We read with interest the article by Bruix et al1 on currently available treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is now the first-line technique for HCC ablation. RFA produces tumour necrosis in situ through temperature modification. Compared with RFA, microwave ablation (MWA) is one relatively recent advancement of thermoablative technology, which shows multiple theoretical advantages over RFA.2–4 We wish to report the results of a phase III randomised controlled trial (RCT) by comparing ultrasound-guided percutaneous cooled-probe MWA and RFA in ≤5 cm HCC (NCT 02539212).
From October 2008 to June 2015, 203 (265 nodules) subjects were randomised to MWA and 200 (251 nodules) were randomised to RFA. The indications were as follows: tumour size ≤5 cm in diameter, tumour number ≤3, Child–Pugh class A or B classification, no evidence of extrahepatic metastasis, vein or bile duct tumour embolus, lesions visible on ultrasound with an acceptable puncture path, an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0–1, and no any other anticancer treatment previously. All the patients were percutaneously treated by a cooled-shaft microwave system (KY-2000, Kangyou Medical, China) or radiofrequency system (WB991029, CelonLab Power, Germany).
The median follow-up period was 35.2 (2.0–81.9) months. The demographics and preablation liver function tests of both groups were similar. For the MWA group, the tumour size was 2.7±1.0 (0.7–5.0) cm, with 28.3% (75/265) of nodules >3.0 cm and 50.6% (134/265) of them were in risky locations (adjacent to large vessel, gastroenterology tract, diaphragm, or gallbladder). For the RFA group, the tumour size was 2.6±1.0 (0.9–5.0) cm, with 30.7% (77/251) of nodules >3.0 cm, and 50.2% (126/251) of them in risky location. MWA needed significantly fewer sessions, applicator puncture and ablation durations, with lower hospitalisation cost than that for RFA (table 1).
Table 1.
Patients' treatment parameters between MWA and RFA groups
| Category | MWA | RFA | t Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power (W) | 50.2±2.2 | 60.1±10.6 | −13.03 | <0.001 |
| Time (min) | 9.0±4.6 | 24.4±10.6 | −18.97 | <0.001 |
| Energy (kJ) | 27.3±13.9 | 48.3±24.8 | −10.51 | <0.001 |
| Ablation needle | 1.9±0.3 | 2.0±0.3 | −3.35 | <0.001 |
| Ablation session (cm) | 1.3±0.5 | 1.5±0.5 | −4.02 | <0.001 |
| ≤3.0 | 1.3±0.4 | 1.4±0.5 | −2.12 | 0.04 |
| 3.1–5.0 | 1.4±0.5 | 1.7±0.5 | −5.72 | <0.001 |
| Puncture (cm) | 2.6±1.3 | 3.2±1.3 | −4.63 | <0.001 |
| ≤3.0 | 2.3±1.0 | 2.8±1.1 | −4.54 | <0.001 |
| 3.1–5.0 | 3.3±1.6 | 3.9±1.4 | −3.79 | <0.001 |
| Cost (T RMB) | 43.2±14.5 | 50.3±9.8 | −4.88 | <0.001 |
MWA, microwave ablation; RFA, radiofrequency ablation; T RMB, thousand RMB.
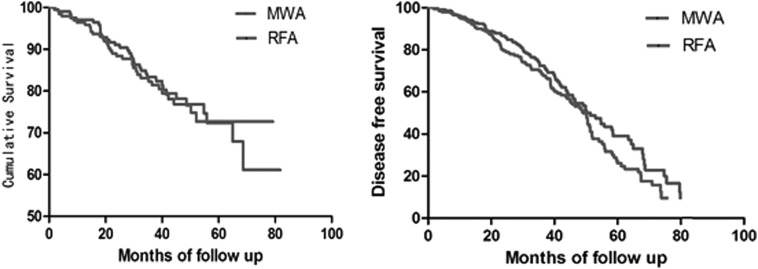
The technique effectiveness was 99.6% (264/265) in tumours treated by MWA and 98.8% (248/251) by RFA (p=0.95). The 1-year, 3-year and 5-year local tumour progression rates were 1.1%, 4.3%, 11.4% for MWA versus 2.1%, 5.8%, 19.7% for RFA (p=0.11), which also showed no significant differences in subsets of tumours (including ≤3.0 cm, 3.1–5.0 cm tumours and tumours in risky locations). The 1-year, 3-year and 5-year intrahepatic metastatic rates were 3.5%, 22.9% and 58.7% for MWA versus 3.8%, 23.2% and 67.8% for RFA (p=0.30). The 1-year, 3-year and 5-year extrahepatic metastatic rates were 1.6%, 5.9% and 13.2% for MWA versus 2.2%, 11.2% and 19.3% for RFA (p=0.12). The 1-year, 3-year, 5-year overall survival rates were 96.4%, 81.9% and 67.3% for MWA versus 95.9%, 81.4% and 72.7% for RFA (p=0.91), and the 1-year, 3-year, 5-year disease free survival rates were 94.0%, 70.6% and 36.7% for MWA versus 93.8%, 66.0% and 24.1% for RFA (p=0.07) (figure 1). The major complication rates were 3.4% (7/203) for MWA and 2.5% (5/200) for RFA (p=0.59), including needle seeding, GI bleeding and bulk pleural effusion.
Figure 1.
Survival comparison between microwave ablation (MWA) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). (A) Overall survival curves after MWA and RFA of HCC. There is no significant difference between two treatments (P=0.91). (B) Disease free survival curves after MWA and RFA of HCC. There is no significant difference between two treatments (P=0.07).
The comparison between MWA and RFA in HCC has being paid a great deal of attention in recent years, but only with one RCT in 2002 and very limited prospective studies.5–8 Though our results showed favourable long-term prognosis for both modalities, MWA showed some advantages due to higher thermal efficiency as follows. First, even if without statistic difference, MWA showed better tumour inactivation ability over RFA for 3–5 cm tumours (6.7% vs 13.0%) and tumours adjacent to vessels (4.3% vs 7.7%) and gallbladder (0% vs 7.1%). Second, MWA needed a fewer number of ablation sessions and application puncture, which contributed to less invasion and costs. Third, with MWA, it was possible to decrease the time required for ablation by 60%, which provided patients unable to tolerate intravenous anaesthesia due to comorbidities a chance to undergo treatment.
Findings in this large-sample RCT study suggest that both MWA and RFA are suitable options for early-stage HCC, with better prospects for MWA due to its higher thermal efficiency.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by two grants 81401436 and 81430039 from the National Scientific Foundation Committee of China.
Footnotes
Contributors: PL and JY had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: PL, JY. Acquisition of data: PL, JY, X-lY, Z-gC, Z-yH, F-yL, M-jM and F-yL. Analysis and interpretation of data: PL, JY, H-yZ. Drafting of the manuscript: JY. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: JY, PL.
Funding: National Scientific Foundation Committee of China (grant no. 81401436; 81430039).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Ethics approval: Chinese PLA General Hospital.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Bruix J, Gores GJ, Mazzaferro V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut 2014;63:844–55. 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306627 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Lope CR, Tremosini S, Forner A, et al. Management of HCC. J Hepatol 2012;56(Suppl 1):S75–87. 10.1016/S0168-8278(12)60009-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chu KF, Dupuy DE. Thermal ablation of tumours: biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2014;14:199–208. 10.1038/nrc3672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yu J, Liang P, Yu X, et al. A comparison of microwave ablation and bipolar radiofrequency ablation both with an internally cooled probe: results in ex vivo and in vivo porcine livers. Eur J Radiol 2011;79:124–30. 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.12.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 2002;223:331–7. 10.1148/radiol.2232010775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Qian GJ, Wang N, Shen Q, et al. Efficacy of microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: experimental and clinical studies. Eur Radiol 2012;22:1983–90. 10.1007/s00330-012-2442-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Abdelaziz A, Elbaz T, Shousha HI, et al. Efficacy and survival analysis of percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an Egyptian multidisciplinary clinic experience. Surg Endosc 2014;28:3429–34. 10.1007/s00464-014-3617-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huo YR, Eslick GD. Microwave ablation compared to radiofrequency ablation for hepatic lesions: a meta-analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2015;26:1139–46. 10.1016/j.jvir.2015.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]