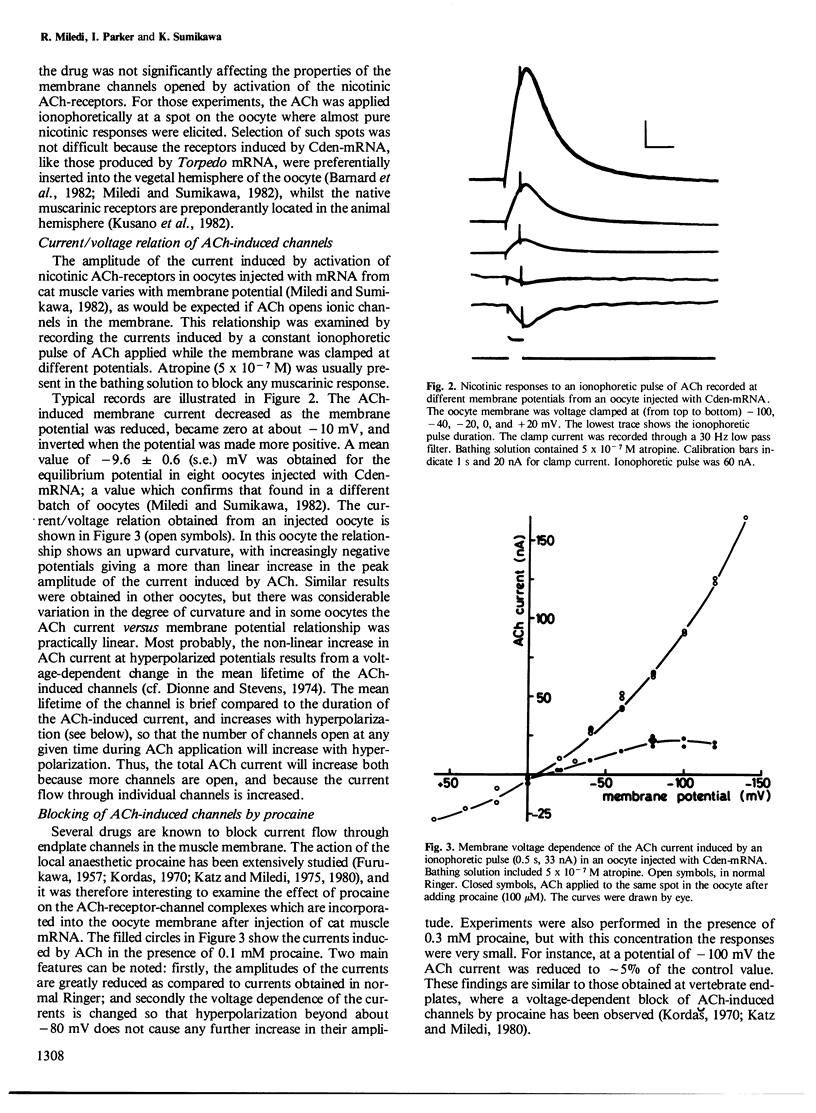
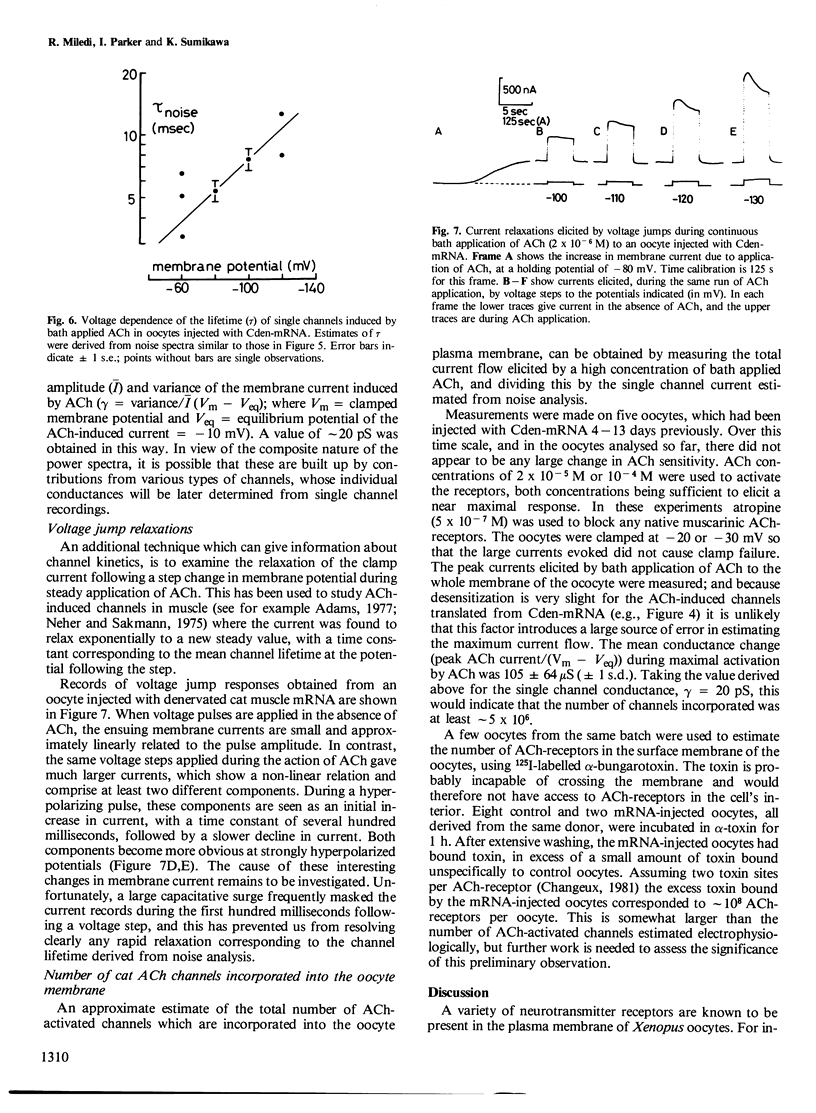
Abstract
Poly(A)+ mRNA, extracted from denervated skeletal muscles of the cat, directs the synthesis of acetylcholine receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. The receptors are inserted in the oocyte membrane where they form acetylcholine receptor-channel complexes which have properties like those of the native receptors in the muscle membrane.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Relaxation experiments using bath-applied suberyldicholine. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):271–289. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Stevens C. F. Voltage dependence of agonist effectiveness at the frog neuromuscular junction: resolution of a paradox. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):245–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T. Properties of the procaine end-plate potential. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;7(3):199–212. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Klein W. H., Davis M. M., Wold B. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Structural gene sets active in embryos and adult tissues of the sea urchin. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further observations on acetylcholine noise. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio232124b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of procaine on the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):269–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Acetylcholine receptors in the oocyte membrane. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):739–741. doi: 10.1038/270739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Voltage-dependence of drug-induced conductance in frog neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Emtage J. S., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. Active multi-subunit ACh receptor assembled by translation of heterologous mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):862–864. doi: 10.1038/292862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray D. Noise analysis and channels at the postsynaptic membrane of skeletal muscle. Prog Drug Res. 1980;24:9–56. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7108-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray D. Prolonged exposure to acetylcholine: noise analysis and channel inactivation in cat tenuissimus muscle. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:37–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



