Abstract
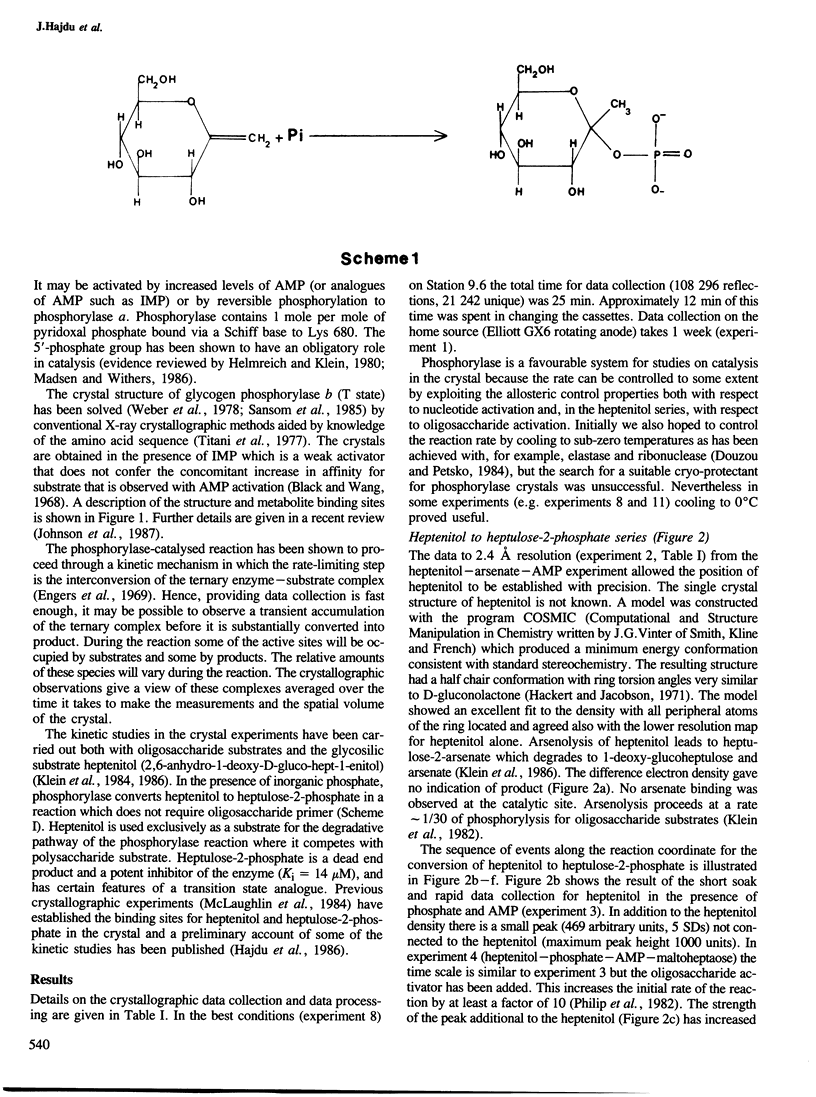
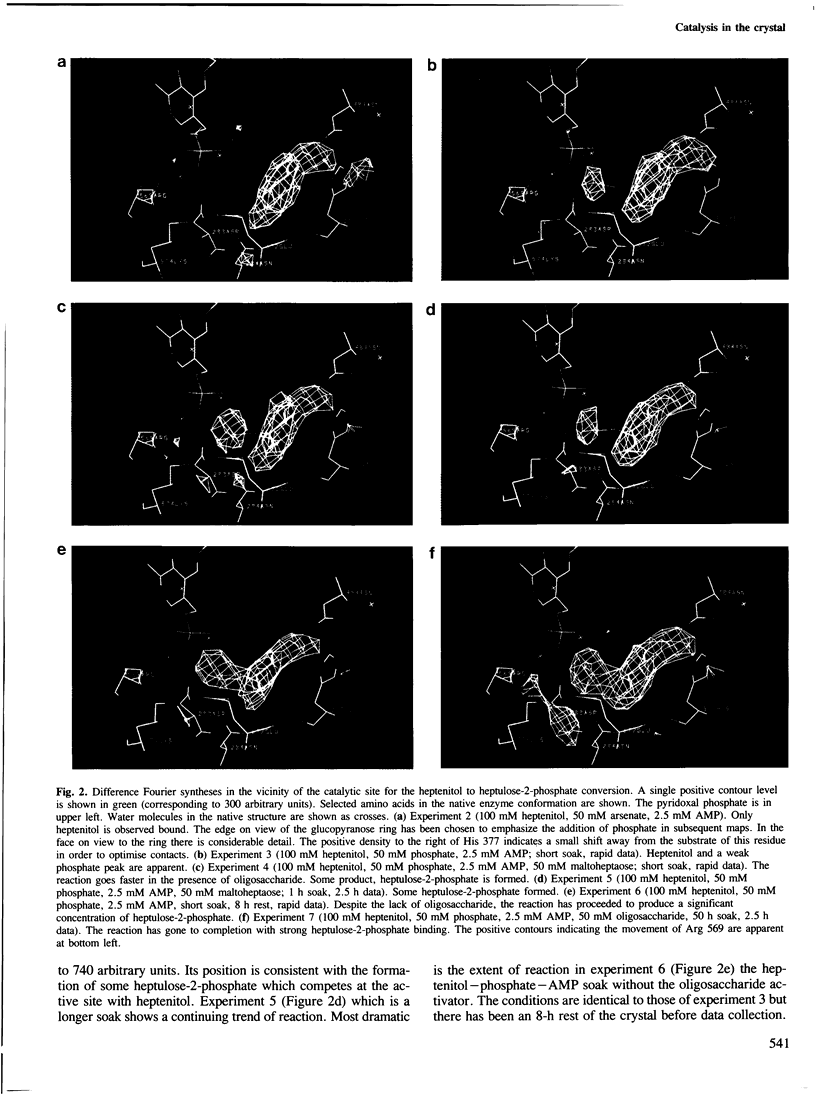
Direct observation of the progress of a catalysed reaction in crystals of glycogen phosphorylase b has been made possible through fast crystallographic data collection achieved at the Synchrotron Radiation source at Daresbury, UK. In the best experiments, data to 2.7 A resolution (some 108,300 measurements; 21,200 unique reflections) were measured in 25 min. In a series of time-resolved studies in which the control properties of the enzyme were exploited in order to slow down the reaction, the conversion of heptenitol to heptulose-2-phosphate, the phosphorylysis of maltoheptaose to yield glucose-1-phosphate and the oligosaccharide synthesis reaction involving maltotriose and glucose-1-phosphate have been monitored in the crystal. Changes in electron density in the difference Fourier maps are observed as the reaction proceeds not only at the catalytic site but also the allosteric and glycogen storage sites. Phosphorylase b is present in the crystals in the T state and under these conditions exhibits low affinity for both phosphate and oligosaccharide substrates. There are pronounced conformational changes associated with the formation and binding of the high-affinity dead-end product, heptulose-2-phosphate, which show that movement of an arginine residue, Arg 569, is critical for formation of the substrate-phosphate recognition site. The results are discussed with reference to proposals for the enzymic mechanism of phosphorylase. The feasibility for time-resolved studies on other systems and recent advances in this area utilizing Laue diffraction are also discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black W. J., Wang J. H. Studies on the allosteric activation of glycogen phosphorylase b by Nucleotides. I. Activation of phosphorylase b by inosine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5892–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrádi V. Structural aspects of the catalytic and regulatory function of glycogen phosphorylase. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(2):125–139. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douzou P., Petsko G. A. Proteins at work: "stop-action" pictures at subzero temperatures. Adv Protein Chem. 1984;36:245–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Vandenbunder B., Buc H. Mechanism of allosteric activation of glycogen phosphorylase probed by the reactivity of essential arginyl residues. Physicochemical and kinetic studies. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3634–3642. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Bridger W. A., Madsen N. B. Kinetic mechanism of phosphorylase b. Rates of initial velocities and of isotope exchange at equilibrium. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5936–5942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engers H. D., Madsen N. B. The effect of anions on the activity of phosphorylase b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajdu J., Acharya K. R., Stuart D. I., McLaughlin P. J., Barford D., Klein H., Johnson L. N. Time-resolved structural studies on catalysis in the crystal with glycogen phosphorylase b. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Jun;14(3):538–541. doi: 10.1042/bst0140538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmreich E. J., Klein H. W. The role of pyridoxal phosphate in the catalysis of glycogen phosphorylases. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1980;19(6):441–445. doi: 10.1002/anie.198004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. A., Johnson L. N., Stuart D. I., Stura E. A., Wilson K. S., Zanotti G. Phosphorylase: control and activity. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):23–41. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Jenkins J. A., Wilson K. S., Stura E. A., Zanotti G. Proposals for the catalytic mechanism of glycogen phosphorylase beta prompted by crystallographic studies on glucose 1-phosphate binding. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 15;140(4):565–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90271-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Madsen N. B., Mosley J., Wilson K. S. The crystal structure of phosphorylase beta at 6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 25;90(4):703–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Stura E. A., Sansom M. S., Babu Y. S. Oligosaccharide binding to glycogen phosphorylase b. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Apr;11(2):142–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A. Diffraction methods for biological macromolecules. Interactive computer graphics: FRODO. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:157–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasvinsky P. J., Madsen N. B. Activity of glycogen phosphorylase in the crystalline state. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6852–6859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasvinsky P. J., Madsen N. B., Fletterick R. J., Sygusch J. X-ray crystallographic and kinetic studies of oligosaccharide binding to phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1290–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasvinsky P. J., Madsen N. B., Sygusch J., Fletterick R. J. The regulation of glycogen phosphorylase alpha by nucleotide derivatives. Kinetic and x-ray crystallographic studies. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3343–3351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. W., Im M. J., Palm D., Helmreich E. J. Does pyridoxal 5'-phosphate function in glycogen phosphorylase as an electrophilic or a general acid catalyst? Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5853–5861. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. W., Im M. J., Palm D. Mechanism of the phosphorylase reaction. Utilization of D-gluco-hept-1-enitol in the absence of primer. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. W., Palm D., Helmreich E. J. General acid-base catalysis of alpha-glucan phosphorylases: stereospecific glucosyl transfer from D-glucal is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and orthophosphate (arsenate) dependent reaction. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6675–6684. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorek A., Wilson K. S., Sansom M. S., Stuart D. I., Stura E. A., Jenkins J. A., Zanotti G., Hajdu J., Johnson L. N. Allosteric interactions of glycogen phosphorylase b. A crystallographic study of glucose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate binding to di-imidate-cross-linked phosphorylase b. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):45–60. doi: 10.1042/bj2180045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin P. J., Stuart D. I., Klein H. W., Oikonomakos N. G., Johnson L. N. Substrate-cofactor interactions for glycogen phosphorylase b: a binding study in the crystal with heptenitol and heptulose 2-phosphate. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5862–5873. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomakos N. G., Melpidou A. E., Johnson L. N. Crystallization of pig skeletal phosphorylase b. Purification, physical and catalytic characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 20;832(3):248–256. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90257-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip G., Gringel G., Palm D. Rabbit muscle phosphorylase derivatives with oligosaccharides covalently bound to the glycogen storage site. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3043–3050. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A. Carbohydrate-binding proteins: tertiary structures and protein-sugar interactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:287–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotiroudis T. G., Oikonomakos N. G., Evangelopoulos A. E. Phosphorylase b covalently bound to glycogen: properties of the complex. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):573–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stura E. A., Zanotti G., Babu Y. S., Sansom M. S., Stuart D. I., Wilson K. S., Johnson L. N., Van de Werve G. Comparison of AMP and NADH binding to glycogen phosphorylase b. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):529–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Fukui T., Shimomura S. Catalytic mechanism of glycogen phosphorylase: pyridoxal(5')diphospho(1)-alpha-D-glucose as a transition-state analogue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3716–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Koide A., Hermann J., Ericsson L. H., Kumar S., Wade R. D., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Fischer E. H. Complete amino acid sequence of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4762–4766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Johnson L. N., Wilson K. S., Yeates D. G., Wild D. L., Jenkins J. A. Crystallographic studies on the activity of glycogen phosphorylase b. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):433–437. doi: 10.1038/274433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers S. G., Madsen N. B., Sprang S. R., Fletterick R. J. Catalytic site of glycogen phosphorylase: structural changes during activation and mechanistic implications. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5372–5382. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers S. G., Madsen N. B., Sykes B. D., Takagi M., Shimomura S., Fukui T. Evidence for direct phosphate-phosphate interaction between pyridoxal phosphate and substrate in the glycogen phosphorylase catalytic mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10759–10762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff H. W., Doscher M., Tsernoglou D., Inagami T., Johnson L. N., Hardman K. D., Allewell N. M., Kelly D. M., Richards F. M. Design of a diffractometer and flow cell system for X-ray analysis of crystalline proteins with applications to the crystal chemistry of ribonuclease-S. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]