Abstract
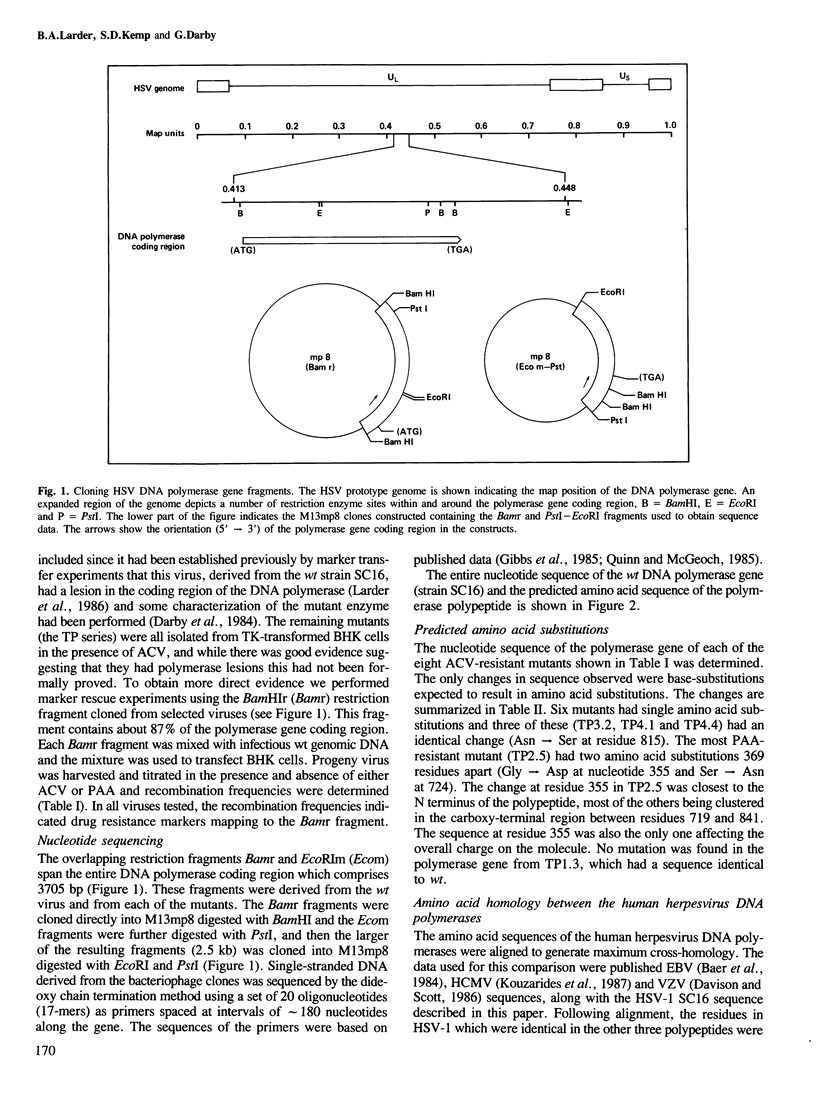
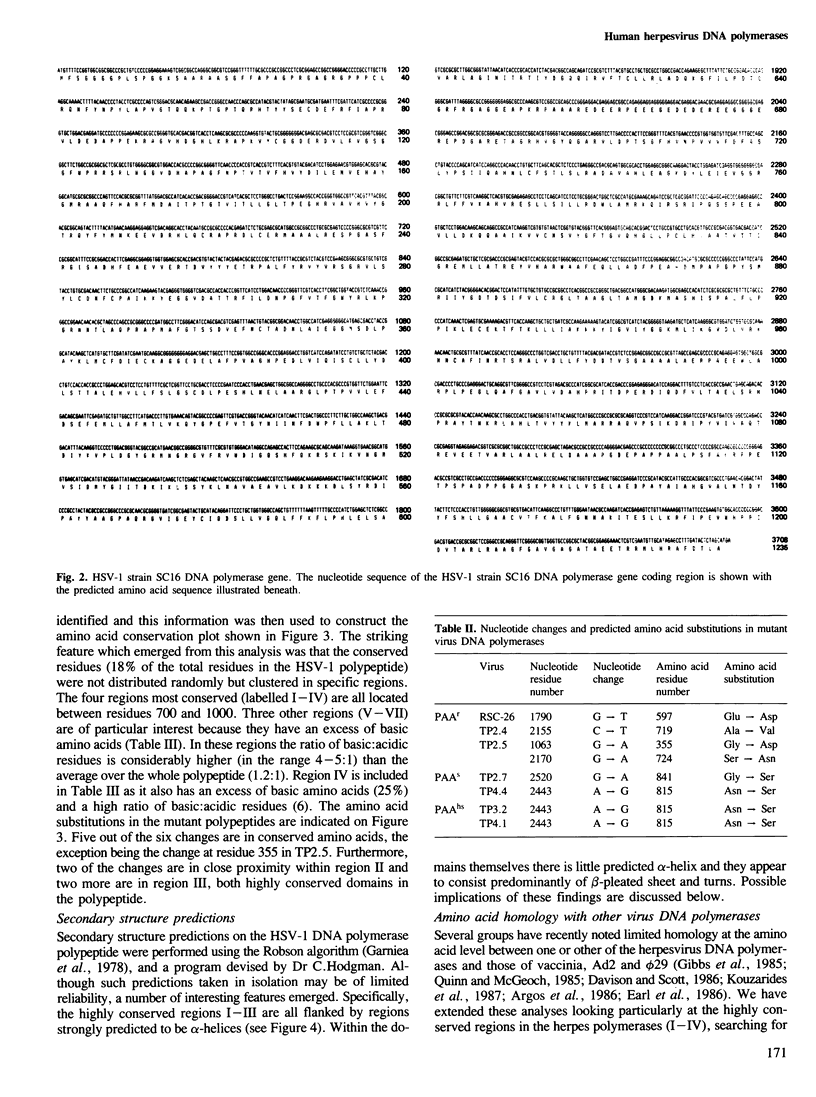
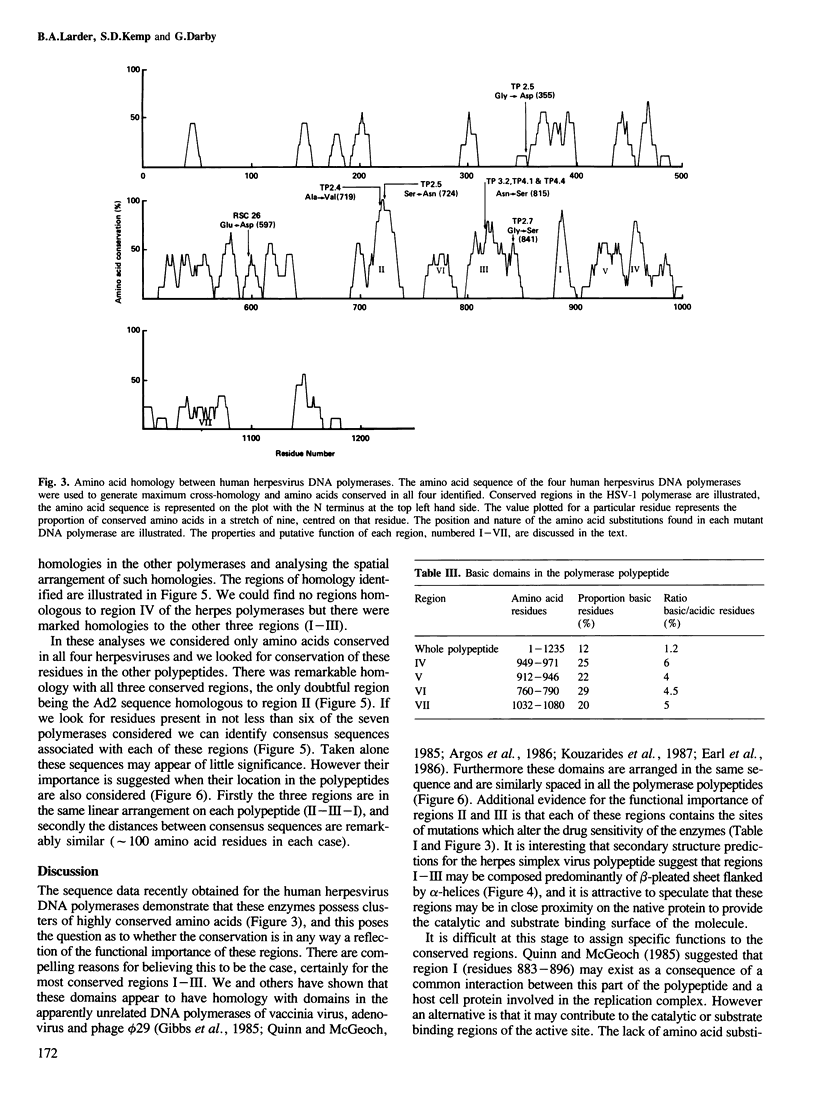
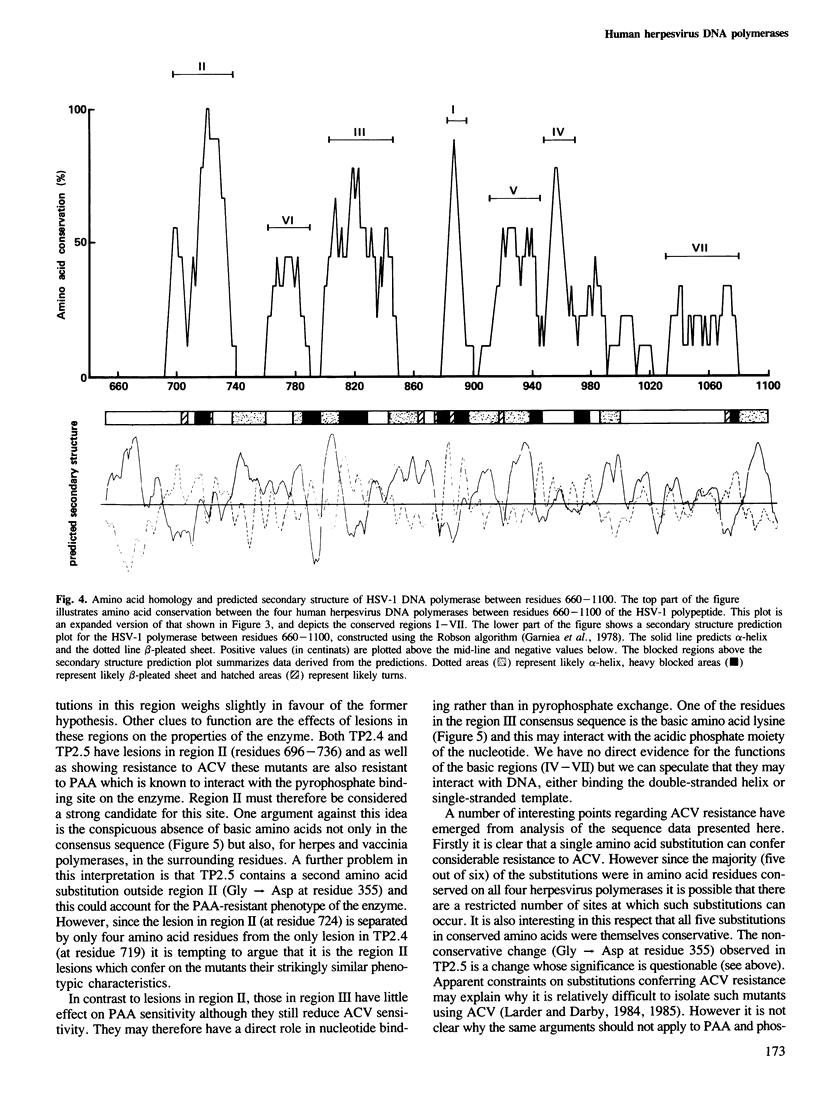
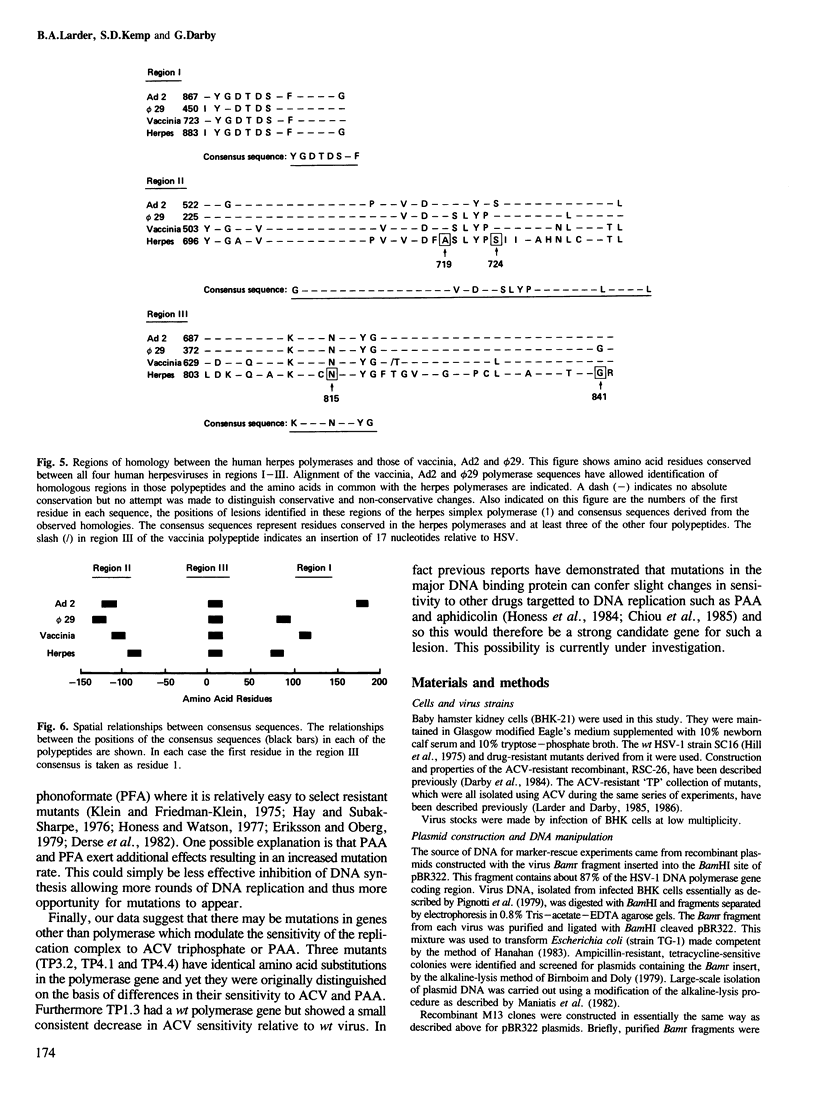
Analysis of the lesions in several drug-resistant DNA polymerase mutants of herpes simplex virus along with comparative analysis of the published polymerase sequences of other human herpesviruses has shown that most lesions (five out of six) are substitutions at amino acid residues conserved in all four polymerases. Furthermore, the majority of lesions are in regions of the polypeptide where there are marked clusterings of conserved residues. On the basis of these data we have identified several domains within the polypeptide which we believe may have important functional roles in the action of the enzyme. The apparent restriction in the potential sites of lesions conferring drug resistance may explain the difficulty in selecting such mutants using acyclovir (ACV) in culture and their failure to emerge so far during ACV therapy. Extension of the comparative analysis to the polymerases of adenovirus type 2, vaccinia virus and phage phi 29 suggests that these enzymes also possess domains homologous to those most conserved in the herpes polymerases (regions I-III) and that these domains have a similar linear spatial distribution on the polypeptides. The results are discussed in relation to the known function of the DNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF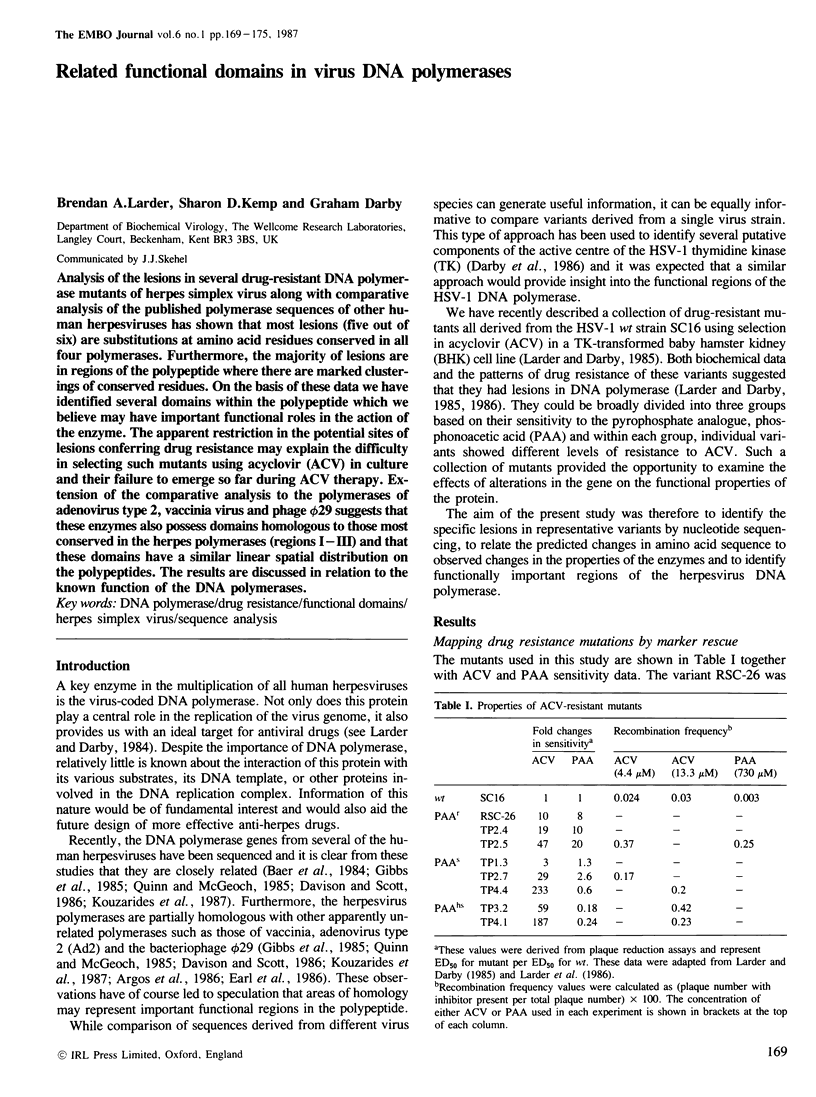

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Tucker A. D., Philipson L. Primary structural relationships may reflect similar DNA replication strategies. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):208–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou H. C., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Mutations in the herpes simplex virus major DNA-binding protein gene leading to altered sensitivity to DNA polymerase inhibitors. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby G., Churcher M. J., Larder B. A. Cooperative effects between two acyclovir resistance loci in herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):838–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.838-846.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. Characterization of the DNA polymerases induced by a group of herpes simplex virus type I variants selected for growth in the presence of phosphonoformic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10251–10260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Jones E. V., Moss B. Homology between DNA polymerases of poxviruses, herpesviruses, and adenoviruses: nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Oberg B. Characteristics of herpesvirus mutants resistant to phosphonoformate and phosphonoacetate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):758–762. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Sciaky D., Gelinas R. E., Bing-Dong J., Yen C. E., Kelly M. M., Bullock P. A., Parsons B. L., O'Neill K. E., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequences from the adenovirus-2 genome. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13475–13491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Larder B. A., Inglis M. M. Evidence that the 'active centre' of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase involves an interaction between three distinct regions of the polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):753–758. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 that are resistant to phosphonoacetic acid induce altered DNA polymerase activities in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):145–148. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Field H. J., Blyth W. A. Acute and recurrent infection with herpes simplex virus in the mouse: a model for studying latency and recurrent disease. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):341–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Purifoy D. J., Young D., Gopal R., Cammack N., O'Hare P. Single mutations at many sites within the DNA polymerase locus of herpes simplex viruses can confer hypersensitivity to aphidicolin and resistance to phosphonoacetic acid. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. J., Friedman-Kien A. E. Phosphonoacetic acid-resistant herpes simplex virus infection in hairless mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G. Selection and characterisation of acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1 mutants inducing altered DNA polymerase activities. Virology. 1985 Oct 30;146(2):262–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G. Susceptibility to other antiherpes drugs of pathogenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected for resistance to acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):894–898. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G. Virus drug-resistance: mechanisms and consequences. Antiviral Res. 1984 Apr;4(1-2):1–42. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(84)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Lisle J. J., Darby G. Restoration of wild-type pathogenicity to an attenuated DNA polymerase mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2501–2506. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatti P. F., Cassai E., Meneguzzi G., Chenciner N., Milanesi G. Herpes simplex virus DNA isolation from infected cells with a novel procedure. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Nucleotide sequence of the major early region of bacteriophage phi 29. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



