Abstract
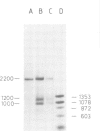
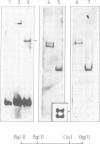
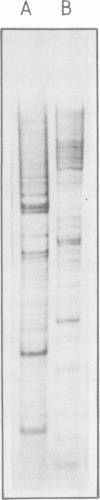
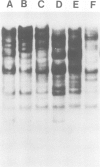
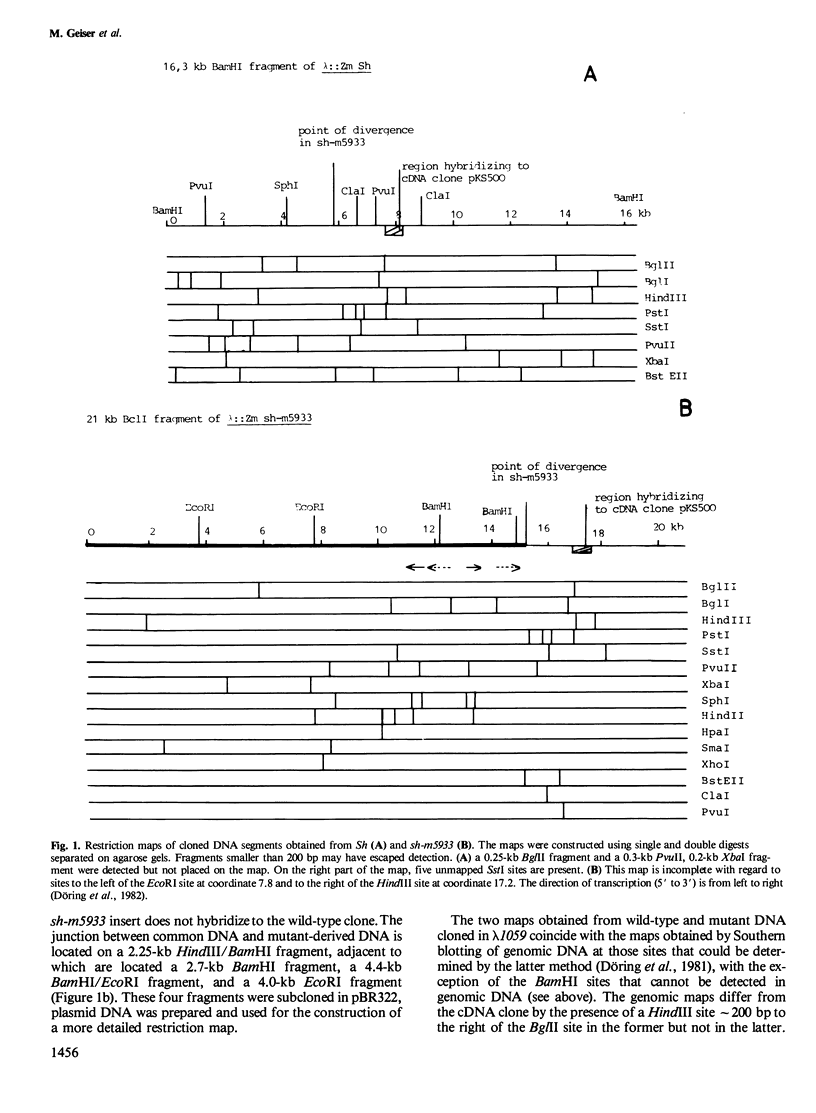
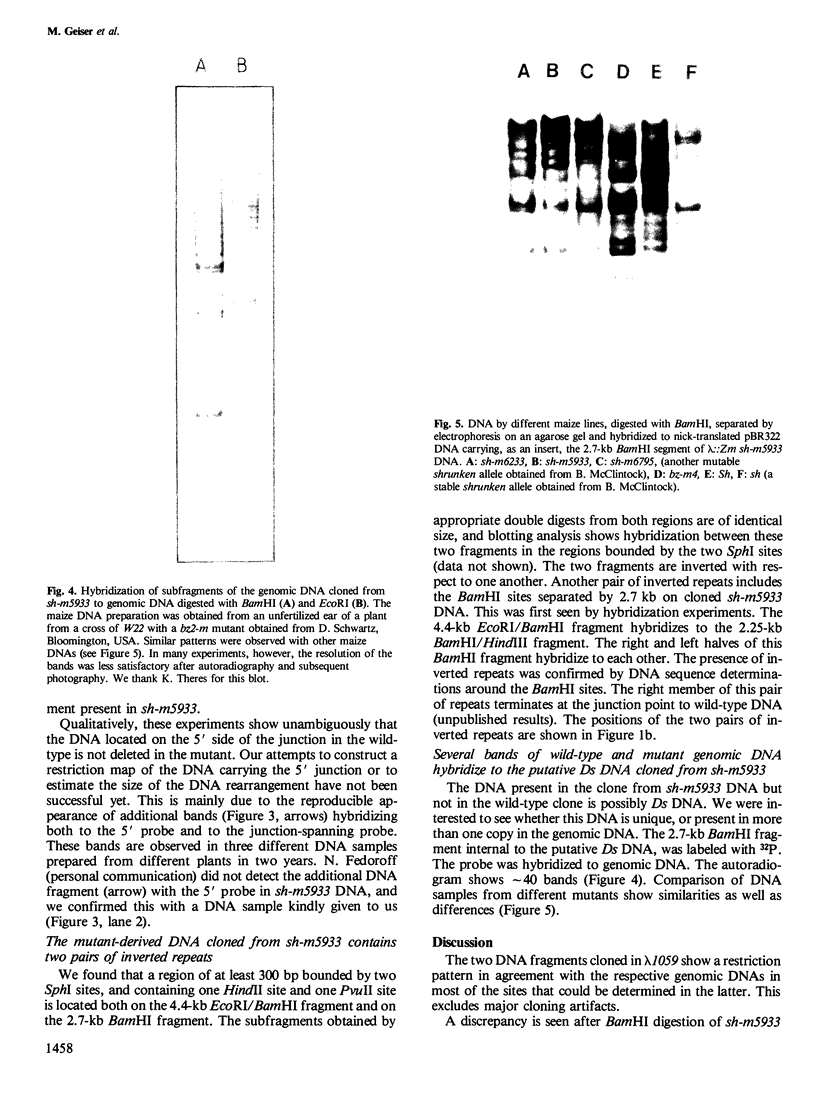
In an attempt to isolate the transposable genetic element Ds from Zea mays L., we cloned DNA fragments hybridizing to a cDNA clone derived from the sucrose synthase gene in a λ vector (λ::Zm Sh). The fragments cloned from wild-type and from the Ds-induced mutant sh-m5933 (λ::Zm sh-m5933) share a segment 6 kb long while a contiguous segment of 15 kb of λ::Zm sh-m5933 (mutant-derived DNA) does not hybridize to the DNA segment cloned from the wild-type. Restriction maps are given, and the junction point between the two DNA segments in the mutant clone was determined. Hybridization of DNA fragments, present in the wild-type DNA of λ::Zm Sh, but not in the mutant clone, λ::Zm sh-m5933, to genomic DNA of sh-m5933 showed that no part of this DNA is deleted. It cannot be said whether the DNA found in the mutant, but not in the wild-type clone, has been brought there by Ds insertion or by another Ds-dependent DNA rearrangement. The mutant-derived DNA was hybridized to genomic DNA of various maize lines digested by several restriction endonucleases. Approximately 40 bands were detected. The mutant-derived DNA contains two pairs of inverted repeats several hundred nucleotide pairs long, one of which is located at the junction to wild-type-derived DNA.
Keywords: endosperm, maize, shrunken gene, sucrose synthase, transposable element Ds
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Betlach M. C., Boyer H. W. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. I. Ampicillin-resistant derivatives of the plasmid pMB9. Gene. 1977;2(2):75–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Controlling-element events at the shrunken locus in maize. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):143–156. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Detection of changes in maize DNA at the shrunken locus due to the intervention of Ds elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):463–465. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Ds controlling elements of maize at the shrunken locus are large and dissimilar insertions. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chourey P. S., Nelson O. E. The enzymatic deficiency conditioned by the shrunken-1 mutations in maize. Biochem Genet. 1976 Dec;14(11-12):1041–1055. doi: 10.1007/BF00485135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Nelson O. E. Controlling element-induced alterations in UDPglucose:flavonoid glucosyltransferase, the enzyme specified by the bronze locus in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L., Sternberg N. In vitro packaging of lambda Dam vectors and their use in cloning DNA fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:281–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser M., Döring H. P., Wöstemeyer J., Behrens U., Tillmann E., Starlinger P. A cDNA clone from Zea mays endosperm sucrose synthetase mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6175–6188. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLINTOCK B. Controlling elements and the gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:197–216. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCLINTOCK B. Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:13–47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S. DNA sequence of a foldback transposable element in Drosophila. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):201–204. doi: 10.1038/297201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder G. S., Farabaugh P. J., Chaleff D. T., Fink G. R. The origins of gene instability in yeast. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1375–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.6251544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Kidwell M. G., Bingham P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):987–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]