Abstract
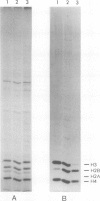
The post-translational methylation of histones in the presence of inhibitors of protein synthesis, was studied during a heat-shock to Drosophila cells in culture. In control cells (23 degrees C), both histones H3 and H4 are methylated. After heat-shock (37 degrees C), there is a dramatic reduction in the methylation of H3 and an increase in the methylation of another core histone identified as H2B. These changes in the pattern of methylation vary with the temperature of the heat-shock. The increased methylation of H2B is also observed in arsenite-treated cells but the methylation of H3 is unchanged, being similar to that observed in control cells. Inhibition of synthesis of heat-shock proteins has no effect on the methylation changes, suggesting that heat-shock proteins are not directly involved in the methylation reaction. These changes could be involved in the extensive transcriptional regulation occurring in these cells during heat-shock.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. V. Responses to environmental treatments. Chromosoma. 1970;31(3):356–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00321231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findly R. C., Pederson T. Regulated transcription of the genes for actin and heat-shock proteins in cultured Drosophila cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):323–328. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V., Vavra K. J., Guttman S. D., Gorovsky M. A. Heat shock and deciliation induce phosphorylation of histone H1 in T. pyriformis. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90271-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamrich M., Greenleaf A. L., Bautz E. K. Localization of RNA polymerase in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2079–2083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Oppermann H., Jackson J., Levinson W. Induction of four proteins in chick embryo cells by sodium arsenite. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6975–6980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagens U., Greenleaf A. L., Bautz E. K. Distribution of RNA polymerase on Drosophila polytene chromosomes as studied by indirect immunofluorescence. Chromosoma. 1976 Dec 16;59(2):157–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00328484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. M. Identification of histone H2b as a heat-shock protein in Drosophila. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):579–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguay R. M., Vincent M. Intracellular translocation of cellular and heat shock induced proteins upon heat shock in Drosophila Kc cells. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):306–315. doi: 10.1139/o82-037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallwork J. C., Quick D. P., Duerre J. A. Properties of soluble rat brain histone lysine methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5977–5980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gomer R. H., Lazarides E. Heat shock proteins are methylated in avian and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]