permeability.
A, LLC cells (106) were implanted subcutaneously into the lower backs of 6- to 8-week-old male WT or LKB1endo−/− mice. Tumors were allowed to grow for 14 days. P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 8). Representative images of tumors. B, B16F10 melanoma cells (106) were implanted subcutaneously into the backs of WT or LKB1endo−/− mice for 14 days. Representative images are shown and the weight of tumors was quantified. P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 8). C, LLC tumor-bearing mice were injected with 70-kDa FITC-conjugated dextran to visualize vessel permeability, then tumor sections were immunostained for CD31 (red); FITC-conjugated dextran appears in green. Bar = 50 μm. Blood vessel permeability was analyzed by area of extravasated dextran. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). D, Vascular permeability in implanted LLC tumors measured by Evans blue extravasation (30 mg/kg intravenously, 30 min) as an index of albumin leakage. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). E, Frozen sections (5 μm) of LLC tumors were stained with fibrinogen and quantified. Bar = 50 μm. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). Data are mean ± SE.
To determine which cell type-derived VEGF contributes to the different tumor growth in WT and LKB1endo−/− mice, we stained LLC tumors from WT and LKB1endo−/− mice for VEGF and found no difference in VEGF staining between the mice (Supplementary Fig. 2A). Then we detected EC- or macrophage-derived VEGF levels by co-staining CD31 or CD68 and VEGF. CD31 and VEGF but not CD68 and VEGF co-staining was significantly increased in tumors from LKB1endo−/− mice (Supplementary Fig. 2B and 2C), which suggests that EC-derived VEGF contributes to the different tumor growth in WT and LKB1endo−/− mice. Moreover, we implanted LLC cells into the backs of WT and macrophage-specific LKB1 knockout (LKB1macro−/−) mice for 14 days. As expected, LLC tumors from WT and LKB1macro−/− mice did not differ in size (Supplementary Fig. 2D), so macrophage-derived VEGF is unlikely the major factor for aberrant tumor growth observed in tumor-implanted LKB1endo−/− mice.
LLC tumors implanted into LKB1endo−/− mice show increased angiogenesis
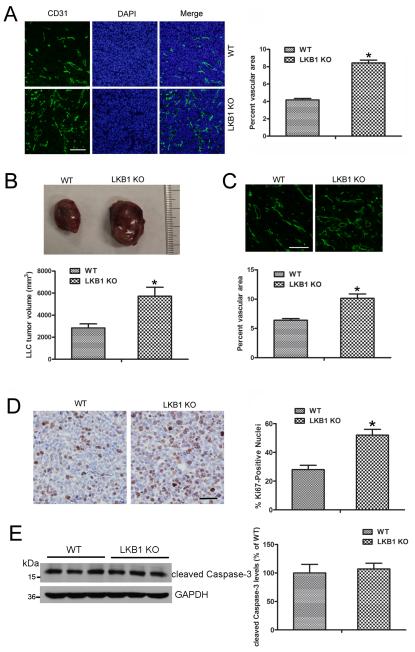
Tumor angiogenesis was evaluated with an antibody to the endothelial-specific marker CD31. The vasculature was more dense for LKB1endo−/− than WT LLC tumors (Fig. 3A). Quantification of CD31-positive areas suggested increased angiogenesis in LLC tumors from LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 3A). To evaluate the effect of endothelial LKB1 on tumor growth for a longer time, LLCs were implanted in WT and LKB1endo−/− mice. After 28 days, LLC tumors were still larger in LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 3B). CD31 staining revealed more vascularization in LKB1endo−/− than WT tumors (Fig. 3C). Then, we examined tumor cell proliferation with an antibody to Ki-67 antigen. Ki-67 staining was greater in tumors from LKB1endo−/− than WT mice (Fig. 3D). To detect apoptosis in tumors, we detected cleaved Caspase-3 level and found no significant difference in level between LKB1endo−/− and WT tumors (Fig. 3E), which suggests that endothelial LKB1 deletion did not affect tumor cell apoptosis. Hence, LKB1endo−/− tumors may grow faster due to increased angiogenesis.
Figure 3. Tumors implanted into LKB1endo−/− mice exhibited increased angiogenesis.
A, Frozen sections of 2-week LLC tumors were stained with CD31, and the vascular area in LLC tumors was quantified. Bar = 100 μm. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 6). B, LLC cells were implanted into WT or LKB1endo−/− mice. After 28 days, tumors were harvested and quantified. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 8). C, Frozen sections of 4-week LLC tumors were stained with CD31 and the vascular area was quantified. Bar = 100 μm. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 6). D, Representative Ki-67 immunohistochemical images. Bar = 50 μm. Ki-67–positive signals in LLC tumors were quantified. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). E, Western blot analysis of cleaved Caspase-3 level in LLC tumors (n=6). Data are mean ± SE.
Injection of the VEGF-neutralizing antibody decreases angiogenesis and tumor growth
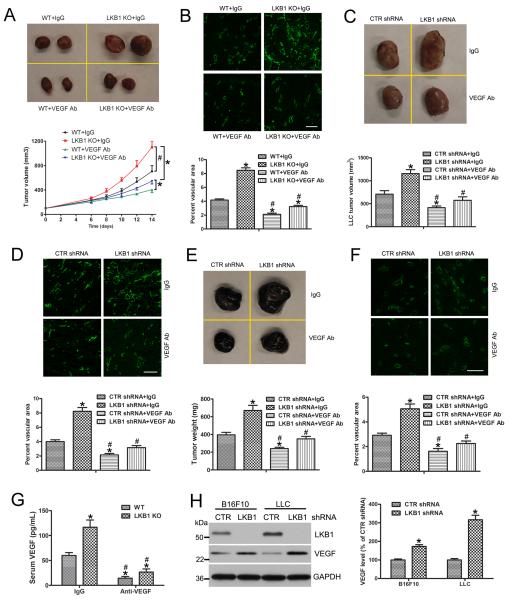
Because LKB1 knockout increased VEGF levels in the endothelium, we determined whether the VEGF-neutralizing antibody could affect tumor growth in LKB1endo−/− mice. Injection of the VEGF-neutralizing antibody decreased serum VEGF level (Fig. 4G) and tumor growth in WT and LKB1endo−/− mice (Fig. 4A); the IgG control antibody had no effect. Immunofluorescence with CD31 revealed that LKB1 deletion increased the vascular density of LLC tumors, and VEGF-neutralizing antibody treatment reduced the vascular density (Fig. 4B). Therefore, LKB1 inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth via a VEGF-mediated autocrine pathway.
Figure 4. Injection of the VEGF-neutralizing antibody decreases tumor growth.
A, WT or LKB1endo−/− mice were injected with the neutralizing monoclonal anti-VEGF antibody or an isotype-matched control intravenously at 100 μg twice weekly, starting on the day of LLC cell implantation. After 14 days, tumors were harvested and quantified (n = 8). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT + IgG. #, P< 0.05, compared with LKB1 KO + IgG. B, Representative immunofluorescence micrographs identifying blood vessels (CD31+) in LLC tumors. Bar = 100 μm. The vascular area in LLC tumors was quantified (n = 6). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT + IgG. #, P< 0.05, compared with LKB1endo−/− + IgG. LLCs (C) or B16F10 cells (E) were transfected with control (CTR) or LKB1 shRNA lentiviral particles to silence LKB1 then implantated into WT mice. At the same time, mice were injected with the neutralizing monoclonal anti-VEGF or control IgG antibody intravenously. After 14 days, tumors were harvested and quantified (n = 8). *, P< 0.05, compared with CTR shRNA + IgG. #, P< 0.05, compared with LKB1 shRNA + IgG. Frozen sections of tumors were stained with CD31, and the vascular area in LLC tumors (D) and B16F10 (F) was quantified (n = 6). Bar = 100 μm. *, P< 0.05, compared with CTR shRNA + IgG. #, P< 0.05, compared with LKB1 shRNA + IgG. G, ELISA of serum VEGF levels in WT and LKB1endo−/− mice after injection of anti-VEGF or control IgG antibody, (n = 6). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT + IgG. #, P< 0.05, compared with LKB1 KO + IgG. H, Western blot analysis of VEGF level after silencing LKB1 in LLC or B16F10 cells (n = 5). *, P< 0.05, compared with CTR shRNA. Data are mean ± SE.
To address whether tumor angiogenesis and growth were mediated by an LKB1/VEGF paracrine pathway, LLC and B16F10 cells were infected with control or LKB1 shRNA lentivirus to silence LKB1, then implanted into WT mice. At the same time, mice were intravenously injected with the neutralizing monoclonal anti-VEGF antibody or control antibody. LKB1 silencing in B16F10 or LLC cells resulted in VEGF overexpression (Fig. 4H) and enhanced tumor growth (Fig. 4C and 4E). However, injection with the VEGF-neutralizing antibody reduced LLC and B16F10 tumor growth (Fig. 4C and 4E). Immunofluorescence assay with CD31 revealed that LKB1 loss increased the vascular density of LLC and B16F10 tumors, and treatment with the VEGF-neutralizing antibody decreased the vascular density (Fig. 4D and 4F). Thus, LKB1/VEGF also regulates tumor angiogenesis and growth via a paracrine pathway.
Increased angiogenesis in LKB1-deficient endothelium
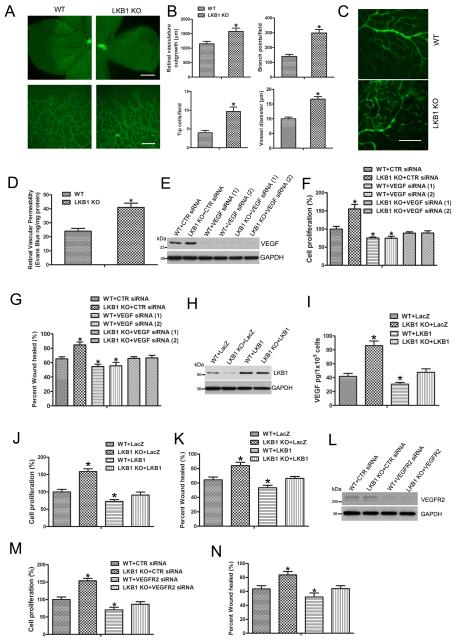
LKB1 deletion increased VEGF levels and permeability. Because vascular permeability contributes to the angiogenesis process in vivo,21 we assessed whether LKB1 deletion affects angiogenesis. The vascular system of the mouse retina provides a useful model to study angiogenesis.22 We examined the developing retinal vasculature of WT and LKB1endo−/− mice and found accelerated retinal vasculature outgrowth at P6 in LKB1endo−/− pups (Fig. 5A). In addition, LKB1endo−/− retinas had more branch points, filopodia-containing tip cells and dilated vessels than WT retinas (Fig. 5B). To detect retinal protein leakage, we injected 70-kDa FITC-dextran into mice via the tail vein. Protein leakage was increased in the retinas of LKB1endo−/− mice (Fig. 5C), which was further confirmed by Evans-blue content measurement (Fig. 5D). To test whether LKB1 regulates angiogenesis via VEGF, we silenced VEGF in WT and LKB1endo−/− ECs, then examined cell proliferation. The proliferation of LKB1-deficient cells was increased, and VEGF knockdown restored the proliferation of LKB1endo−/− cells to normal conditions (Fig. 5F). In addition, results from wound healing assay suggested that LKB1 deletion enhanced cell migration, which could be inhibited by VEGF silencing (Fig. 5G, Supplementary Fig. 3).
Figure 5. Increased endothelial angiogenesis with LKB1 deletion.
A, Mouse retinal vasculature observed by staining with fluorescein-isolectin B4 on postnatal day 6. Upper bar = 500 μm. Lower bar = 100 μm. B, Vascularization, branch points, tip cell numbers and vessel diameter. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). C, WT and LKB1endo−/− mice were injected with 70-kDa FITC-dextran via the tail vein and retinas were mounted on slides. Bar = 100 μm. D, Retinal vascular permeability measured by the Evans blue method. *, P < 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). E, Western blot analysis of VEGF level in ECs transfected with control (CTR) siRNA or two independent VEGF siRNA for 3 days. F, Cell proliferation assayed by ELISA measuring the rate of BrdU incorporation at 450 nm after VEGF was silenced. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT +CTR siRNA (n = 5). G, Cell migration analysis for 16 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT+CTR siRNA (n = 5). H, Western blot analysis of LKB1 level in mouse ECs transfected with LacZ or LKB1 plasmids for 2 days. (I) VEGF levels were measured from cell medium after transfection. Cell proliferation (J) and migration (K). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT +LacZ (n = 5). L, Western blot analysis of VEGFR2 in WT or LKB1endo−/− ECs transfected with CTR or VEGFR2 siRNA for 2 days. Cell proliferation (M) and migration (N). *, P< 0.05, compared with WT +CTR siRNA (n = 5). Data are mean ± SE.
To study the effect of acute knockdown of LKB1 on angiogenesis, HUVECs were transfected with control or LKB1 shRNA lentivirus to silence LKB1, then cell proliferation and migration was examined. Similar to LKB1-deficient lung ECs, LKB1 knockdown increased VEGF expression, cell proliferation and migration (Supplementary Fig. 4). To detect whether re-expression of LKB1 could rescue the phenotype in LKB1-deficient cells, LacZ or LKB1 plasmid was transfected into WT and LKB1endo−/− ECs, then cell proliferation and migration was examined. LKB1 deletion increased VEGF level released from ECs, and re-expression of LKB1 reduced VEGF level (Fig. 5I). As expected, re-expression of LKB1 decreased the over-proliferation and -migration observed in LKB1endo−/− cells (Fig. 5J and 5K).
To further confirm whether LKB1 regulation of endothelial proliferation and migration depends on VEGF, we transfected control or VEGFR2 siRNA into WT or LKB1endo−/− cells, then examined cell proliferation and migration. VEGFR2 knockdown rescued the phenotype of over-proliferation and -migration observed in LKB1endo−/− mice (Fig. 5M and 5N). Hence, LKB1 deficiency enhances angiogenic processes, including cell proliferation and migration, by increasing VEGF level.
LKB1 negatively regulates VEGF expression
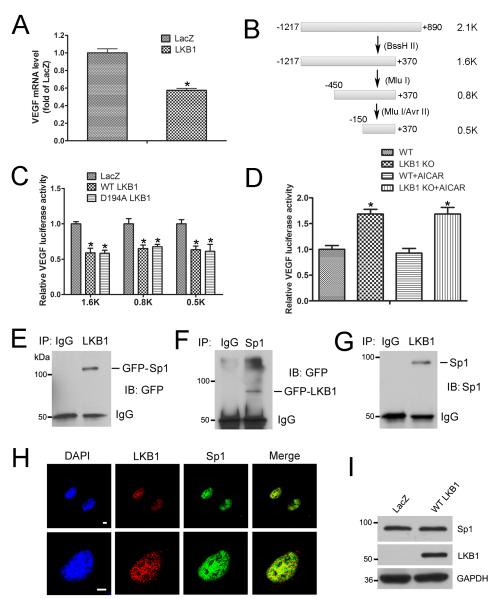
To explore how LKB1 regulates VEGF expression, LKB1-deficient A549 lung cancer cells were transfected with LKB1 or LacZ plasmid; VEGF mRNA level was decreased with LKB1 transfection (Fig. 6A). To assess how LKB1 regulates VEGF transcription, we generated four luciferase plasmids progressively truncated for the mouse VEGF promoter (Fig. 6B). LKB1 transfection repressed luciferase activities in all truncated constructs (Fig. 6C), which suggests that the responsive element, regulated by LKB1, is located within the small and proximal fragment spanning from –150 base pairs to the transcription start site. Moreover, the LKB1 kinase-dead mutant plasmid (D194A) inhibited VEGF expression (Fig. 6C), so LKB1 kinase activity may not be required for VEGF inhibition.
Figure 6. LKB1 negatively regulates VEGF expression.
A, RT-PCR analysis of mRNA level of VEGF in A549 cells transfected with LacZ or LKB1 plasmid for 24 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). B, Different lengths of VEGF-promoter luciferase plasmids constructed according to restriction enzymatic digestion and ligation. C, Luciferase activity assay of A549 cells transfected with LacZ, WT LKB1, or the kinase-dead mutant (D194A) of LKB1, together with the VEGF-promoter luciferase plasmid for 24 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). D, Luciferase activity assay of mouse ECs transfected with VEGF promoter-luciferase plasmid, then treated with AICAR for 24 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). E, HEK293T cells were transfected with WT LKB1 and GFP-Sp1 plasmids, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with IgG or LKB1 antibody, then underwent western blot analysis with anti-GFP antibody. F, HEK293T cells were transfected with WT Sp1 and GFP-LKB1 plasmids, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with IgG or Sp1 antibody, then underwent western blot analysis with anti-GFP antibody. G, Nuclear lysates from mouse lung ECs were immunoprecipitated with IgG or LKB1 antibody, then underwent western blot analysis with anti-Sp1 antibody. H, Immunostaining to determine the localization of LKB1 (red) and Sp1 (green) in mouse ECs. Bar = 5 μm. I, Western blot analysis of A549 cells transfected with LacZ or LKB1 plasmid for 24 hr. Data are mean ± SE.
The Sp1-responsive element is localized at the region between −150 base pairs and the transcription start site of the VEGF promoter. Therefore, LKB1 may regulate VEGF expression through Sp1. AMPK activity was decreased in LKB1endo−/− cells.16 To determine whether AMPK is involved in the regulatory activity of LKB1 in VEGF expression, VEGF-luc plasmids were transfected into WT and LKB1endo−/− cells, followed by AICAR (AMPK activator) treatment. AICAR did not change the VEGF expression (Fig. 6D), which suggests that AMPK is not involved in the regulatory activity of LKB1 in VEGF transcription.
To determine whether LKB1 can bind to Sp1, HEK293T cells were transfected with WT LKB1 and green fluorescent protein (GFP)-Sp1 plasmid. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with IgG or anti-LKB1 antibody, then examined by western blot analysis with anti-GFP antibody. LKB1 bound to Sp1 (Fig. 6E). This finding was further confirmed by reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation with cell lysates transfected with WT Sp1 and GFP-LKB1 (Fig. 6F). To further determine the association of LKB1 and Sp1 in ECs, mouse lung EC lysates were immunoprecipitated with IgG or anti-LKB1 antibody, then examined by western blot analysis with anti-Sp1 antibody. LKB1 was able to bind to Sp1 under physiological conditions (Fig. 6G). The colocalization of LKB1 and Sp1 was observed in the nuclei of ECs (Fig. 6H). However, LKB1 overexpression did not change Sp1 levels (Fig. 6I). Overall, these data indicate that LKB1 negatively regulates VEGF expression.
LKB1 binding with Sp1 inhibits VEGF expression
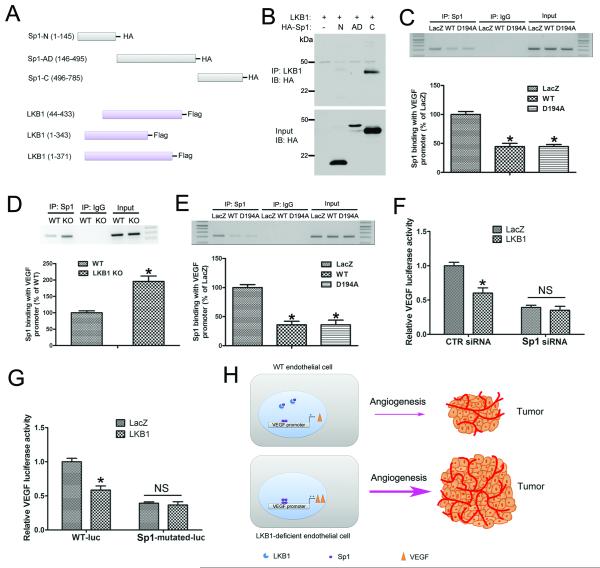
To map their binding domains, we constructed different truncated Sp1 and LKB1 plasmids (Fig. 7A). When the truncated Sp1 plasmids were co-transfected with LKB1 into HEK293T cells, only the C-terminal domain of Sp1 could bind to LKB1 (Fig. 7B). However, Sp1 could not bind to the truncated LKB1 plasmids (data not known), which suggests that full-length LKB1 is required for its binding to Sp1.
Figure 7. LKB1 binding with Sp1 inhibits VEGF expression.
A, A schematic diagram showing the construction of truncated LKB1 and Sp1 plasmids. B, HEK293T cells were transfected with WT LKB1 and HA-tagged truncated Sp1 plasmids, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with LKB1 antibody, then underwent western blot analysis with anti-HA antibody. C, A549 cells were transfected with LacZ, WT or D194A LKB1 plasmid, then underwent DNA ChIP assay to detect the ability of Sp1 to bind to the VEGF promoter. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). D, WT and LKB1endo−/− ECs were used in ChIP assay to detect the ability of Sp1 to bind to the VEGF promoter. *, P< 0.05, compared with WT (n = 5). E, LKB1endo−/− ECs were transfected with LacZ, WT or D194A, then underwent DNA ChIP assay. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). F, Luciferase activity assay of A549 cells transfected with CTR siRNA or Sp1 siRNA for 48 hr, then with LacZ or LKB1, together with VEGF promoter-luciferase plasmids for 24 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). G, Luciferase activity assay of A549 cells transfected with LacZ or LKB1, together with WT or Sp1-mutated VEGF promoter-luciferase plasmids, for 24 hr. *, P< 0.05, compared with LacZ (n = 5). H, A diagram showing the mechanism by which LKB1 regulates endothelial angiogenesis and tumor growth via VEGF. Data are mean ± SE.
To detect whether LKB1 can affect the binding of Sp1 to the VEGF promoter, LacZ, WT or D194A LKB1 plasmid was transfected into A549 cells, and ChIP was performed. Both WT and D194A LKB1 inhibited Sp1 binding to the VEGF promoter (Fig. 7C). In ECs, ChIP assay showed more Sp1 binding with VEGF promoter in LKB1endo−/− ECs (Fig. 7D). In addition, LKB1endo−/− ECs were transfected with LacZ plasmid, WT or D194A LKB1 plasmids followed by DNA ChIP assay. Compared with LacZ, both WT and D194A plasmid inhibited Sp1 to bind with VEGF promoter (Fig 7E), which suggests that the kinase activity of LKB1 is not required in regulating Sp1 binding to the VEGF promoter in ECs. In addition, LKB1 inhibited VEGF promoter activity in control siRNA-transfected A549 cells but could not inhibit VEGF expression in Sp1-deficient cells (Fig. 7F), which suggests that LKB1 inhibits VEGF expression via Sp1. Moreover, mutation of the Sp1 element completely abolished the LKB1-mediated repression of the VEGF promoter (Fig. 7G). Overall, these results demonstrate that LKB1 negatively regulated VEGF expression by competitively binding Sp1.
DISCUSSION
In mammals, two splice variants of LKB1 are expressed because of alternate use of 3′-exons. The long form is the main form widely expressed in tissues, whereas the short form has a unique 39-residue format instead of the last 63 residues in the long form and is a minor form in most tissues but is highly expressed in haploid spermatids.23,24 In our Cre/LoxP system, both LKB1 isoforms could be deleted in the endothelium. Our study is the first to show that EC-specific LKB1 knockout in mice increased VEGF levels, thus increasing angiogenesis and tumor growth. In WT ECs, LKB1 bound to the VEGF transcription factor Sp1 and decreased VEGF level. However, in LKB1-deficient ECs, the binding of Sp1 to the VEGF promoter was increased, and VEGF level, angiogenesis, and tumor growth were enhanced (Fig. 7H). Moreover, treatment with VEGF-neutralizing antibody decreased angiogenesis and tumor growth in LKB1endo−/− mice. Thus, LKB1 plays a critical role in regulating VEGF expression via Sp1 to maintain normal angiogenesis.
VEGF expression can be regulated by many transcription factors such as Sp1.8 Sp1 can directly interact with the E3 ligase pVHL, thereby inhibiting Sp1 binding to the VEGF promoter.25 In addition, p53 can form a complex with Sp1 to inhibit its binding with the VEGF promoter.26 VEGF mRNA levels in LKB1−/− embryos at embryonic day (E) 8.5 and E9.5 are elevated, so LKB1 negatively regulates VEGF expression under normal conditions.18 A recent study reported that LKB1 overexpression decressed Sp1 level, thereby downregulating VEGF.27 However, we found that LKB1 did not alter Sp1 protein levels (Fig. 6I). We demonstrate that LKB1 could bind to Sp1 and inhibit its binding to the VEGF promoter, which may explain why LKB1 overexpression is significantly associated with a decrease in microvessel density28 and LKB1 loss enhances the vascularity of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome polyps.29 Besides affecting VEGF-mediated angiogenesis, LKB1 can affect other endothelial functions such as decreasing eNOS activity with its deletion.16
Knockdown of LKB1 with shRNA significantly lowers VEGF, so tumor cells are important sources of VEGF. Beside tumor cells, other cells including macrophages and ECs can be potential sources of VEGF. To determine the relative contributions of ECs versus macrophages, we first co-stained VEGF with ECs (CD31) or macrophages (CD68). As expected, we found a strong co-staining of CD31 and VEGF in LKB1endo−/− mice, with no difference of CD68 and VEGF co-staining in LKB1endo−/− and WT mice. To further determine the contributions of macrophage-derived VEGF, LLC cells were implanted in WT and macrophage-specific LKB1 knockout (LKB1macro−/−) mice. As expected, LLC tumors from WT and LKB1macro−/− mice did not differ in size, which suggests that macrophage-derived VEGF did not contribute to the tumor growth in LKB1endo−/− mice.
Findings from this study may have broad implications beyond cardiovascular diseases. Because the generation of blood supply in tumor is a rate-limiting step for tumor growth, any therapy for normalizing LKB1 expression or activity will suppress intra-tumoral microvessel formation, which will lead to limiting the supply of circulating blood that is crucial for tumor growth. Indeed, anti-angiogenic therapy has been found effective in preclinical cancer studies, and numerous anti-angiogenic agents are being clinically evaluated. Notably, the US Food and Drug Administration has approved several anti-angiogenic drugs that target the VEGF signaling pathway.
In summary, this study identified the molecular mechanism of increased angiogenesis and tumor growth with LKB1 deficiency. LKB1 loss triggered the binding of Sp1 to the VEGF promoter, thereby enhancing VEGF expression. The development of therapeutic agents that target LKB1 in the treatment of pathological angiogenesis and tumor progression should be considered.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice
The generation and characteristics of endothelium-specific LKB1-knockout mice (LKB1endo−/−) and macrophage-specific LKB1-knockout mice (LKB1macro−/−) were previously described.16,30 The animals were housed under specific pathogen-free conditions with a 12-hr light/dark cycle with food and water freely available. At least 5 mice in each group were used in the animal study. A neutralizing monoclonal anti-VEGF antibody (2G11-2A05, Bio-legend) or an isotype-matched control (RTK2758) was injected intravenously at 100 μg twice weekly, starting on the day of tumor implantation. All experiments were performed in accordance with the Animal Care and Use Committee of Georgia State University.
Tumor implantation
A total of 1 million Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) or B16F10 melanoma cells were injected subcutaneously into the backs of male WT or LKB1endo−/− mice (6-8 weeks old). Tumors developed for 14 or 28 days and were measured every 2 days with use of calipers to assess tumor volume (length × height × width × 0.5236). In addition, LLC or B16F10 cells were infected with control or LKB1 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) lentiviral particles to silence LKB1, then implanted into WT mice.
Transfection and luciferase assay
A549 cells or ECs were transfected with the VEGF promoter-driven firefly luciferase plasmid, thymidine kinase promoter-driven renilla luciferase construct, and the β-galactosidase (LacZ) control or LKB1 construct by using the 4D-Nucleofecto System (LONZA, Walkersville, MD). At 24 hr after transfection, luciferase activity was measured by using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI).
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SE. After confirming the normal distribution of data by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, differences between two groups were analyzed by Student t test. Assuming α = 0.5, β = 0.90, and a ratio of (expected effect size)/ (expected standard deviation) = 1.20, we needed at least 5 samples per group. P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Dr. Lexi Ding who helped with the retinal angiogenesis experiments. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570393 to W.Z.), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2015HM002 to W.Z.), the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province of China (tsqn20161066 to W.Z.) and the National Institute of Health (CA213022, HL080499, HL089920, HL110488, and HL105157 to M-H.Z.).
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
REFERENCES
- 1.Pasula S, Cai X, Dong Y, Messa M, McManus J, Chang B, et al. Endothelial epsin deficiency decreases tumor growth by enhancing VEGF signaling. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4424–4438. doi: 10.1172/JCI64537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. 2011;473:298–307. doi: 10.1038/nature10144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983;219:983–985. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:359–371. doi: 10.1038/nrm1911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G, Pollefeyt S, Kieckens L, Gertsenstein M, et al. Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature. 1996;380:435–439. doi: 10.1038/380435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Levy NS, Chung S, Furneaux H, Levy AP. Hypoxic stabilization of vascular endothelial growth factor mrna by the RNA-binding protein HuR. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6417–6423. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.11.6417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stein I, Itin A, Einat P, Skaliter R, Grossman Z, Keshet E. Translation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by internal ribosome entry: Implications for translation under hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:3112–3119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.6.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pagès G, Pouysségur J. Transcriptional regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene--a concert of activating factors. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:564–573. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ryuto M, Ono M, Izumi H, Yoshida S, Weich HA, Kohno K, et al. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha in human glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28220–28228. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.45.28220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Giardiello FM, Trimbath JD. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and management recommendations. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:408–415. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2005.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Katajisto P, Vallenius T, Vaahtomeri K, Ekman N, Udd L, Tiainen M, et al. The LKB1 tumor suppressor kinase in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1775:63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Alessi DR, Sakamoto K, Bayascas JR. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:137–163. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shackelford DB, Shaw RJ. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:563–575. doi: 10.1038/nrc2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ollila S, Mäkelä TP. The tumor suppressor kinase LKB1: Lessons from mouse models. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3:330–340. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjr016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xie Z, Dong Y, Zhang J, Scholz R, Neumann D, Zou MH. Identification of the serine 307 of LKB1 as a novel phosphorylation site essential for its nucleocytoplasmic transport and endothelial cell angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:3582–3596. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01417-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang W, Wang Q, Wu Y, Moriasi C, Liu Z, Dai X, et al. Endothelial cell-specific LKB1 deletion causes endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in mice in vivo. Circulation. 2014;129:1428–1439. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.004146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ylikorkala A, Rossi DJ, Korsisaari N, Luukko K, Alitalo K, Henkemeyer M, et al. Vascular abnormalities and deregulation of VEGF in LKB1-deficient mice. Science. 2001;293:1323–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.1062074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Roberts WG, Palade GE. Increased microvascular permeability and endothelial fenestration induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2369–2379. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.6.2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jensen JS. Renal and systemic transvascular albumin leakage in severe atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:1324–1329. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.9.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dvorak HN, Senger DR, Dvorak AM, Harvey VS, McDonagh J. Regulation of extravascular coagulation by microvascular permeability. Science. 1985;227:1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.3975602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Greenberg Y, King M, Kiosses WB, Ewalt K, Yang X, Schimmel P, et al. The novel fragment of tyrosyl tRNA synthetase, mini-TyrRS, is secreted to induce an angiogenic response in endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2008;22:1597–1605. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9973com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Uemura A, Kusuhara S, Katsuta H, Nishikawa S. Angiogenesis in the mouse retina: a model system for experimental manipulation. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312:676–683. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Denison FC, Hiscock NJ, Carling D, Woods A. Characterization of an alternative splice variant of LKB1. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:67–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806153200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Towler MC, Fogarty S, Hawley SA, Pan DA, Martin DM, Morrice NA, et al. A novel short splice variant of the tumour suppressor LKB1 is required for spermiogenesis. Biochem J. 2008;416:1–14. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mukhopadhyay D, Knebelmann B, Cohen HT, Ananth S, Sukhatme VP. The von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor gene product interacts with Sp1 to repress vascular endothelial growth factor promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:5629–5639. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.9.5629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pal S, Datta K, Mukhopadhyay D. Central role of p53 on regulation of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) expression in mammary carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6952–6957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liang X, Li ZL, Jiang LL, Guo QQ, Liu MJ, Nan KJ. Suppression of lung cancer cell invasion by LKB1 is due to the downregulation of tissue factor and vascular endothelial growth factor, partly dependent on SP1. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:1989–97. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhuang ZG, Di GH, Shen ZZ, Ding J, Shao ZM. Enhanced expression of LKB1 in breast cancer cells attenuates angiogenesis, invasion, and metastatic potential. Mol Cancer Res. 2006;4:843–849. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shackelford DB, Vasquez DS, Corbeil J, Wu S, Leblanc M, Wu CL, et al. mTOR and HIF-1alpha-mediated tumor metabolism in an LKB1 mouse model of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106:11137–11142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900465106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liu Z, Zhang W, Zhang M, Zhu H, Moriasi C, Zou MH. Liver kinase B1 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:2312–20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.616441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.