Abstract
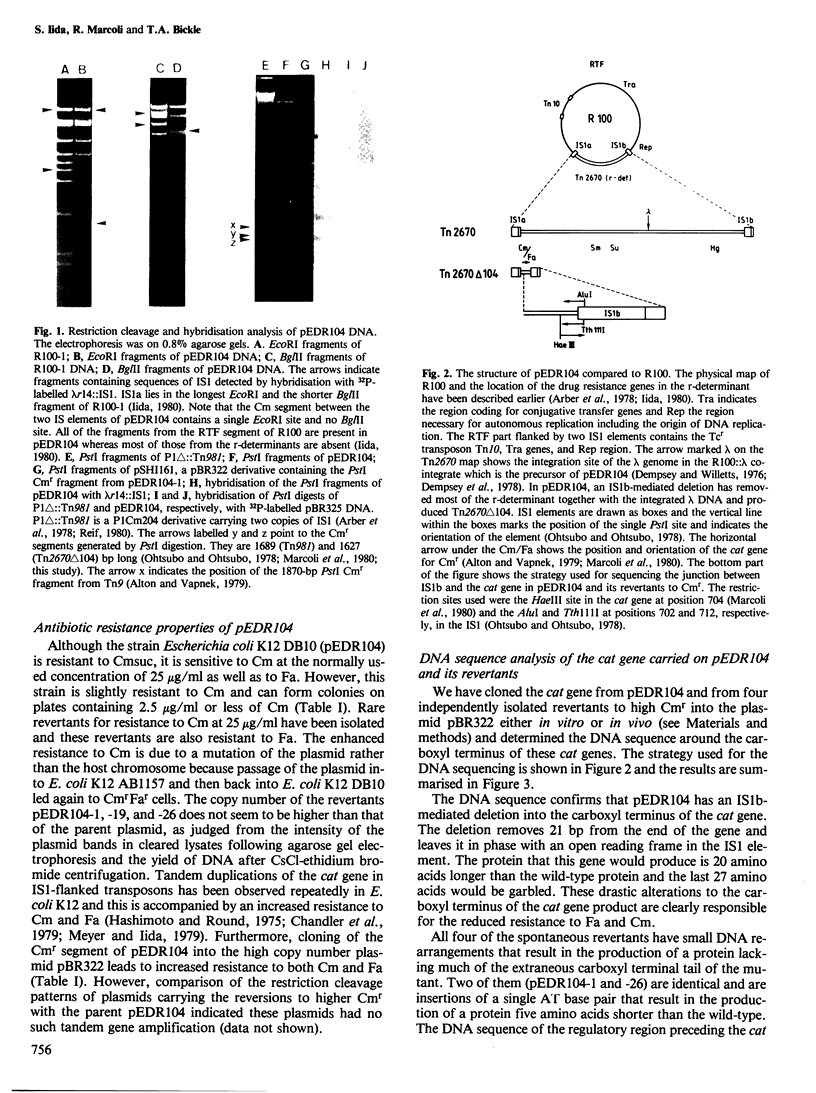
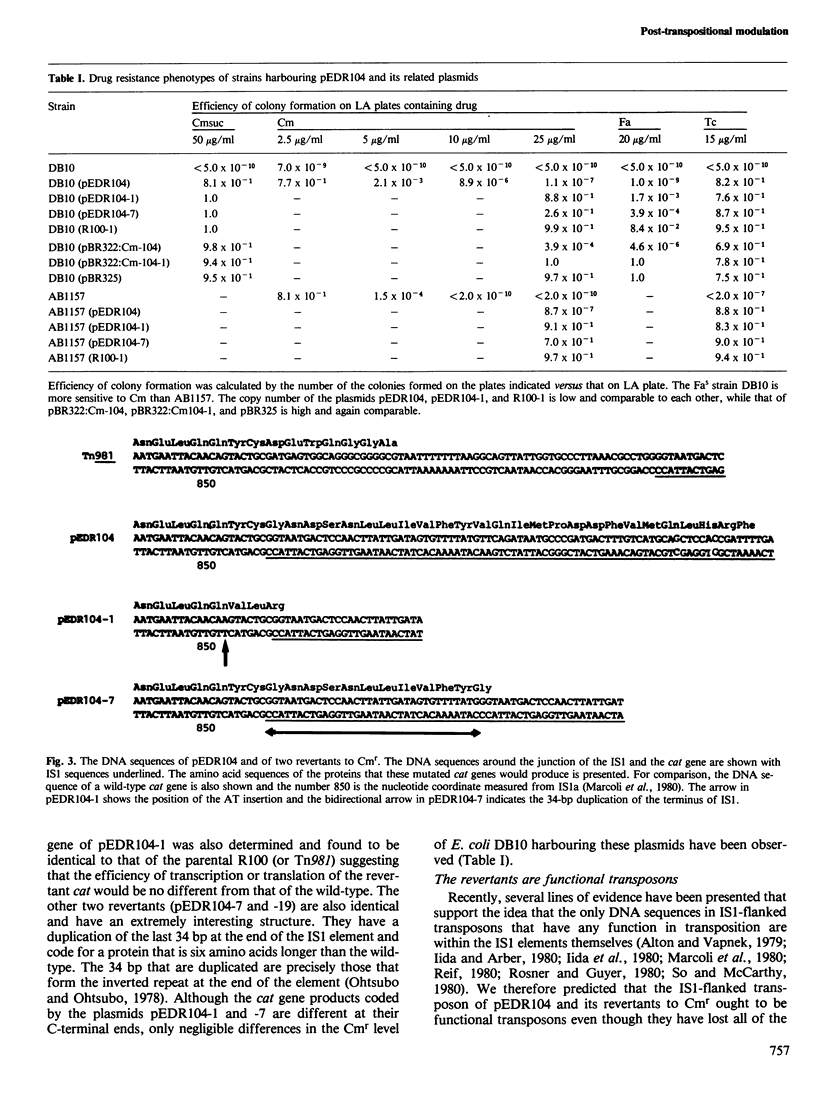
We have physically characterised a deletion mutant of the R plasmid R100 which has lost all of the antibiotic resistances, including chloramphenicol resistance (Cmr), coded by its IS1-flanked r-determinant. The deletion was mediated by one of the flanking IS1 elements and terminates within the carboxyl terminus of the Cmr gene. DNA sequence analysis showed that the mutated gene would produce a protein 20 amino acids longer than the wild-type due to fusion with an open reading frame in the IS element. Surprisingly for a deletion mutation, rare, spontaneous Cmr revertants could be recovered. Two of the four revertants studied had frame shifts due to the insertion of a single AT base pair at the same position; the revertants would code for a protein five amino acids shorter than the wild-type. The other two revertants had acquired duplications of the 34-bp inverted terminal repeat sequences of the IS1 element and would direct the synthesis of a protein six amino acids longer than the wild-type. The reverted Cmr markers were still capable of transposition. These observations suggest a role for point mutations and small DNA rearrangements in the formation of new gene organisations produced by mobile genetic elements.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A., Bidwell K., Musso R. Internal rearrangements of IS2 in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):141–151. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arber W., Iida S., Jütte H., Caspers P., Meyer J., Hänni C. Rearrangements of genetic material in Escherichia coli as observed on the bacteriophage P1 plasmid. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1197–1208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerswald E. A., Ludwig G., Schaller H. Structural analysis of Tn5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):107–113. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besemer J., Görtz G., Charlier D. Deletions and DNA rearrangements within the transposable DNA element IS2. A model for the creation of palindromic DNA by DNA repair synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5825–5833. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Transposable elements. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):579–595. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A., Berg D. E., Botstein D., Lederberg E. M., Novick R. P., Starlinger P., Szybalski W. Nomenclature of transposable elements in prokaryotes. Gene. 1979 Mar;5(3):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A., Starlinger P., Berg D. E., Botstein D., Lederberg E. M., Novick R. P., Szybalski W. Nomenclature of transposable elements in prokaryotes. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):466–473. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M., de la Tour E. B., Willems D., Caro L. Some properties of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):221–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00273216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W., Becker D., Davies J. Plasmid-determined fusidic acid resistance in the Enterobacteriaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jul;83(0):191–196. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey W. B., McIntire S. A., Willetts N., Schottel J., Kinscherf T. G., Silver S., Shannon W. A., Jr Properties of lambda transducing bacteriophages carrying R100 plasmid DNA: mercury resistance genes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):1084–1093. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.1084-1093.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey W. B., Willetts N. S. Plasmid co-integrates of prophage lambda and R factor R100. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):166–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.166-176.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler J. A., van Bree M. P. The nucleotide sequence and protein-coding capability of the transposable element IS5. Gene. 1981 Aug;14(3):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. Sequence analysis of Tn9 insertions in the lacZ gene. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 25;144(1):19–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Gross J., Saedler H. DNA sequence of IS2--7 and generation of mini-insertions by replication of IS2 sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1193–1196. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Saedler H. DNA sequence of the mini-insertion IS2--6 and its relation to the sequence of IS2. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):611–617. doi: 10.1038/275611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal D., Saedler H. IS2-61 and IS2-611 arise by illegitimate recombination from IS2-6. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):233–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00273217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Rosner J. L. Acquisition of a determinant for chloramphenicol resistance by coliphage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Kleckner N. A symmetrical six-base-pair target site sequence determines Tn10 insertion specificity. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Rownd R. H. Transition of the R factor NR1 and Proteus mirabilis: level of drug resistance of nontransitioned and transitioned cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):56–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.56-68.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. J., Starlinger P., Brachet P. Two kinds of insertions in bacterial genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):191–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00333858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Otsubo E., Davidson N., Saedler H. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among bacterial plasmids: identification and mapping of the insertion sequences IS1 and IS2 in F and R plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):764–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.764-775.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänni C., Meyer J., Iida S., Arber W. Occurrence and properties of composite transposon Tn2672: evolution of multiple drug resistance transposons. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1266–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1266-1273.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S. A cointegrate of the bacteriophage P1 genome and the conjugative R plasmid R100. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):278–290. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Arber W. On the role of IS1 in the formation of hybrids between the bacteriophage P1 and the R plasmid NR1. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):261–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00267437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Arber W. Plaque forming specialized transducing phage P1: isolation of P1CmSmSu, a precursor of P1Cm. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):259–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00431591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Hänni C., Echarti C., Arber W. Is the IS1-flanked r-determinant of the R plasmid NR1 a transposon? J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Oct;126(2):413–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-2-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Arber W. Cointegrates between bacteriophage P1 DNA and plasmid pBR322 derivatives suggest molecular mechanisms for P1-mediated transduction of small plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00271186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Meyer J., Arber W. Genesis and natural history of IS-mediated transposons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):27–43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONDO E., MITSUHASHI S. DRUG RESISTANCE OF ENTERIC BACTERIA. IV. ACTIVE TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE P1 CM PRODUCED BY THE COMBINATION OF R FACTOR WITH BACTERIOPHAGE P1. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1266–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1266-1276.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaer R., Kühn S., Fritz H. J., Tillmann E., Saint-Girons I., Habermann P., Pfeifer D., Starlinger P. Studies on transposition mechanisms and specificity of IS4. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):215–224. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcoli R., Iida S., Bickle T. A. The DNA sequence of an IS/-flanked transposon coding for resistance to chloramphenicol and fusidic acid. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Iida S. Amplification of chloramphenicol resistance transposons carried by phage P1Cm in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):209–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00273215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Iida S., Arber W. Does the insertion element IS1 transpose preferentially into A+T-rich DNA segments? Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):471–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00270502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of an insertion element, IS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Karch F., Iida S., Meyer J. The plasmid cloning vector pBR325 contains a 482 base-pair-long inverted duplication. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif H. J. Genetic evidence for absence of transposition functions from the internal part of Tn981 a relative of Tn9. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;177(4):667–674. doi: 10.1007/BF00272678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif H. J., Saedler H. IS1 is involved in deletion formation in the gal region of E. coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;137(1):17–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00332538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L., Guyer M. S. Transposition of IS1-lambdaBIO-IS1 from a bacteriophage lambda derivative carrying the IS1-cat-IS1 transposon (Tn9). Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00267219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Jorgensen R. A., Postle K., Reznikoff W. S. The inverted repeats of Tn5 are functionally different. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):795–805. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. The functional differences in the inverted repeats of Tn5 are caused by a single base pair nonhomology. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedler H., Cornelis G., Cullum J., Schumacher B., Sommer H. IS1-mediated DNA rearrangements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):93–98. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Cullum J., Saedler H. IS2-43 and IS2-44: new alleles of the insertion sequence IS2 which have promoter activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Aug;175(1):53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00267855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P. IS elements and transposons. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):241–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völker T. A., Iida S., Bickle T. A. A single gene coding for resistance to both fusidic acid and chloramphenicol. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]