Abstract
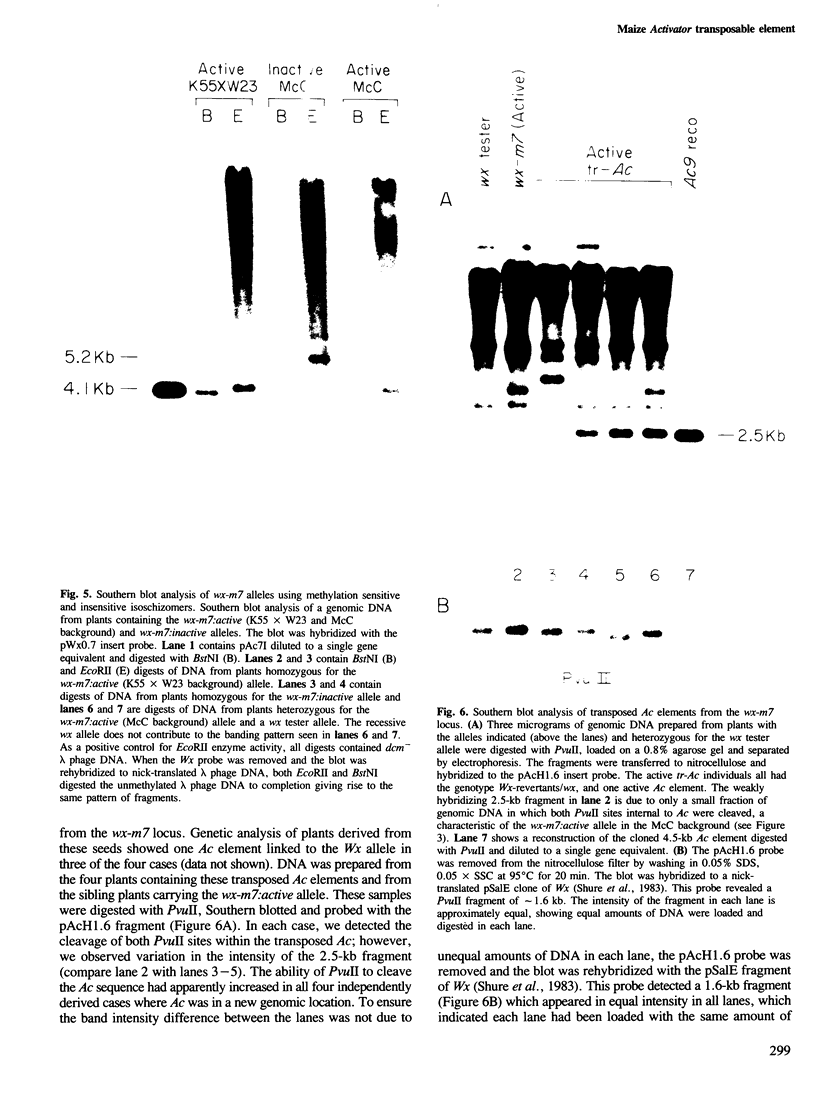
The Activator (Ac) element at the waxy locus (wx-m7 allele) has the ability to undergo changes in its genetic activity and cycles between an active and inactive phase. Comparison of active Ac elements at several loci and the inactive Ac at wx-m7 by Southern blot analysis revealed that the inactive Ac sequence was not susceptible to digestion by the methylation sensitive enzyme PvuII while active elements were susceptible to PvuII digestion. Restriction digest comparisons between the clones of the active and inactive Ac elements were indistinguishable. Further analyses with the enzymes SstII and the methylation sensitive and insensitive isoschizomers EcoRII and BstNI showed the inactive Ac sequence was methylated at these sites, whereas the active Ac was hypomethylated. Although the active Ac at the wx-m7 allele in different genetic backgrounds showed differences in the Ac DNA modification pattern, at least a fraction of genomic DNA contained Ac sequences that were unmethylated at all of the internal sites we assayed. These data may suggest a role for DNA modification in the ability of Ac to transpose from the waxy locus and to destabilize unlinked Ds elements.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandler V. L., Walbot V. DNA modification of a maize transposable element correlates with loss of activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1767–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and its functional significance: studies on the adenovirus system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;108:79–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69370-0_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Tillmann E., Starlinger P. DNA sequence of the maize transposable element Dissociation. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):127–130. doi: 10.1038/307127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V., Furtek D. B., Nelson O. E. Cloning of the bronze locus in maize by a simple and generalizable procedure using the transposable controlling element Activator (Ac). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Naveh-Many T., Cedar H., Razin A. Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):860–862. doi: 10.1038/292860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. G. The sensitivity of bacteriophage lambda DNA to restriction endonuclease RII. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):645–647. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirnos M. D., Aleksandrushkina N. I., Vaniushin B. F. 5-Metiltsitozin v pirimidinovykh posledovatel'nostiakh DNK rastenii i zhivotnykh: spetsifichnost' metilirovaniia. Biokhimiia. 1981 Aug;46(8):1458–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLINTOCK B. Controlling elements and the gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:197–216. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. The effect of sequence specific DNA methylation on restriction endonuclease cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5859–5866. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON O. E., RINES H. W. The enzymatic deficiency in the waxy mutant of maize. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 31;9:297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Fedoroff N. V., Messing J. The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. IS10 transposition is regulated by DNA adenine methylation. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Doerfler W. Methylation of integrated adenovirus type 12 DNA sequences in transformed cells is inversely correlated with viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., Gerlach W. L., Peacock W. J., Schwartz D. Molecular analysis of ds controlling element mutations at the adh1 locus of maize. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4642.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanyushin B. F. Replicative DNA methylation in animals and higher plants. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;108:99–114. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69370-0_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Kressmann A., Cedar H., Maechler M., Doerfler W. Expression of a cloned adenovirus gene is inhibited by in vitro methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherwax P. A Rare Carbohydrate in Waxy Maize. Genetics. 1922 Nov;7(6):568–572. doi: 10.1093/genetics/7.6.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Levy D., Perucho M. The somatic replication of DNA methylation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]