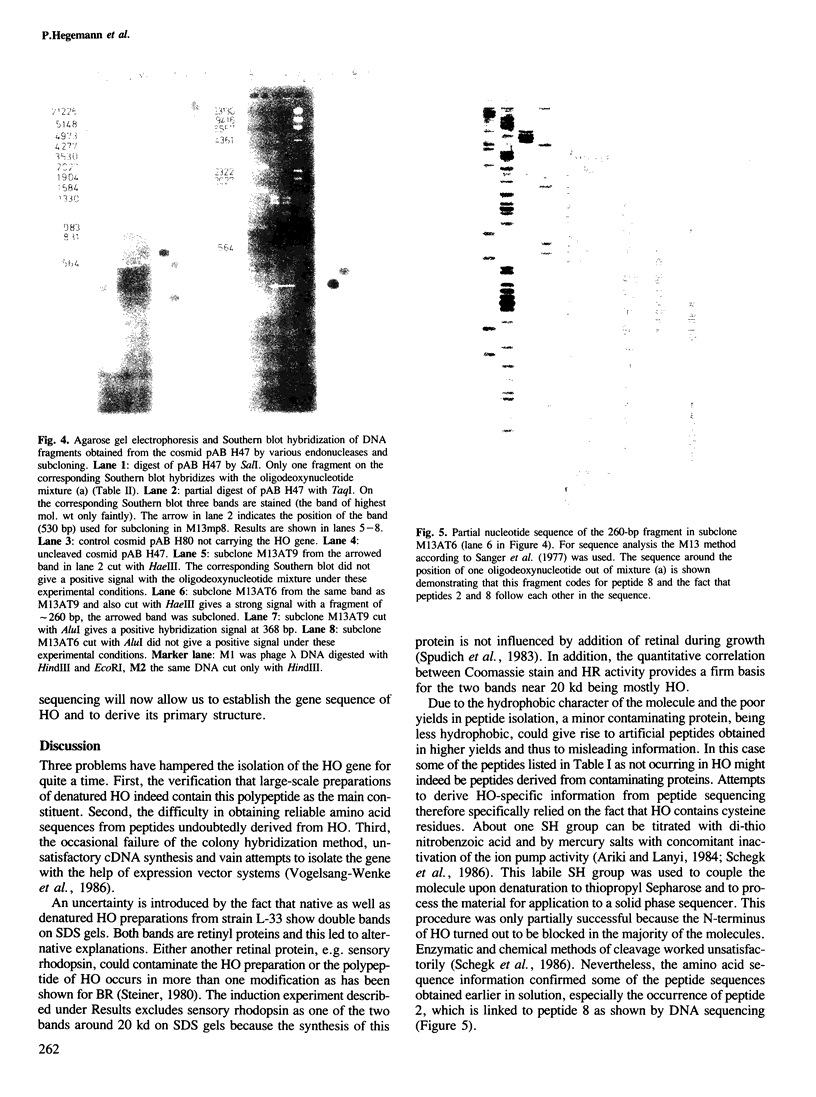
Abstract
Halorhodopsin (HR), the light-driven chloride pump in halobacteria, was purified in the denatured as well as in the native state and chemically cleaved into peptide fragments. Isolation of peptide and liquid phase sequencing yielded ∼20% of the halo-opsin (HO) structure in non-overlapping peptides. Chemically synthesied oligodeoxynucleotides corresponding to a peptide sequence obtained from both HR preparations were used to screen a cosmid gene bank of Halobacterium halobium strain L-33. A positive clone contained cosmid pAB H47 which by subcloning and nucleotide sequencing was shown to encode at least part of the HO gene.
Keywords: halorhodopsin, chloride pump, partial structure, gene isolation, halobacteria, archaebacteria
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariki M., Lanyi J. K. Evidence for a sulfhydryl group near the retinal-binding site of halorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3504–3510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Friedman J., Boyer H. W., Pfeifer F. Characterization of a halobacterial gene affecting bacterio-opsin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7949–7959. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanck A., Oesterhelt D. The halo-opsin gene. II. Sequence, primary structure of halorhodopsin and comparison with bacteriorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):265–273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn R., McCoy J., Simsek M., Majumdar A., Chang S. H., Rajbhandary U. L., Khorana H. G. The bacteriorhodopsin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6744–6748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann P., Steiner M., Oesterhelt D. Isolation and characterization of the retinal-binding component of halorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1177–1183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Konigsberg W. A micromethod for complete removal of dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorana H. G., Gerber G. E., Herlihy W. C., Gray C. P., Anderegg R. J., Nihei K., Biemann K. Amino acid sequence of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5046–5050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Oesterhelt D. Identification of the retinal-binding protein in halorhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2674–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F., Kellermann J., Henschen A., Rauth G., Müller-Esterl W. Human low-molecular-mass kininogen. Amino-acid sequence of the light chain; homology with other protein sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Abdulaev N. G., Feigina M. Y., Kiselev A. V., Lobanov N. A. The structural basis of the functioning of bacteriorhodopsin: an overview. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich E. N., Bogomolni R. A., Spudich J. L. Genetic and biochemical resolution of the chromophoric polypeptide of halorhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):332–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91835-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M., Oesterhelt D. Isolation and properties of the native chromoprotein halorhodopsin. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1379–1385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang H., Oertel W., Oesterhelt D. Isolation of the bacterioopsin gene by colony hybridization. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:226–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]