Abstract
Amyloid-β (Aβ) protein causes neurotoxicity and its abnormal aggregation into amyloid is a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Cellular proteins able to interact with Aβ or its precursor, AβPP (amyloid-β protein precursor), may regulate Aβ production and neurotoxicity. We identified a brain-enriched type I transmembrane protein, tomoregulin (TR), that directly binds Aβ and Aβ oligomers (AβO). TR co-immunoprecipitated with Aβ and AβO in cultured cells and co-localized with amyloid plaques and intraneuronal Aβ in the 5xFAD AD mouse model. TR was also enriched in astrocytic processes reactive to amyloid plaques. Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy studies showed that the extracellular domain of TR binds to AβO with a high affinity (KD = 76.8 nM). Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy also demonstrated a physical interaction between spin-labeled Aβ and the TR extracellular domain in solution. Furthermore, TR also interacted with AβPP and enhanced its cleavage by α-secretase. Both cellular expression of TR and application of recombinant TR extracellular domain protected N2a neurons from AβO-induced neuronal death. These data provide first evidence that neuronal and astrocytic expression of TR is intimately related to Aβ metabolism and toxicity, and could be neuroprotective through its direct interaction with Aβ and AβPP.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, amyloid, binding, neuroprotection, neurotoxicity, tomoregulin
INTRODUCTION
Amyoid-β(Aβ), a amphipathic protein derived from proteolytic processing of the amyloid-β protein precursor (AβPP), self aggregates into amyloid fibrils and deposits as amyloid plaques, one of the pathological hallmarks of AD. Although quite heterogeneous at its carboxyl termini, Aβ peptides have been characterized based on two major forms, Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 [1]. In addition to fibrillar forms, Aβ exists in various smaller assemblies in AD brains, which may mediate diverse toxic effects at different stages of the disease. Although these smaller aggregates, variously named as oligomers (AβO), protofibrils, amyloid pores, or AD diffusible ligands, have been considered transient or metastable intermediates in fibril formation [2], some of them may not be obligate intermediates in the fibril formation pathway and can be stable [3, 4]. Importantly, in vitro and in vivo studies have revealed that the build-up of soluble AβO may be an early and central event in the pathogenesis of AD [5–8]. The strong and rapidly disruptive effect of AβO on synaptic plasticity and neuronal integrity is hypothesized to cause memory problems in AD [6, 7, 9–11]. Initial oligomerization of Aβ appears to occur intraneuronally [12]; extracellular AβO could be derived from intraneuronal AβO [12, 13]. It is therefore conceivable that during the process of AβO formation, release, and cellular targeting, several proteins may interact with AβO to regulate or mediate its aggregation, transport, diffusion, and action on cells, thereby modifying its toxicity.
In an effort to seek potential endogenous modifiers of Aβ toxicity, we discovered a protein, tomoregulin (TR), that is able to bind AβO and inhibit its toxicity. TR, also named TMEFF2, TENB2, TPEF, and HPP1, is a type I transmembrane protein expressed in embryo but only selectively expressed in adult nervous system and prostate. It contains a short cytoplasmic tail and a unique extracellular region (ectodomain) with one epidermal growth factor-like motif and two follistatin-like domains (Fig. 1). The ectodomain is released by a membrane-anchored metalloproteinase ADAM17, and could be a ligand for erbB-4- or erbB-4-related receptor tyrosine kinase [14, 15]. TR is widely expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as by the enteric neurons of the gastrointestinal tract [16, 17]. Despite its selective expression pattern, the physiological and pathological roles of TR in the brain remain little studied. Here we report that TR could be an endogenous modulator of AβO actions including its toxicity. In addition, TR is associated with cellular AβPP and enhances the generation of a secreted form of AβPP released by α-secretase.
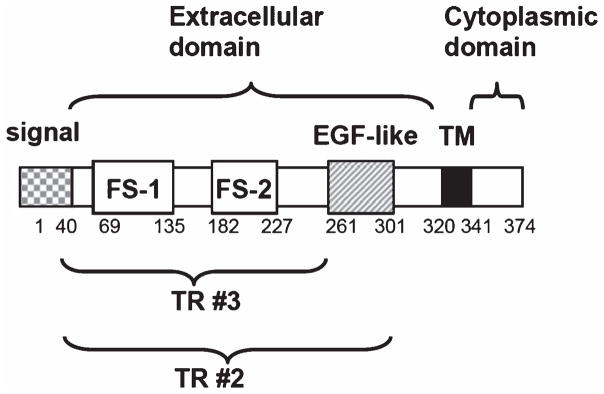
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrations of the TR domain structure in relation to the amino acid number and the expression constructs used in this study. EGF, epidermal growth factor; FS-1, follistatin-like domain 1; FS-2, follistatin-like domain 2; TM, transmembrane domain.
MATRIALS AND METHODS
Materials
The polyclonal antibody against full-length, recombinant TR was obtained from R&D System. Mouse monoclonal antibody 48G2 was raised against the recombinant human TR using hybridoma technology at Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals (San Francisco, CA). Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy (SPR) showed that 48G2 in the flow phase bound immobilized TR with a high affinity (KD = 0.88 nM). The affinity is comparable to a TR-specific monoclonal antibody 2H8 (KD = 1.24 nM), which was previously characterized extensively [18]. In an ELISA assay, 48G2 bound TR with an EC50 value of 0.17 nM, but showed minimal binding to human TMEFF1, a TR-related protein [19]. Furthermore, 48G2 bound to the surface of human TR-transfected PC-3 (human prostatic cancer) cells, assessed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and by whole-cell binding assay (data not shown).
Monoclonal antibodies 4G8 and 6E10 against Aβ were purchased from Signet Laboratories (Dedham, MA). The carboxyl end-specific polycloncal anti-Aβ40 and anti-Aβ42 were purchased from Calbiochem. The polyclonal antibody against mouse TMEFF1 was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX). Highly cross-adsorbed Alexa Fluor-488 or 594-conjugated F(ab′)2 fragments of anti-mouse or anti-goat IgG (H + L) were from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR, USA). Affinity purified goat anti-mouse and anti-goat IgG (H + L) conjugated to horseradish peroxidase were from Jackson Laboratories (Ben Harbor, ME). The polyclonal antibodies specific for the secreted forms of AβPP, which are AβPPα released by α-secretase and AβPPβ released by β-secretase, were provided by Dr. Inhee Mook-Jung at the Seoul National University College of Medicine. Spin-labeled Aβ1-40 containing the TOAC nitroxide at position 26 was synthesized as previously described [20, 21].
TR cDNA construct and expression
The TR cDNA clone was purchased from Open Biosystems (clone#23671). For mammalian expression, the PCR fragment obtained using TOPO sequence containing primer set (5′-CAC CAT GGT GCT GTG GGA GTC C-3′/5′-GAT TAA CCT CGT GGA CGC-3′) was cloned into pcDNA3.1-Directional TOPO Expression vector (Invitrogen). The accuracy of the TOPO/PCR cloning was later confirmed by sequencing. The TR-expressing plasmid was transiently transfected into N2a or N2a-AβPP cells using Lipofectamine LTX and Plus reagent (Invitrogen). For bacterial expression, the PCR fragment obtained using TOPO sequence containing primer sets (5′-C ACC TGC TCT GGT TAT GAT GAC AGA-3′ paired with 5′-TCA TTC ACA GTG TTG TCC AGT ATA AC-3′ or 5′-TCA TTC TCT GGC ACT TTC TTC TAA-3′ to generate TR#2 or TR#3, respectively, see Fig. 1) was cloned into pET100/D-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) and the accuracy of the cloning was confirmed by sequencing. BL21 cells were transformed with the plasmids and protein expression was induced by Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). Expressed TR fragments were purified using HiTrap 1 ml Chelating HP column (Pharmacia Inc.) charged with 0.1 M NiSO4. Briefly, BL21 cells harboring TR plasmids were cultured overnight in 3 ml of LB medium and then transferred to new LB medium with 500 μM of IPTG. The cells were cultured with shacking at 37° for 4 h. The cells were harvested and lysed with Guanidinium Lysis Buffer (Probond Purification System, Invitrogen). Lysates were passed through HiTrap 1 ml Chelating HP column and TR fragments were eluted using His-Select Elution Buffer (Sigma). Imidazole was removed by dialysis and TR fragments were concentrated using Vivaspin4 10K MWCO (Sartorius, Goettingen, Germany)
Cell cultures
MC65 human neuroblastoma cells were grown in the presence of 1 μg/ml tetracycline (TC) as described [22, 23]. The cell toxicity was induced by the removal of TC to induce expression of AβPP-C99 (the carboxyl 99 amino acids of AβPP which gives rise to Aβ after cleavage by β-secretase). To do so, the cells were washed extensively, and plated at a density of 1.2–1.5 × 105 cells/cm2 in Opti-MEM (without phenol-red) from Gibco/BRL (Carlsbad, CA) without serum and without TC. The N2a-AβPP neuroblastoma line expressing AβPP with the Swedish mutation was a gift from Dr. Sangram Sisodia at University of Chicago. The preparation of cell homogenates and western blotting were performed as previously described [23, 24].
5xFAD mice
All experimental protocols were carried out with approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of California Davis. The line Tg6799 5xFAD mice co-express human AβPP695 with the Swedish (K670N, M671L), Florida (I716V), and London (V717I) mutations and human PS1 harboring M146L and L286V mutations was obtained from Dr. Robert Vassar at Northwestern University [25]. Mice were sacrifice and their brains were cut in half sagittally. The left hemispheres were snap frozen. The right hemispheres were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for immunohistochemical studies.
Co-immunoprecipitation
To determine the co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of AβPP or Aβ with TR, cells were lysed in 300 μL of co-IP buffer (0.5% Triton X-100/in Tris-buffered saline, pH 7.4) containing protease inhibitors for 30 min at 4°. After centrifugation at 10,000× g for 15 min, the lysates (supernatants) were pre-cleared with Protein G-Sepharose CL-4B and subsequently were incubated with anti-TR, anti-Aβ, or anti-AβPP antibody overnight at 4°C. The resulting immunocomplexes were precipitated by Protein G-Sepharose CL-4B. In some experiments, the protein complexes were pulled down by anti-His antibody conjugated beads or glutathione sepharose GS4B agarose beads (Pharmacia) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Beads were washed four times (5 min each) at 4° with co-IP buffer before elution. Eluted proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with specified antibodies and Enhanced Chemilumescent (ECL) reagents (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Inc., Piscataway, NJ).
Preparation of unaggregated and oligomeric Aβ solutions
Solutions of seedless, unaggregated Aβ and oligomeric, non-fibrillar Aβ were prepared according to established protocols [9, 26]. Briefly, dried Aβ peptides were first dissolved in ddH2O with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). The solution was dialyzed against 0.1% TFA and lyophilized. Lyophilized peptides were then completely dissolved in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) at room temperature for 1–3 h and lyophilized. The resulting Aβ film was dissolved with DMSO and stored at −20°. To generate unaggregated (mostly monomeric) Aβ solutions, the Aβ stock in DMSO was diluted directly into PBS. To make oligomers, the 10 μM unaggregated Aβ solution was incubated at 4° for 48 h with stirring at 300 RPM. The resulting oligomers were verified by atomic force microscopy as described [23], aliquoted, and stored at −20°.
Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy (SPR)
The method to determine the binding kinetics between TR in the flow phase and AβO(1-42) immobilized on the SPR sensor chip was described in detail in a previous article [27].
Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) of spin-labeled Aβ
EPR measurements were carried out in a JEOL TE-100 X-band spectrometer (JEOL USA, Peabody, MA) fitted with a loop-gap resonator Molecular Specialties, Milwaukee, WI). A fresh stock of Aβ in DMSO was prepared as described above. A solution of mostly unaggregated (monomers and small oligomers) Aβ was then prepared by diluting the peptide stock to a final concentration of 10 μM into either PBS or PBS containing 10 μM of the TR fragment. Immediately after mixing, approximately 5 μl of the sample was loaded into a sealed quartz capillary tube and scanned by EPR. The spectra were obtained by averaging three 2-min scans with a sweep width of 100 G at a microwave power of 2 mW and modulation amplitude of 1 G. All the spectra were recorded at room temperature.
Immunofluorescent staining and confocal microscopy
Immunofluorescence labeling and confocal microscopy for Aβ-immunoreactive aggregates and TR were performed according to our published protocols 23].
Gene silencing by RNA interference
RNAi plasmids (shRNAmir) designed to knock down TR expression and for control transfection were purchased from Open Biosystems. For transfection, cells were plated onto six-well plates and transfected with 2.5 μg of shRNAmir using 12 μL of lipofectamine LTX and Plus reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) for 48 h.
Statistics
We examined the statistical significance of differences between groups by applying one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post-hoc Tukey test or Bonferroni tests, using the SigmaStat 3.1 (Systat Inc. Point Richmond, CA) software program.
RESULTS
TR interacts with Aβ
We immunoprecipitated intracellular Aβ from the MC65 human neuroblastoma cells and used mass spectrometry to identify co-immunoprecipitated proteins. In MC65 cells, the expression of AβPP-C99 and subsequent generation of Aβ was controlled by a promoter activated by withdrawal of TC from the medium. The MC65 culture has been used as a model of neuronal death due to accumulation of intraneuronal Aβ [23, 28], which might play a significant role in the early stage of amyloid cascade in AD [29–31]. Relevant to AD, the intracellular Aβ in MC65 cells aggregates into SDS-stable dimeric, trimeric, and tetrameric units [23], confirmed by mass spectroscopic analysis [32]. These oligomers (AβO) were immunoreactive to A11 [23], an antibody recognizing specifically the conformation of prefibrillary oligomers [26], and anti-Aβ40, an antibody specific to the carboxyl end of Aβ1-40 [23]. The induced generation of AβO in MC65 cells eventually leads to cell death in three days. We lysed MC65 cells in 1% CHAPSO at 24 h after the induction of Aβ generation but prior to the starting of cytotoxicity, and immunoprecipitated Aβ and associated proteins with the 6E10 (anti-Aβ3-8) antibody. Liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis of the immunoprecipitate revealed several non-Aβ proteins. Among them, TR, a predominantly brain and prostate protein, gave the most significant MASCOT scores. TR was previously found extensively in amyloid plaques [33], therefore was studied further.
We confirmed the association of Aβ and TR by determining if Aβ is present in the anti-TR immunoprecipitate from MC65 cell lysate. We used two TR-specific antibodies. 48G2 is a monoclonal antibody that recognizes the ectodomain of TR and its specificity has been extensively characterized by SPR, fluorescence-activated cell sorting, and whole-cell binding assays (see Methods). The second one was a commercially available affinity-purified goat anti-human polyclonal antibody. Both antibodies yielded essentially identical results. Figure 2A shows that Aβ dimer and trimer were present in the anti-TR immunoprecipitate obtained from the MC65 cell lysate. The identification of these Aβ immunoreactive bands in MC65 cells as SDS-stable oligomeric Aβ was previously confirmed [23, 32]. The MC65 cell lysate also contained Aβ tetramer; however, its presence in the anti-TR immunoprecipitate could not be certain because its corresponding band was masked by the immunoglobulins. In contrast, the immunoprecipitates of pre-immune goat IgG and IgG recognizing TMEFF-1, a related protein also enriched in the brain [19], did not contain Aβ, supporting the specificity of our assay.
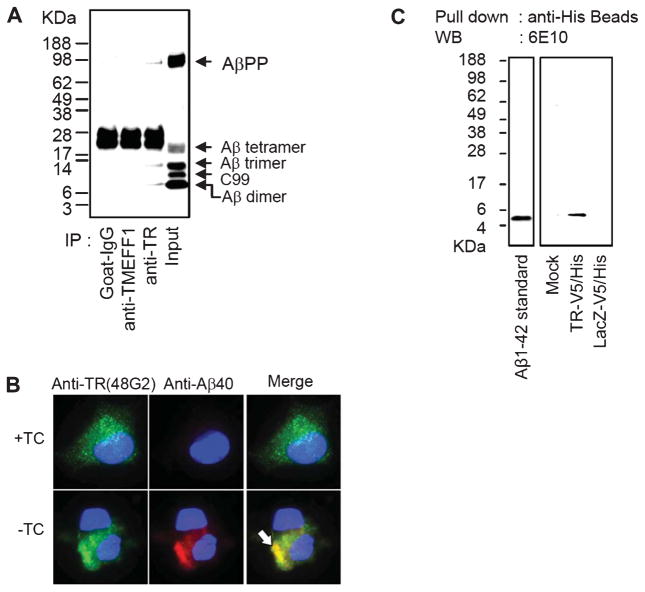
Fig. 2.
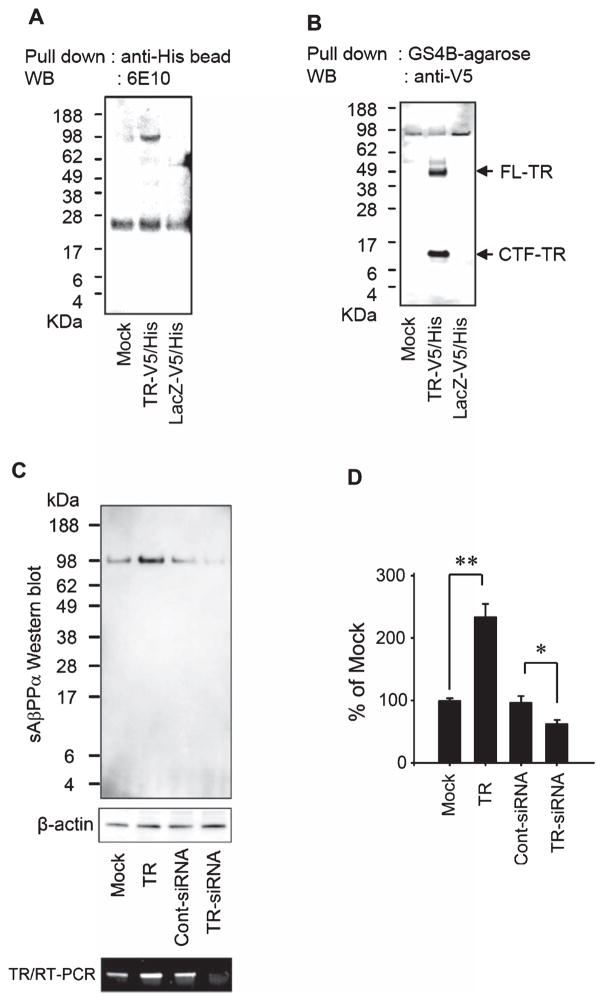
TR is associated with Aβ. A) MC65 cells were induced to express Aβ by withdrawal of TC from the medium for 24 h and were lysed with a lysis buffer containing 1% CHAPS. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with goat IgG (non-specific control), anti-TMEFF1, or anti-TR (goat polyclonal). The lane labeled “Input” contained the input MC65 lysate without immunoprecipitation by an antibody. The immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using 6E10. Aβ dimer, Aβ trimer, and AβPP were co-immunoprecipitated with TR. The non-specific bands around 28 kDa in the first three lanes represent antibody components such as the light chain of IgG, which were not present in the Input lane. B) MC65 cells were cultured in the presence of TC (+TC) or were induced to express Aβ (−TC) for 24 h and were doubly immunostained with anti-TR (green) and anti-Aβ40 (red), and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Representative fluorescent images of cells are shown. Arrows point to Aβ40-positive intraneuronal Aβ aggregates in −TC cells, which were also heavily stained with anti-TR. C) Extracts of N2a cells mock transfected, transfected with TR-V5/His or LacZ-V5/His were incubated with Aβ1-42 in the presence of 1% CHAPSO. The recombinant proteins and associated proteins were then pulled down by anti-His beads. Western blot (WB) using 6E10 showed that Aβ1-42 was pulled down together with recombinant TR.
We previously showed that the neurotoxic events in MC65 cells come from intracellular accumulation of Aβ40 immunoreactive AβO [23]. Co-immunostaining of MC65 cells with anti-TR and anti-Aβ40 at 24 h after Aβ induction showed that TR also colocalized with the aggregates of AβO (Fig. 2B, arrow). In contrast, in control MC65 cells without Aβ induction, anti-TR stained a fine cytoplasmic granular profile, while anti-Aβ40 did not show any positive staining (Fig. 2B, upper panels). This result is consistent with an interaction of TR with Aβ. The granular cytoplasmic rather than a membrane profile of TR immunoreactivity is consistent with previous results in adult human, mouse, and cat neurons [33, 34], and suggests rapid internalization of TR in neuronal cells [18].
To determine if TR also interacts with synthetic Aβ1-42, the other major species of Aβ deposited in AD brains, we expressed in N2a neuroblastoma cells a recombinant TR protein with a C-terminal V5/His tag (TR-V5/His), which consists of simian virus 5/poly-histidine residues to facilitate protein identification and isolation by specific anti-V5 and anti-His antibodies. N2a cells expressing LacZ-V5/His were used as a negative control. After incubating the extracts of the two groups of cells with synthetic Aβ1-42 in the presence of 1% CHAPSO, we pulled down TR with anti-His beads and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by 6E10 western blotting. As shown in Fig. 2C, Aβ1-42 was clearly pulled down by TR-V5/His but not by the negative control LacZ-V5/His.
TR co-localizes with amyloid plaques, intraneuronal Aβ, and reactive astrocytes in the AD model 5xFAD mice
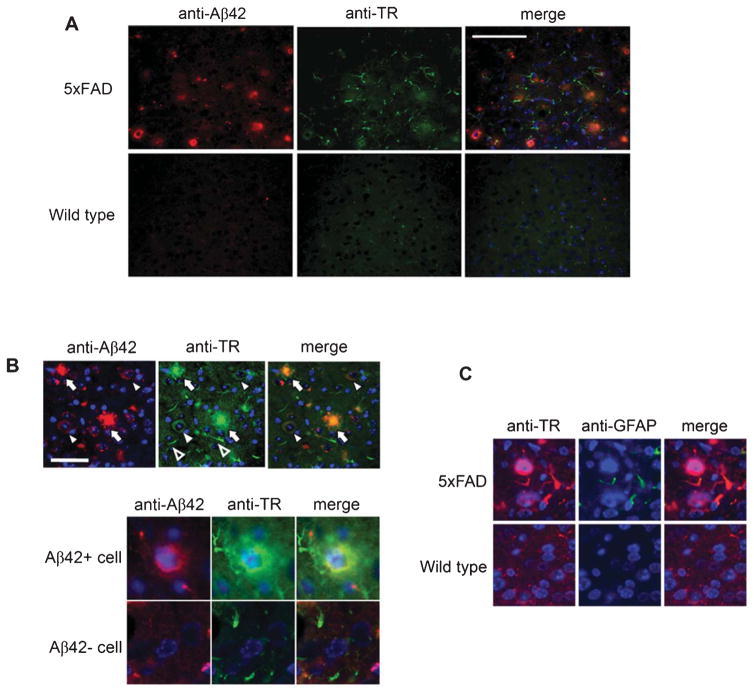
Neurons in 5xFAD mice were engineered to generate a large quantity of Aβ1-42, which results in robust Aβ accumulation and aggregation in the brain [25]. At three months of age, the mice demonstrate numerous small amyloid plaques as well as neurons with cytoplasmic Aβ aggregates including AβO [35]. Immunohistochemical studies showed that TR colocalized extensively with amyloid plaques (Fig. 3A, B). In addition, TR was localized to cytoplasm of neurons, which were also immunoreactive to anti-Aβ42. In contrast, all neurons without intraneuronal Aβ42 invariably had low to non-detectable immunoreactivities to anti-TR (Fig. 3B). Because anti-Aβ42 only recognizes peptides with Aβ42 carboxyl terminal ends, its intraneuronal immunoreactivity does not represent AβPP or other non-Aβ42 AβPP metabolites. Rather, those neurons with intensive Aβ42 immunoreactivity were those with intraneuronal Aβ42 accumulation and aggregation (Fig. 3B, lower panel). This result indicates an upregulation of TR expression in neurons with intraneuronal Aβ. This result also suggests association between TR and Aβ in vivo. In addition, anti-TR immunostained curvilinear processes that appeared to be associated with amyloid plaques (Fig. 3A, B). Double immunostaining for TR and the astrocytic marker GFAP revealed that these were processes of reactive astrocytes that were not seen in non-amyloid regions in 5xFAD mice and not seen in all brain regions of the wild-type littermates (Fig. 3C).
Fig. 3.
TR is associated with amyloid plaques and intraneuronal Aβ, and is expressed in reactive astrocytes in 5xFAD mice. A) Cortical sections of 5xFAD and age-matched wild-type littermate mice were co-immunostained with anti-Aβ42 and anti-TR. Scale bar = 100 μm. B) Three TR-immunoreactive structures are indicated: Arrows: amyloid plaques; Filled arrowheads: neurons with intraneuronal Aβ; and Empty arrowheads: curvilinear profiles. Scale bar = 50 μm. The lower panel shows magnified images of a neuron with intraneuronal Aβ in comparison to one without. C) Co-immunostaining with anti-TR and anti-GFAP showed that the TR-positive curvilinear profiles were processes of reactive astrocytes in the neighborhood amyloid plaques.
TR directly binds Aβ in solution
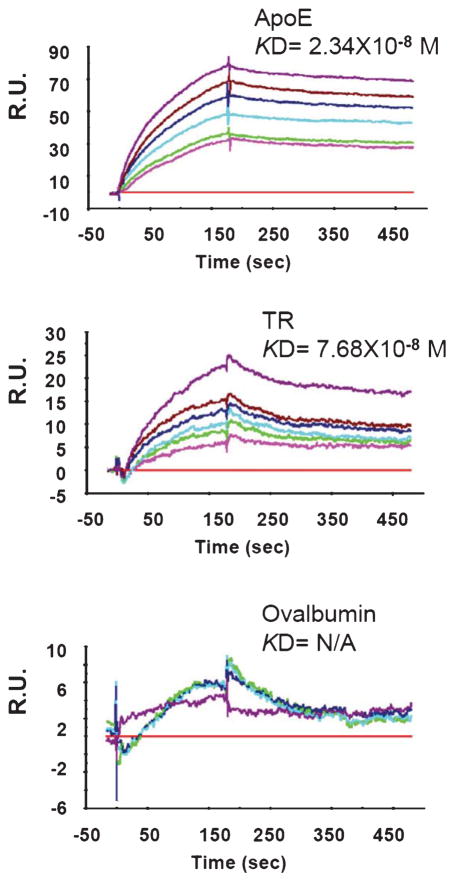
The above data suggest that TR is physically associated with Aβ in extracellular amyloid plaques and in intraneuronal compartments. We asked whether TR directly binds Aβ. For this purpose, we employed a sensitive SPR method with which the binding between TR in the flow phase and the AβO(1-42) immobilized on the sensor chip can be analyzed in real time, as previously described [27]. The size and neurotoxic properties of our AβO(1-42) preparations were analyzed by atomic force microscopy and cell-based neurotoxic assays, as previously described. The result showed that the TR segment containing the extracellular domain (ectodomain) (TR#2 in Fig. 1) directly binds AβO with a high affinity (KD = 76.8 nM). The binding is only slightly weaker than ApoE (KD = 23.4 nM), a protein known to directly bind Aβ and its oligomers [20, 36]. The negative control protein ovalbumin showed no binding to AβO (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
The ectodomain of TR binds AβO with a high affinity. ApoE, TR#2, and ovalbumin applied to the flow phase and their binding to AβO (prepared from the peptide Aβ1-42) immobilized on the chip was analyzed in real time. Shown are representative SPR response curves elicited by indicated protein ligands with a series of concentrations. RU, Response Unit.
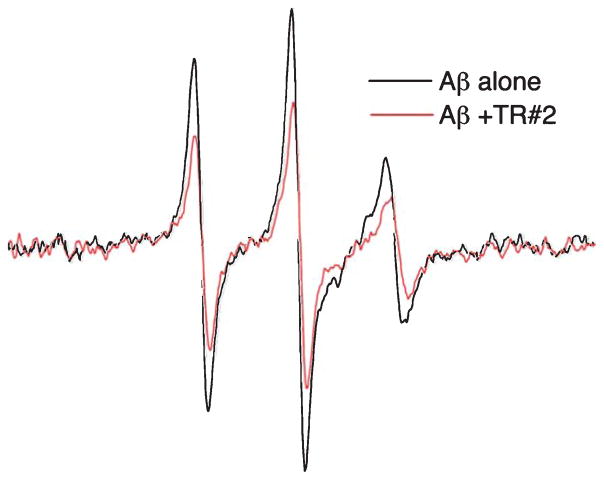
To further investigate the direct interaction between Aβ and TR, we performed EPR spectroscopy to observe the conformational dynamics of the Aβ peptide as a function of TR binding [35, 37]. EPR signals were analyzed from a TOAC nitroxide probe targeted specifically to the 26th residue within the loop domain of Aβ [20]. Aβ containing spin-labeled peptide was previously shown to have a comparable degree of toxicity to N2A cells and a similar particle size distribution as the unlabeled Aβ [20]. We therefore examined whether alteration in the dynamics of the spin-labeled Aβ could provide indication of interaction between the peptide and the recombinant TR extracellular domain (TR#2 in Fig. 1). Our experiment analyzed Aβ in its nascent state, consisting of monomers and small oligomers by introducing Aβ to a final concentration of 10 μM followed by EPR scanning. The EPR results are shown in Fig. 5. In the absence of TR, the EPR spectrum shows a sharp line shape with a correlation time of 1 ns or less, consistent with a small disordered Aβ species [20, 21]. In the presence of TR, however, the EPR spectrum is broadened, indicating a decreased rotational correlation time of the imbedded spin-label. Given the obligate low spin concentrations of these samples, broad features are difficult to resolve in the spectra. Nevertheless, the broadening of the Aβ spectrum upon TR addition appears largely homogeneous. Thus in addition to a restriction in rotational dynamics upon TR binding, a dipolar relaxation among flexible labels likely contributes to the spectral broadening [38]. This suggests that much of the TR-bound peptide in these experiments is in the oligomeric state, with a conformation that maintains the TOAC labels within a close proximity. While we cannot quantitatively ascribe the broadening contributions among a reduction in spin label correlation time, an increase in dipolar spin interaction, or a combination of both, the change in the Aβ EPR spectrum provides evidence for a physical interaction between Aβ and the TR extra-cellular domain.
Fig. 5.
EPR spectra of spin-labeled Aβ (10 μM) in the absence (black trace) and presence (red trace) of the TR ectodomain TR#2 (10 μM). Shown is a scan over a magnetic field of 100 G.
TR also binds AβPP and modulates α-secretase processing of AβPP
Although we started with the goal to search for binding partners for AβO, we found that AβPP was also immunoprecipitated by anti-TR, but not by negative control immunoglobulins (Fig. 2A). We confirmed this association by further co-immunoprecipitation experiments using N2a cells. First, we transfected N2a-AβPP cells, a permanent line of N2a overexpressing AβPP, with plasmids expressing TR-V5/His or LacZ-V5/His, lysed the cells, and incubated the lysates with anti-His beads to pull down the expressed proteins. As shown in Fig. 6A, AβPP was co-immunoprecipitated with TR but not with LacZ. This association should involve the full length or at least the carboxyl segments of TR because the engineered V5/His sequence was located at the carboxyl terminus. Aβ was not co-immunoprecipitated because N2a-AβPP cells generate little amount of Aβ. Next, we examined if full-length AβPP can also pull down TR. We transfected N2a cells (expressing little endogenous AβPP) with a plasmid expressing TR-V5/His or LacZ-V5/His, lysed the cells, and incubated the lysates with recombinant GST-AβPP (expressing full length AβPP) in the presence of 1% CHAPS. GST-AβPP and associated proteins were subsequently pulled down using GS4B agarose beads. Western blotting with the anti-V5 antibody showed that AβPP pulled down proteins of 50–56 kDa. These likely represent the full-length TR (predicted molecular weight of the core peptide: 38 kDa) with various N-linked glycosylation and other post-translational modifications, as shown previously [14]. In addition, there was a small carboxyl-terminal fragment of TR (CTF-TR), which may correspond to the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain of TR after the shedding of the ectodomain (predicted molecular weight: 8 kDa) (Fig. 6B).
Fig. 6.
TR is associated with AβPP and affects the level of sAβPPα. A) N2a-AβPP cells were mock-transfected (Mock), transfected with TR-V5/His or with LacZ-V5/His. The recombinant proteins and associated proteins in the cell extracts were then pulled down by anti-His beads. Western blot (WB) using 6E10 showed that AβPP was pulled down together with recombinant TR. B) Extracts of N2a cells mock transfected, transfected with TR-V5/His or LacZ-V5/His were incubated with GST-AβPP. The recombinant GST-AβPP and associated proteins were then pulled down by GS4B agarose beads. WB using anti-V5 showed that two TR-related proteins were pulled down together with AβPP, which correspond to the full-length (FL-TR) and a C-terminal fragment (CTF-TR) of TR. C) N2a-AβPP cells were mock-transfected, transfected with a TR-expressing plasmid, a control siRNA, or a siRNA specific to TR to downregulate TR. The level of sAβPPα in the 24-h conditioned medium was evaluated by WB using an antibody specific to sAβPPα. The level of TR transcript was estimated by RT-PCR. D) The bar graph shows the band intensity of sAβPPα in each condition adjusted by the respective band intensity of β-actin and then normalized to that of mock transfection (Mock) in the WB. n = 3, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001.
Due to the association of cellular AβPP with TR, especially that the metalloproteinase ADAM17 that cleaves TR also functions as an α-secretase to cleave AβPP, we asked if expression of TR alters AβPP metabolism. Figure 6C and D shows that plasmid-directed expression of TR in N2a-AβPP cells increased the level of the secreted ectodomain of AβPP cleaved by α-secretase (sAβPPα), while downregulation of TR by a siRNA decreased the level of sAβPPα in the conditioned medium. We also evaluate the influence of TR expression on the level of sAβPPβ (the secreted ectodomain of AβPP cleaved by β-secretase) but did not find significant changes following alterations of TR expression (data not shown).
TR protects neurons from Aβ-induced toxicity
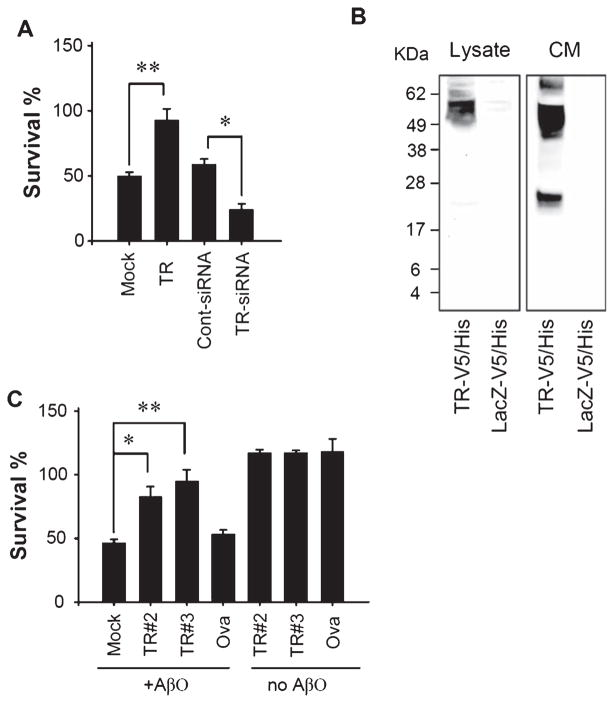
Aβ-induced neurtoxicity has been widely accepted as a central event in AD pathogenesis. In particular, accumulating evidence supports that AβO is likely the most toxic species. Because TR directly interacts with AβO, we asked if the presence of TR alters Aβ neurtoxicity. N2a cells have been a widely used model for testing AβO toxicity [9] and was used to evaluate the effect of TR. Overexpression of TR in N2a cells almost completely protected neurons from death induced by AβO added to the culture media. In contrast, when the endogenous TR was downregulated to 20–30% of the control level by a siRNA (Fig. 6C), the AβO-induced neuronal death was significantly enhanced (Fig. 7A). This result indicates that TR is able to blocks AβO-induced neurotoxicity, likely via its interaction with AβO. The mechanism for this protective effect may include binding of AβO to TR on the cell surface or to TR released into the medium, because we also detected an increased level of TR in the conditioned medium of N2a after overexpressing TR (Fig. 7B). Indeed, co-application of two recombinant TR extra-cellular segments, TR#2 and TR#3 (Fig. 1), with AβO to the culture medium also blocked AβO-induced neuronal death. Co-application of a negative control protein ovalbumin showed no such effect (Fig. 7C). Because the EGF-like domain in TR#2 conferred no additional protective effect compared to TR#3 without this domain, this result suggests that the amino acid sequence N-terminal to the EGF-like domain is required for neuroprotection.
Fig. 7.
TR protects neurons from Aβ-induced neurotoxicity. A) N2a cells were mock-transfected, transfected with a TR-expressing plasmid, a control siRNA, or a siRNA specific to TR, and then treated with 1 μM AβO(1-42) for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay and presented as % survival relative to solvent treated controls (set as 100% survival). B) The conditioned media (CM) from N2a cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were analyzed by western blot using anti-V5. TR fragments were abundantly present in the CM of cells expressing TR. C) N2a cells were treated with 1 μM AβO(1-42) in the presence of the indicated proteins for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay and presented as % survival relative to solvent treated controls (set as 100% survival). n = 3, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001.
DISCUSSION
Proteins of different functional categories have been found to bind Aβ in the extracellular or intracellular milieu and mediate various cellular effects of Aβ. These include apolipoproteins, membrane receptors, extracellular matrix components, molecular chaperons, adhesion molecules, and intracellular enzymes. A large majority of these identified Aβ-binding proteins were shown to be required for neurotoxicity. Examples of putative membrane receptors mediating Aβ neurotoxicity include the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) [39], the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRα7) [40], cellular prion protein [41, 42], and interestingly, AβPP, the precursor of Aβ [43]. TR, similar to AβPP, is a type I transmembrane protein; our data imply that it could also serve as a membrane receptor for Aβ aggregates. Also similar to AβPP, the secreted ectodomain of TR can bind to Aβ aggregates. Moreover, TR binds full-length AβPP and modulates α-secretase processing of AβPP. This binding might involve residues of TR carboxyl to the ectodomain because a CTF-TR fragment was also pulled down by AβPP (Fig. 6B). However, immunoprecipitation of TR, either ectodomain or full-length, failed to pull down AβPP-C99 (Figs. 2 and 6) which spans the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of AβPP, even in the MC65 line overexpressing AβPP-C99. It is possible that the conformation and cellular compartmentalization of AβPP-C99 may be different from the full-length AβPP and therefore preclude its binding to TR. Further studies are required to delineate the mechanisms of binding between TR and Aβ as well as between TR and AβPP.
Distinct from AβPP and all the above putative Aβ receptors which mediate Aβ toxicity, TR is unique in its ability to protect neurons from Aβ toxicity. Our data suggestthatneuroprotectionislikelyduetotheabilityof TR to bind AβO with a high affinity and neutralize AβO toxicity. Alternatively, TR could inhibit Aβ oligomer or fibril formation, which is not explored here. The other possible mechanisms of neuroprotection include the neurotrophic actions of the secreted ectodomain of TR and sAβPPα, the production of which can be enhanced by expression of TR. The finding that TR is physically associated with cellular AβPP and TR expression enhances α-secretase cleavage of AβPP can have two implications. First, because α-secretase cleaves AβPP in the middle of the Aβ sequence to preclude the production of Aβ, TR expression may therefore reduce Aβ production. Our ELISA method was not sensitive enough to measure the small amount of Aβ released by N2a-AβPPcellsandmoresensitivemethodsareneeded to address this possibility. Second, because ADAM17 as an α-secretase cleaves both AβPP and TR, TR could serve as an anchor for α-secretase processing of AβPP. Our results should prompt further studies on the mechanisms of TR-Aβ/TR-AβPP interactions.
Most studies regarding TR functions so far have been concerned with its role in tumor growth because of its overexpression in prostate cancer and a variety of other cancers. The differential roles of holo-TR and secreted TR ectodomain in regulating prostatic cancer growth were reported [44]. In contrast, except for the observation that the ectodomain of TR increased survival of cultured hippocampal and mesencephalic neurons [16], little is known about the function of TR in the nervous system. Using subtractive hybridization, Siegel et al. identified TR as one of the two genes possibly related to initiation of primary dendrites seen in normal newborn and a model of GM2 gangliosidosis [34]. TR knockout mice were born normal, but showed growth retardation and died around weaning age. However, no structural abnormalities in the brain, the spinal cord, the enteric nervous system, or the prostate were found to explain the premature death [45]. Relevant to AD, TR immunoreactivity was found extensively within individual amyloid plaques and pervasively in plaques throughout human AD cortices [33], consistent with our findings in 5xFAD mice, further supporting the physical association of TR with Aβ aggregates. Intriguingly, the same investigators failed to show TR immunoreactivity in the plaques of a line of presenilin-1 (PS1)/AβPP mouse model of AD [33], indicating that some PS1/AβPP models may not have amyloid plaques fully representing those of humans.
Aβ deposition appears to enhance TR expression in reactive astrocytes. This could provide an interesting non-neuronal mechanism to regulate Aβ metabolism and toxicity. Two proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), were shown to induce release of the TR ectodomain by A172 human glioma cells, which suggests a role of TR in tissue growth and repair following neuroinflammation [46]. The Aβ-initiated neuroinflammation is known to produce TNF-α and IL-1β; this, together with overexpression of TR in astrocytes, would lead to increased extracellular level of TR ectodomain, which would bind AβO with a high affinity. This mechanism could contribute to neutralization of Aβ toxicity, enhanced internalization of Aβ, and amyloid plaque formation. In summary, our data provide the first line of evidence to suggest that TR is a brain-enriched endogenous modulator of Aβ neurotoxicity and an enhancer of α-secretase processing of AβPP.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the UC Davis Alzheimer’s Disease Center (AG010129), and NIH grants AG025500 and AG031362.
Authors’ disclosures available online (http://j-alz.com/manuscript-disclosures/15-0318r1).
References
- 1.Masters CL, Selkoe DJ. Biochemistry of Amyloid beta-Protein and Amyloid Deposits in Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2:a006262. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Caughey B, Lansbury PT. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: Separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.010302.081142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Necula M, Kayed R, Milton S, Glabe CG. Small molecule inhibitors of aggregation indicate that amyloid beta oligomerization and fibrillization pathways are independent and distinct. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:10311–10324. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608207200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Glabe CG. Structural classification of toxic amyloid oligomers. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:29639–29643. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800016200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lambert MP, Barlow AK, Chromy BA, Edwards C, Freed R, Liosatos M, Morgan TE, Rozovsky I, Trommer B, Viola KL, Wals P, Zhang C, Finch CE, Krafft GA, Klein WL. Diffusible, nonfibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:6448–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.11.6448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lesne S, Koh MT, Kotilinek L, Kayed R, Glabe CG, Yang A, Gallagher M, Ashe KH. A specific amyloid-beta protein assembly in the brain impairs memory. Nature. 2006;440:352–357. doi: 10.1038/nature04533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ. Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med. 2008;14:837–842. doi: 10.1038/nm1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Roychaudhuri R, Yang M, Hoshi MM, Teplow DB. Amyloid beta-protein assembly and Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:4749–4753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800036200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dahlgren KN, Manelli AM, Stine WB, Jr, Baker LK, Krafft GA, LaDu MJ. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-beta peptides differentially affect neuronal viability. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32046–32053. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201750200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lacor PN, Buniel MC, Chang L, Fernandez SJ, Gong Y, Viola KL, Lambert MP, Velasco PT, Bigio EH, Finch CE, Krafft GA, Klein WL. Synaptic targeting by Alzheimer’s-related amyloid beta oligomers. J Neurosci. 2004;24:10191–10200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3432-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Walsh DM, Tseng BP, Rydel RE, Podlisny MB, Selkoe DJ. The oligomerization of amyloid beta-protein begins intracellularly in cells derived from human brain. Biochemistry. 2000;39:10831–10839. doi: 10.1021/bi001048s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Oddo S, Caccamo A, Smith IF, Green KN, LaFerla FM. A dynamic relationship between intracellular and extracellular pools of Abeta. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:184–194. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Uchida T, Wada K, Akamatsu T, Yonezawa M, Noguchi H, Mizoguchi A, Kasuga M, Sakamoto C. A novel epidermal growth factor-like molecule containing two follistatin modules stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of erbB-4 in MKN28 gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;266:593–602. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ali N, Knauper V. Phorbol ester-induced shedding of the prostate cancer marker transmembrane protein with epidermal growth factor and two follistatin motifs 2 is mediated by the disintegrin and metalloproteinase-17. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:37378–37388. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702170200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Horie M, Mitsumoto Y, Kyushiki H, Kanemoto N, Watanabe A, Taniguchi Y, Nishino N, Okamoto T, Kondo M, Mori T, Noguchi K, Nakamura Y, Takahashi E, Tanigami A. Identification and characterization of TMEFF2, a novel survival factor for hippocampal and mesencephalic neurons. Genomics. 2000;67:146–152. doi: 10.1006/geno.2000.6228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Heanue TA, Pachnis V. Expression profiling the developing mammalian enteric nervous system identifies marker and candidate Hirschsprung disease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:6919–6924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602152103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhao XY, Liu HL, Liu B, Willuda J, Siemeister G, Mahmoudi M, Dinter H. Tomoregulin internalization confers selective cytotoxicity of immunotoxins on prostate cancer cells. Transl Oncol. 2008;1:102–109. doi: 10.1593/tlo.08124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kanemoto N, Horie M, Omori K, Nishino N, Kondo M, Noguchi K, Tanigami A. Expression of TMEFF1 mRNA in the mouse central nervous system: Precise examination and comparative studies of TMEFF1 and TMEFF2. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;86:48–55. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(00)00257-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Petrlova J, Hong HS, Bricarello DA, Harishchandra G, Lorigan GA, Jin LW, Voss JC. A differential association of Apolipoprotein E isoforms with the amyloid-beta oligomer in solution. Proteins. 2011;79:402–416. doi: 10.1002/prot.22891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Petrlova J, Kalai T, Maezawa I, Altman R, Harishchandra G, Hong HS, Bricarello DA, Parikh AN, Lorigan GA, Jin LW, Hideg K, Voss JC. The influence of spin-labeled fluorene compounds on the assembly and toxicity of the abeta peptide. PLoS One. 2012;7:e35443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maezawa I, Jin LW, Woltjer RL, Maeda N, Martin GM, Montine TJ, Montine KS. Apolipoprotein E isoforms and apolipoprotein AI protect from amyloid precursor protein carboxy terminal fragment-associated cytotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2004;91:1312–1321. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maezawa I, Hong HS, Wu HC, Battina SK, Rana S, Iwamoto T, Radke GA, Pettersson E, Martin GM, Hua DH, Jin LW. A novel tricyclic pyrone compound ameliorates cell death associated with intracellular amyloid-beta oligomeric complexes. J Neurochem. 2006;98:57–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jin LW, Shie FS, Maezawa I, Vincent I, Bird T. Intracellular accumulation of amyloidogenic fragments of amyloid-beta precursor protein in neurons with Niemann-Pick type C defects is associated with endosomal abnormalities. Am J Pathol. 2004;164:975–985. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63185-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Oakley H, Cole SL, Logan S, Maus E, Shao P, Craft J, Guillozet-Bongaarts A, Ohno M, Disterhoft J, Van Eldik L, Berry R, Vassar R. Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J Neurosci. 2006;26:10129–10140. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kayed R, Head E, Thompson JL, McIntire TM, Milton SC, Cotman CW, Glabe CG. Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science. 2003;300:486–489. doi: 10.1126/science.1079469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maezawa I, Hong HS, Liu R, Wu CY, Cheng RH, Kung MP, Kung HF, Lam KS, Oddo S, Laferla FM, Jin LW. Congo red and thioflavin-T analogs detect Abeta oligomers. J Neurochem. 2008;104:457–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu Y, Dargusch R, Maher P, Schubert D. A broadly neuroprotective derivative of curcumin. J Neurochem. 2008;105:1336–1345. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:329–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0909142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wirths O, Bayer TA. Intraneuronal Abeta accumulation and neurodegeneration: Lessons from transgenic models. Life Sci. 2012;91:1148–1152. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gouras GK, Willen K, Tampellini D. Critical role of intraneuronal Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease: Technical challenges in studying intracellular Abeta. Life Sci. 2012;91:1153–1158. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.06.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Woltjer RL, Nghiem W, Maezawa I, Milatovic D, Vaisar T, Montine KS, Montine TJ. Role of glutathione in intra-cellular amyloid-alpha precursor protein/carboxy-terminal fragment aggregation and associated cytotoxicity. J Neurochem. 2005;93:1047–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Siegel DA, Davies P, Dobrenis K, Huang M. Tomoregulin-2 is found extensively in plaques in Alzheimer’s disease brain. J Neurochem. 2006;98:34–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Siegel DA, Huang MK, Becker SF. Ectopic dendrite initiation: CNS pathogenesis as a model of CNS development. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2002;20:373–389. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(02)00055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hong HS, Maezawa I, Budamagunta M, Rana S, Shi A, Vassar R, Liu R, Lam KS, Cheng RH, Hua DH, Voss JC, Jin LW. Candidate anti-A beta fluorene compounds selected from analogs of amyloid imaging agents. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:1690–1699. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.09.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD. Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hubbell WL, Cafiso DS, Altenbach C. Identifying conformational changes with site-directed spin labeling. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:735–739. doi: 10.1038/78956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McHaourab HS, Oh KJ, Fang CJ, Hubbell WL. Conformation of T4 lysozyme in solution. Hinge-bending motion and the substrate-induced conformational transition studied by site-directed spin labeling. Biochemistry. 1997;36:307–316. doi: 10.1021/bi962114m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM. RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1996;382:685–691. doi: 10.1038/382685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang HY, Lee DH, D’Andrea MR, Peterson PA, Shank RP, Reitz AB. beta-Amyloid(1-42) binds to alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with high affinity. Implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5626–5632. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lauren J, Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Gilbert JW, Strittmatter SM. Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-beta oligomers. Nature. 2009;457:1128–1132. doi: 10.1038/nature07761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Um JW, Nygaard HB, Heiss JK, Kostylev MA, Stagi M, Vortmeyer A, Wisniewski T, Gunther EC, Strittmatter SM. Alzheimer amyloid-beta oligomer bound to postsynaptic prion protein activates Fyn to impair neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:1227–1235. doi: 10.1038/nn.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lorenzo A, Yuan M, Zhang Z, Paganetti PA, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Mautino J, Vigo FS, Sommer B, Yankner BA. Amyloid beta interacts with the amyloid precursor protein: A potential toxic mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:460–464. doi: 10.1038/74833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chen X, Overcash R, Green T, Hoffman D, Asch AS, Ruiz-Echevarria MJ. The tumor suppressor activity of the transmembrane protein with epidermal growth factor and two follistatin motifs 2 (TMEFF2) correlates with its ability to modulate sarcosine levels. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16091–16100. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.193805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen TR, Wang P, Carroll LK, Zhang YJ, Han BX, Wang F. Generation and characterization of Tmeff2 mutant mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;425:189–194. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lin H, Wada K, Yonezawa M, Shinoki K, Akamatsu T, Tsukui T, Sakamoto C. Tomoregulin ectodomain shedding by proinflammatory cytokines. Life Sci. 2003;73:1617–1627. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(03)00514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]