Abstract
The translation of polycistronic mRNAs in mammalian cells was studied. Transcription units, constructed to contain one, two or three open reading frames (ORFs), were introduced stably into Chinese hamster ovary cells and transiently into COS monkey cells. The analysis of mRNA levels and protein synthesis in these cells demonstrated that the mRNAs transcribed were translated to generate multiple proteins. The efficiency of translation was reduced approximately 40- to 300-fold by the insertion of an upstream ORF. The results support a modified 'scanning' model for translation initiation which allows for translation initiation at internal AUG codons. High-level expression of human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor was achieved utilizing a vector that contains a polycistronic transcription unit encoding an amplifiable dihydrofolate reductase marker gene in its 3' end. Thus, polycistronic expression vectors can be exploited to obtain high-level expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF
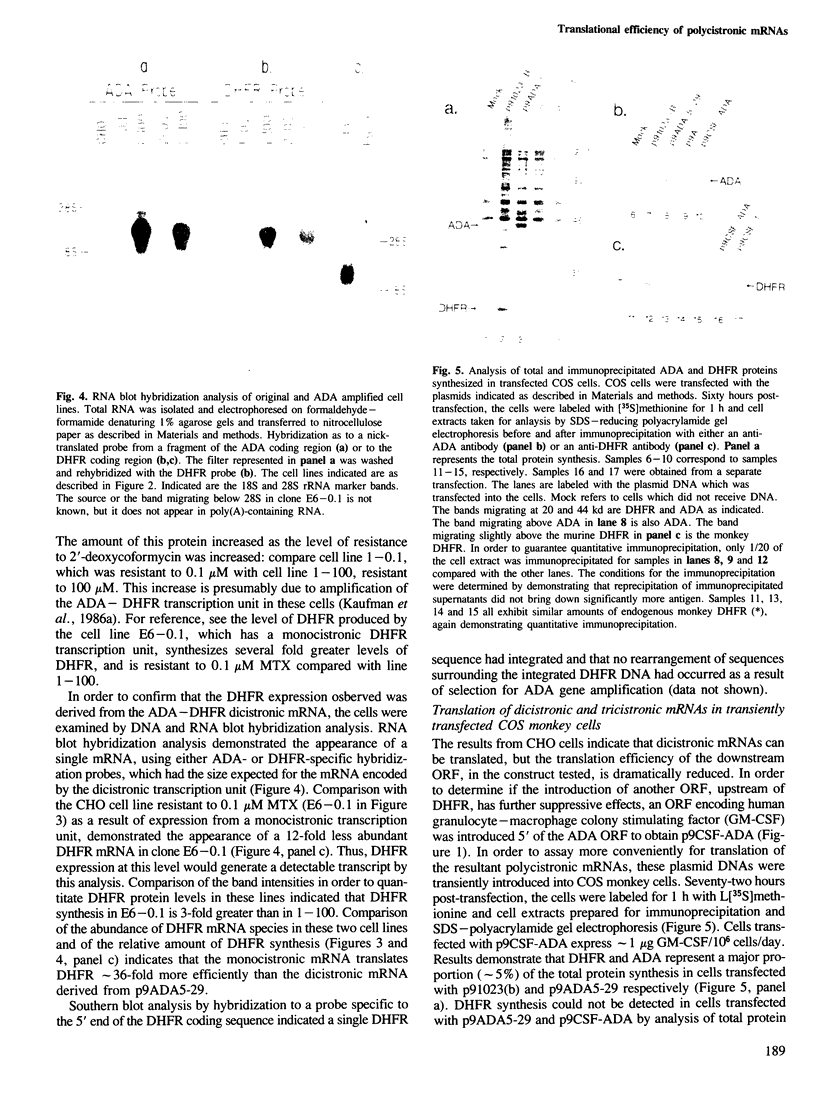

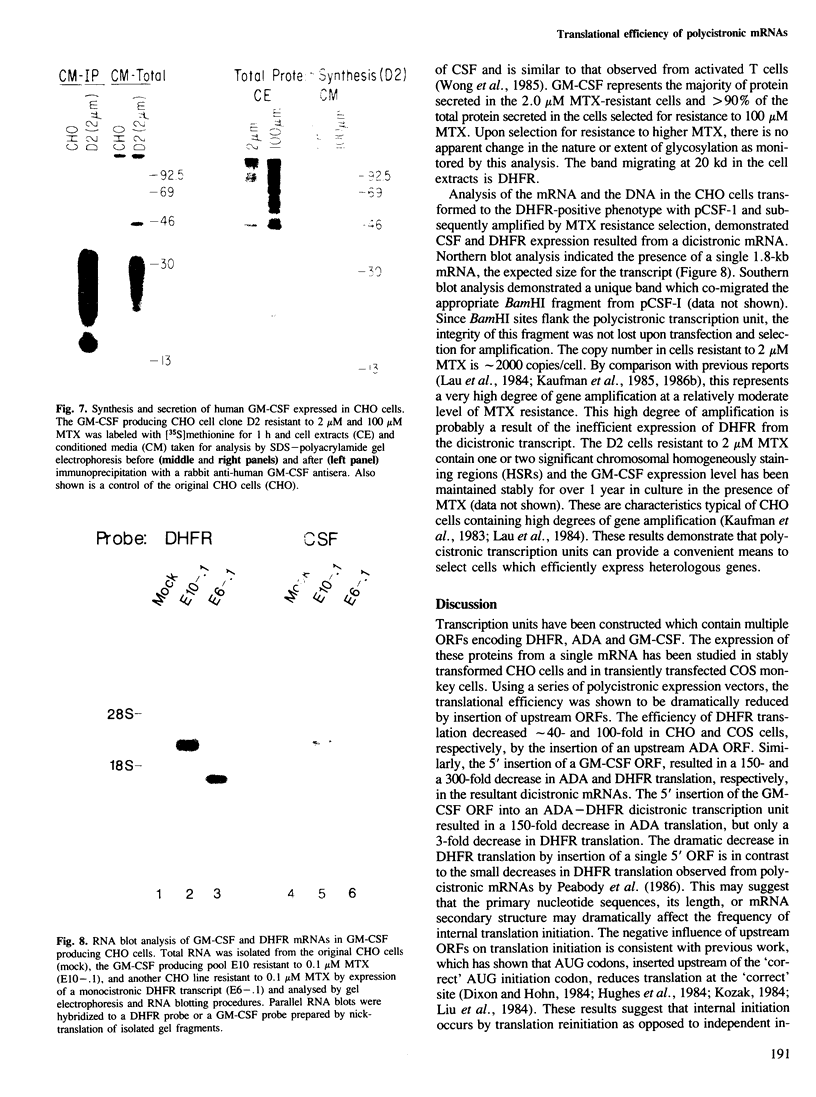


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos J. L., Polder L. J., Bernards R., Schrier P. I., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J., van Ormondt H. The 2.2 kb E1b mRNA of human Ad12 and Ad5 codes for two tumor antigens starting at different AUG triplets. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90366-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerx-van Haaster C. M., Akashi H., Auperin D. D., Bishop D. H. Nucleotide sequence analyses and predicted coding of bunyavirus genome RNA species. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):119–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.119-128.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Hohn T. Initiation of translation of the cauliflower mosaic virus genome from a polycistronic mRNA: evidence from deletion mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2731–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Choudary P. V., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. The 5'-terminal leader sequence of late 16 S mRNA from cells infected with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3643–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Tosi M., Schibler U., Bovey R., Wellauer P. K., Young R. A. Mouse liver and salivary gland alpha-amylase mRNAs differ only in 5' non-translated sequences. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):643–646. doi: 10.1038/289643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes J., Weissmann C. Constitutive, long-term production of human interferons by hamster cells containing multiple copies of a cloned interferon gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):687–706. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendy G. N., Kronenberg H. M., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNAs encoding human preproparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7365–7369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C. Internal initiation of translation on the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein mRNA yields a second protein. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.797-804.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S., Mellstrom K., Kosik E., Tamanoi F., Brugge J. Mutation of a termination codon affects src initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1738–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia D. E., Yeung C. Y., Orengo I. F., Harrison M. L., Frayne E. G., Rudolph F. B., Kellems R. E. Purification and characterization of adenosine deaminase from a genetically enriched mouse cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13261–13267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Identification of the components necessary for adenovirus translational control and their utilization in cDNA expression vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P., Ingolia D. E., Yeung C. Y., Kellems R. E. Selection and amplification of heterologous genes encoding adenosine deaminase in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3136–3140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Amplification and expression of sequences cotransfected with a modular dihydrofolate reductase complementary dna gene. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):601–621. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Construction of a modular dihydrofolate reductase cDNA gene: analysis of signals utilized for efficient expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1304–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A., Latt S. A. Evolution of chromosomal regions containing transfected and amplified dihydrofolate reductase sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):699–711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Furie B. C., Furie B., Shoemaker C. B. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant gamma-carboxylated factor IX synthesized in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9622–9628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Spiliotes A. J., Gossels S. D., Latt S. A., Larsen G. R., Kay R. M. Coamplification and coexpression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator and murine dihydrofolate reductase sequences in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1750–1759. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M., Filipowicz W., Domdey H., Gross H. J. Binding of ribosomes to linear and circular forms of the 5'-terminal leader fragment of tobacco-mosaic-virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):221–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Evaluation of the "scanning model" for initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Inability of circular mRNA to attach to eukaryotic ribosomes. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):82–85. doi: 10.1038/280082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Migration of 40 S ribosomal subunits on messenger RNA when initiation is perturbed by lowering magnesium or adding drugs. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4731–4738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Role of ATP in binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Migration of 40 S ribosomal subunits on messenger RNA in the presence of edeine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6568–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Lin C. C., Kan Y. W. Amplification and expression of human alpha-globin genes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1469–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in mammalian cells. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):82–85. doi: 10.1038/309082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Haarr L., Preston C. M. Processing of herpes simplex virus proteins and evidence that translation of thymidine kinase mRNA is initiated at three separate AUG codons. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):434–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.434-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Trahey M., Innis M., Dieckmann B., Ringold G. Inducible expression of amplified human beta interferon genes in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Murphy A., Barkan A. Mutants deleted in the agnogene of simian virus 40 define a new complementation group. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):36–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.36-46.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Subramani S., Berg P. Effect of upstream reading frames on translation efficiency in simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2704–2711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. High-frequency transfer of cloned herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences to mammalian cells by protoplast fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):743–752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scahill S. J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W. Expression and characterization of the product of a human immune interferon cDNA gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4654–4658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI mediates a translational stimulation which is not restricted to the viral mRNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI: a positive regulator of mRNA translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):736–742. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region and part of the gag gene of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):535–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.535-541.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Ohkubo H., Sobel M. E., Yamada Y., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Structure of the promoter for chicken alpha 2 type I collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5334–5338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Gross H. S. Replicative form of Semliki Forest virus RNA contains an unpaired guanosine. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):754–756. doi: 10.1038/282754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Ingolia D. E., Roth D. B., Shoemaker C., Al-Ubaidi M. R., Yen J. Y., Ching C., Bobonis C., Kaufman R. J., Kellems R. E. Identification of functional murine adenosine deaminase cDNA clones by complementation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10299–10307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo O. J., Powell C. T., Agarwal K. L. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of full-length of cDNA coding for porcine gastrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1049–1053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]