Abstract
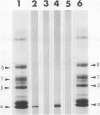
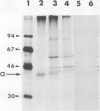
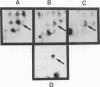
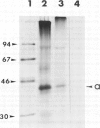
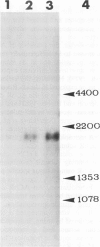
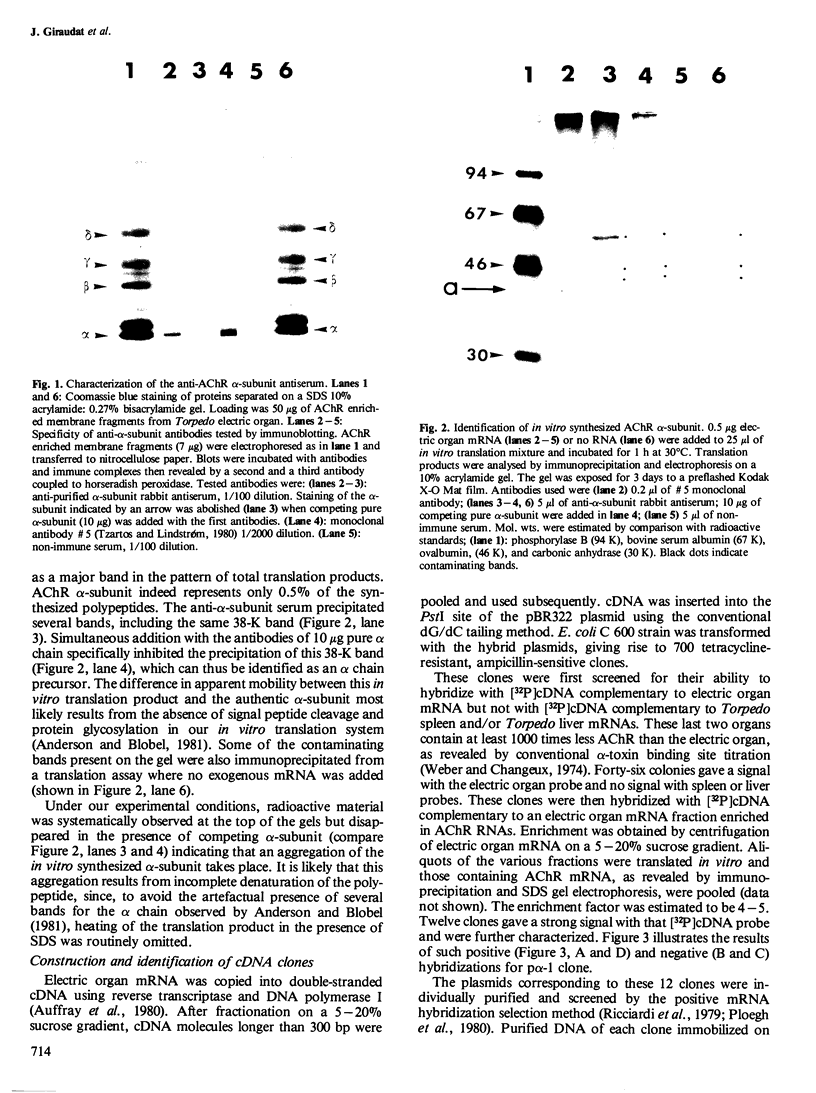
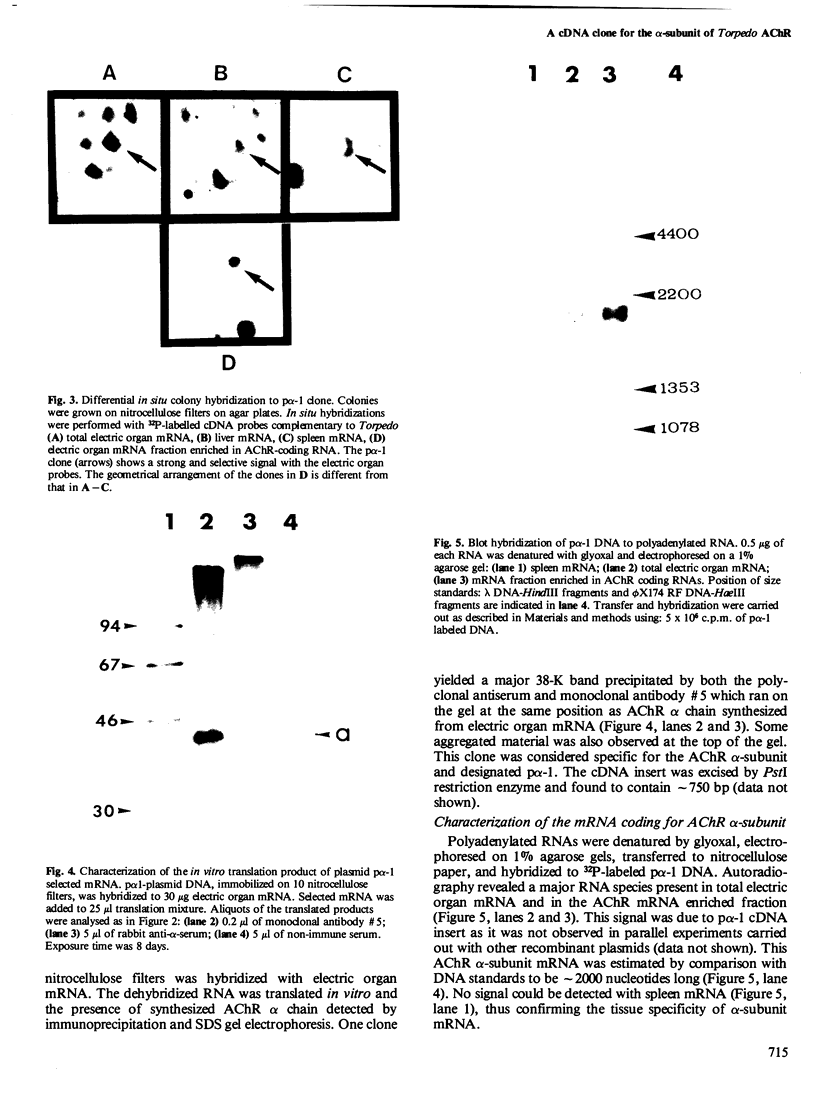
A recombinant DNA plasmid has been constructed that contains sequences of the gene coding for the acetylcholine binding subunit (alpha-subunit, 40 000 daltons) of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor protein (AChR). Polyadenylated RNA purified from Torpedo electric organ was used to construct a cDNA library. The AChR alpha-subunit cDNA clone was then identified by a two-step screening of 700 recombinant clones. As AChR is present in Torpedo electric organ but not in Torpedo liver or spleen, differential screening led to the selection of 12 clones specific for the electric organ. We then tested the ability of cDNA inserts to hybridize alpha-subunit mRNA specifically, as judged by cell-free translation and immunoprecipitation. The insert from one clone, p alpha-1, selectively hybridized with a mRNA species which elicited the synthesis of a 38 000 mol. wt. polypeptide. This polypeptide was precipitated by: (1) a rabbit serum raised against purified denatured alpha-subunit (the pure alpha-subunit displaced the complex); and (2) a rat monoclonal antibody specific for the denatured alpha-subunit. It was thus identified as a precursor of the alpha chain. Blot hybridization analysis of polyadenylated RNA from Torpedo electric organ with the p alpha-1 probe revealed a major species of 2.0 kb, which thus contains approximately 800 non-coding nucleotides.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. In vitro synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane insertion of the four subunits of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Chambraud B., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: a bacterial plasmid containing the entire coding sequence for a pre-gamma 2a heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Changeux J. P., Paroutaud P., Strosberg A. D. The amino-terminal sequence of the 40,000 molecular weight subunit of the acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M. Control of acetylcholine receptors in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):165–227. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Stroud R. M., Klymkowsky M. W., Lalancette R. A., Fairclough R. H. Structure and function of an acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):371–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84685-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez B., Valenzuela P., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Cell-free synthesis of acetylcholine receptor polypeptides. Science. 1980 Aug 8;209(4457):695–697. doi: 10.1126/science.7394526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Changeux J. P., Gros F. Skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptor. Purification, characterization, and turnover in muscle cell cultures. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2882–2891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor subunits transit a precursor pool before acquiring alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3605–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Delronche M., Lheureux M., Vervoort T., Bloch J., Gannon F., Steinert M. Cloning and characterization of DNA sequences complementary to messenger ribonucleic acids coding for the synthesis of two surface antigens of Trypanosoma brucei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5965–5981. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Molecular cloning of a human histocompatibility antigen cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Kourilsky P., Mach B. Insertion of a rabbit beta-globin gene sequence into an E. coli plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Dec;2(12):2365–2378. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.12.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Mach B. Cloning and amplification of rabbit alpha- and beta-globin gene sequences into Escherichia coli plasmids. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2209–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougeon F., Mach B. Stepwise biosynthesis in vitro of globin genes from globin mRNA by DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Oswald R., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Conditions for the selective labelling of the 66 000 dalton chain of the acetylcholine receptor by the covalent non-competitive blocker 5-azido-[3H]trimethisoquin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel A., Weber M., Changeux J. P. Large-scale purification of the acetylcholine-receptor protein in its membrane-bound and detergent-extracted forms from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):215–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Emtage J. S., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. Active multi-subunit ACh receptor assembled by translation of heterologous mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):862–864. doi: 10.1038/292862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. I. Binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin in the absence of effector. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]