Abstract
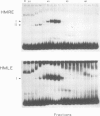
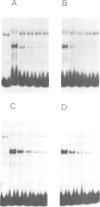
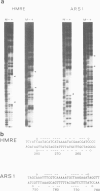
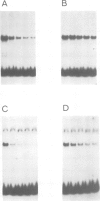
The `silent' yeast mating-type loci (HML and HMR) are repressed by sequences (HMLE and HMRE) located over 1 kb from their promoters which have properties opposite those of enhancers, and are called `silencers'. Both silencers contain autonomously replicating sequences (ARS). Silencer activity requires four trans-acting genes called SIR (silent information regulator). We have identified two DNA binding factors, SBF-B and SBF-E, which bind to known regulatory elements at HMRE. SBF-B binds to a region involved in both the silencer and ARS functions of HMRE, but does not bind to HMLE. This factor also binds to the unlinked ARS1 element. SBF-E recognizes a sequence found at both silencers. These results suggest that the two silencers may be composed of different combinations of regulatory elements at least one of which is common to both. Neither factor appears to be a SIR gene product. Hence the SIR proteins may not directly interact with the silencer control sites.
Keywords: ARS elements, DNA binding proteins, mating type, silencer, transcriptional control
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Regulation of mating-type information in yeast. Negative control requiring sequences both 5' and 3' to the regulated region. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):307–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcangioli B., Lescure B. Identification of proteins involved in the regulation of yeast iso- 1-cytochrome C expression by oxygen. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2627–2633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celniker S. E., Sweder K., Srienc F., Bailey J. E., Campbell J. L. Deletion mutations affecting autonomously replicating sequence ARS1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2455–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Leighton T., Rabinowitz J. C. Purification of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase with heparin-agarose. In vitro transcription of phi 29 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9220–9226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. B., Hicks J. B., Broach J. R. Identification of sites required for repression of a silent mating type locus in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):815–834. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., George J. P. A mutation that permits the expression of normally silent copies of mating-type information in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1979 Sep;93(1):13–35. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivy J. M., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B. Cloning and characterization of four SIR genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):688–702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Fogel S., Macleod K. MAR1-a Regulator of the HMa and HMalpha Loci in SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE. Genetics. 1979 Sep;93(1):37–50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine G. T., Sinha P., Tye B. K. Mutants of S. cerevisiae defective in the maintenance of minichromosomes. Genetics. 1984 Mar;106(3):365–385. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Nasmyth K. A. Role of DNA replication in the repression of silent mating type loci in yeast. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):247–251. doi: 10.1038/312247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. A. The role of DNA replication in the repression of the yeast mating-type silent loci. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:105–113. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. Molecular genetics of yeast mating type. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:439–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. The regulation of yeast mating-type chromatin structure by SIR: an action at a distance affecting both transcription and transposition. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B., Herskowitz I. A suppressor of mating-type locus mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for and identification of cryptic mating-type loci. Genetics. 1979 Dec;93(4):877–901. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell R., Rine J. A position effect on the expression of a tRNA gene mediated by the SIR genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):494–501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Squire M., Nasmyth K. A. Characterization of two genes required for the position-effect control of yeast mating-type genes. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2817–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Simpson R. T. Local protein-DNA interactions may determine nucleosome positions on yeast plasmids. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):250–252. doi: 10.1038/315250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Delta sequences and double symmetry in a yeast chromosomal replicator region. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):293–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]