Abstract
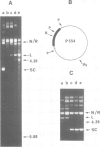
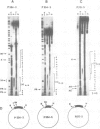
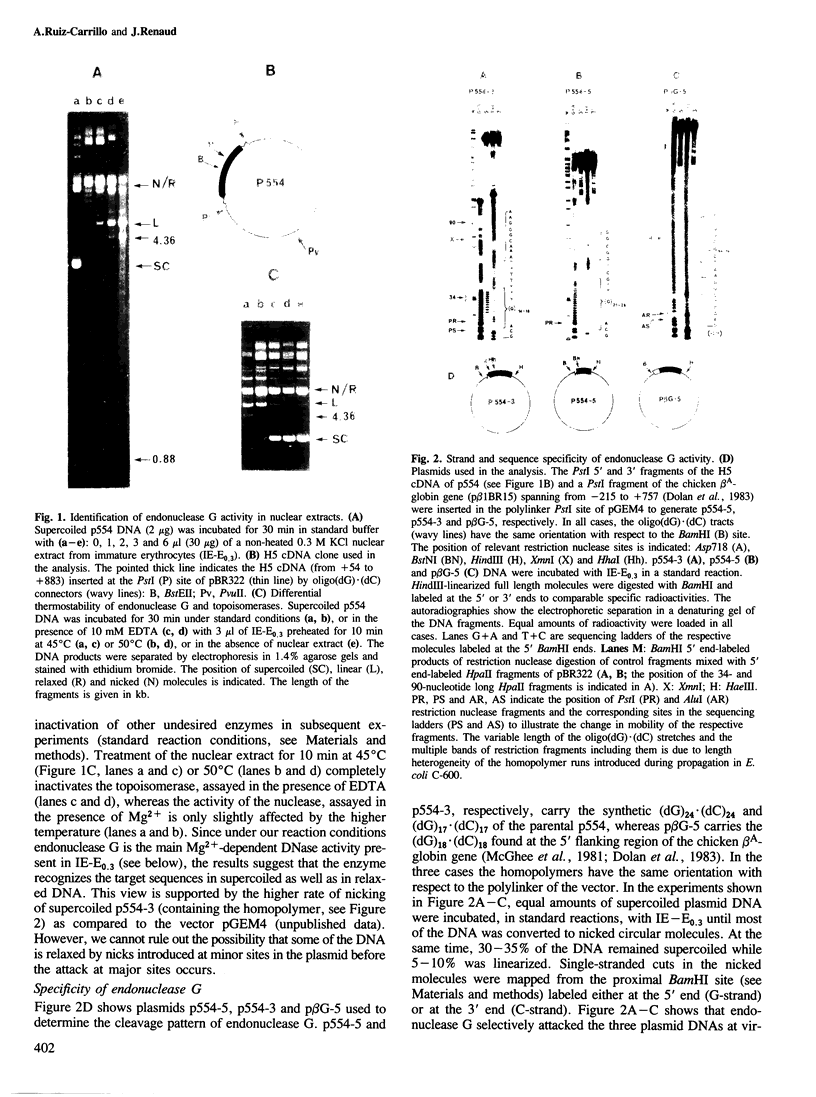
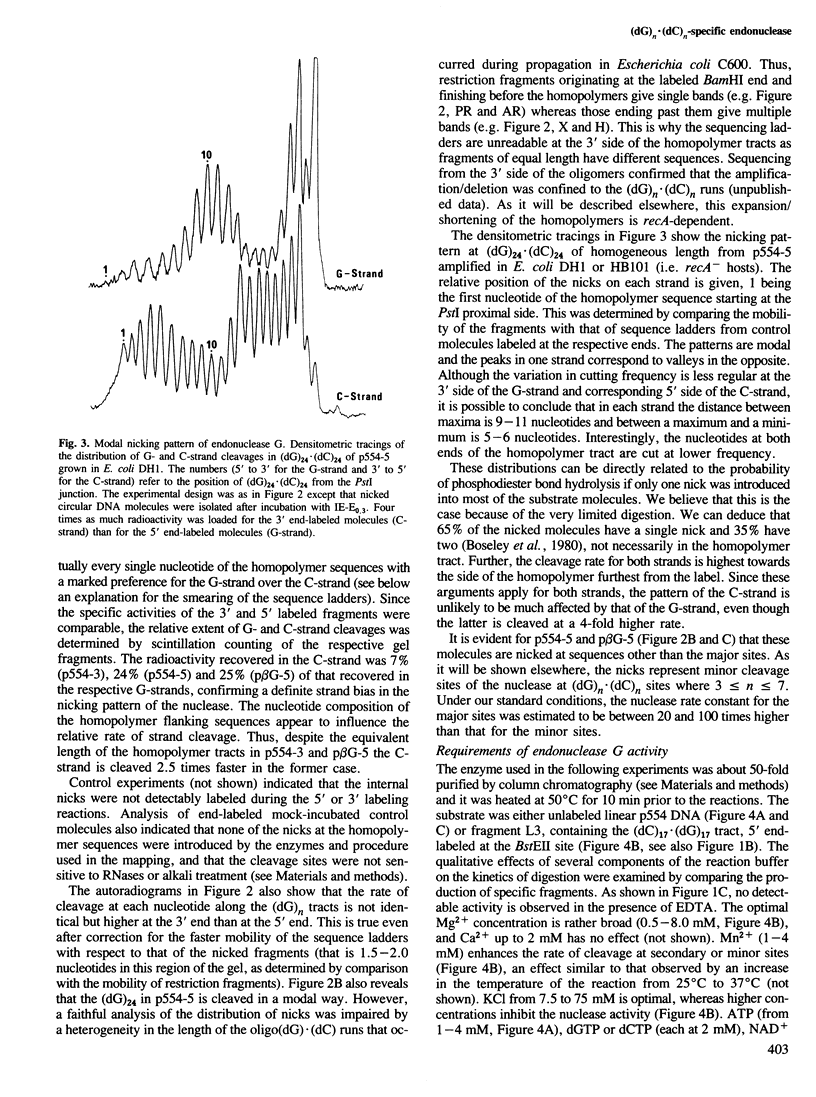
An endonuclease activity (termed endonuclease G) that selectively cleaves DNA at (dG)n X (dC)n tracts has been partially purified from immature chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Sites where n greater than or equal to 9 are cleaved in a manner that resembles types II and III restriction nucleases. The nicking rate of the G-strand is 4- to 10-fold higher than that of the C-strand depending on the length of the (dG)n X (dC)n tract and/or nucleotide composition of the flanking sequences. Endonuclease G hydrolyzes (dG)24 X (dC)24 of supercoiled DNA in a bimodal way every 9-11 nucleotides, the maxima in one strand corresponding to minima in the opposite, suggesting that it binds preferentially to one side of the double helix. The nuclease produces 5' phosphomonoester ends and its activity is dependent on Mg2+ or Mn2+. The wide distribution and high relative activity of endonuclease G in a variety of tissues and species argues for a general role of the enzyme. The striking correlation between genetic instability and poly(dG) X poly(dC) tracts in DNA suggests that these sequences and endonuclease G are involved in recombination processes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Selsing E. Letter: The structure of polydeoxyguanylic acid with polydeoxycytidylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):551–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P. G., Moss T., Birnstiel M. L. 5'-Labeling and poly(dA) tailing. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):478–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram S. Polynucleotide polymorphism in solution. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 6;233(40):161–164. doi: 10.1038/newbio233161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. E., Hirst A. J., Lai E. C., Mace M., Jr, Woo S. L. 5' Domain and nucleotide sequence of an adult chicken chromosomal beta-globin gene. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2091–2098. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes J., Valet J. P., Marceau N. Hepatocytes from newborn and weanling rats in monolayer culture: isolation by perfusion, fibronectin-mediated adhesion, spreading, and functional activities. In Vitro. 1980 Aug;16(8):722–730. doi: 10.1007/BF02619202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio S., Baltimore D. Double-stranded cleavage by cell extracts near recombinational signal sequences of immunoglobulin genes. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):860–862. doi: 10.1038/308860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Analysis of the adult chicken beta-globin gene. Nucleotide sequence of the locus, microheterogeneity at the 5'-end of beta-globin mRNA, and aberrant nuclear RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3983–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA structural variations in the E. coli tyrT promoter. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Structural junctions in DNA: the influence of flanking sequence on nuclease digestion specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4445–4467. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler R. F., Skinner D. M. Eukaryotic DNA diverges at a long and complex pyrimidine.purine tract that can adopt altered conformations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8994–9001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R., Waring M. J. DNA structural variations produced by actinomycin and distamycin as revealed by DNAase I footprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9271–9285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Cory S., Adams J. M. Translocation of the myc cellular oncogene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is an imprecise reciprocal exchange. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., Aguilera R. J., Minie M. E., Sakano H. Endonucleolytic activity that cleaves immunoglobulin recombination sequences. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1141–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.3003919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaaden O. R., Lange S., Stiburek B. Establishment and characterization of chicken embryo fibroblast clone LSCC-H32. In Vitro. 1982 Oct;18(10):827–834. doi: 10.1007/BF02796323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Kondo S., Nishi M., Kodaira M., Honjo T. Isolation and characterization of endonuclease J: a sequence-specific endonuclease cleaving immunoglobulin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):5995–6010. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.5995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobban P. E., Kaiser A. D. Enzymatic end-to end joining of DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M., Brown T., Kennard O. The crystal structure of d(G-G-G-G-C-C-C-C). A model for poly(dG).poly(dC). J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna W. G., Maio J. J., Brown F. L. Purification and properties of a mammalian endonuclease showing site-specific cleavage of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6435–6443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama J., Fujiyoshi T., Nakamura M., Anai M. Purification and properties of an endodeoxyribonuclease from nuclei of bovine small intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1636–1642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. DNA conformation at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Molgaard H. V., Shevack A., Pataryas T., Ruiz-Carrillo A. An improved method for the preparation of undegraded polysomes and active messenger RNA from immature chicken erythrocytes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posakony J. W., Scheller R. H., Anderson D. M., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. III. Nucleotide sequences of cloned repeat elements. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):41–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J., Ruiz-Carrillo A. Fine analysis of the active H5 gene chromatin of chicken erythroid cells at different stages of differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Vazquez R., Ruiz-Carillo A. Construction of chimeric plasmids containing histone H5 cDNA from hen erythrocyte. DNA sequence of a fragment derived from the 5' region of H5 mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2093–2108. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schon E., Evans T., Welsh J., Efstratiadis A. Conformation of promoter DNA: fine mapping of S1-hypersensitive sites. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):837–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. K., Linial M., Goodenow M. M., Hayward W. S. Nucleotide sequence 5' of the chicken c-myc coding region: localization of a noncoding exon that is absent from myc transcripts in most avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4697–4701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Künzler P. Cromatin and core particles formed from the inner histones and synthetic polydeoxyribonucleotides of defined sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1387–1415. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Hall L. M., Maden B. E. Multiple heterogeneities in the transcribed spacers of ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):629–646. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and properties of the human KB cell and mouse L cell D-loop regions of mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5411–5421. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. C., Furth J. J. Mammalian endonuclease, DNase V. Purification and properties of enzyme of calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):116–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. B., Hayday A., Courtneidge S., Fried M. A frameshift at a mutational hotspot in the polyoma virus early region generates two new proteins that define T-antigen functional domains. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90469-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]