Abstract
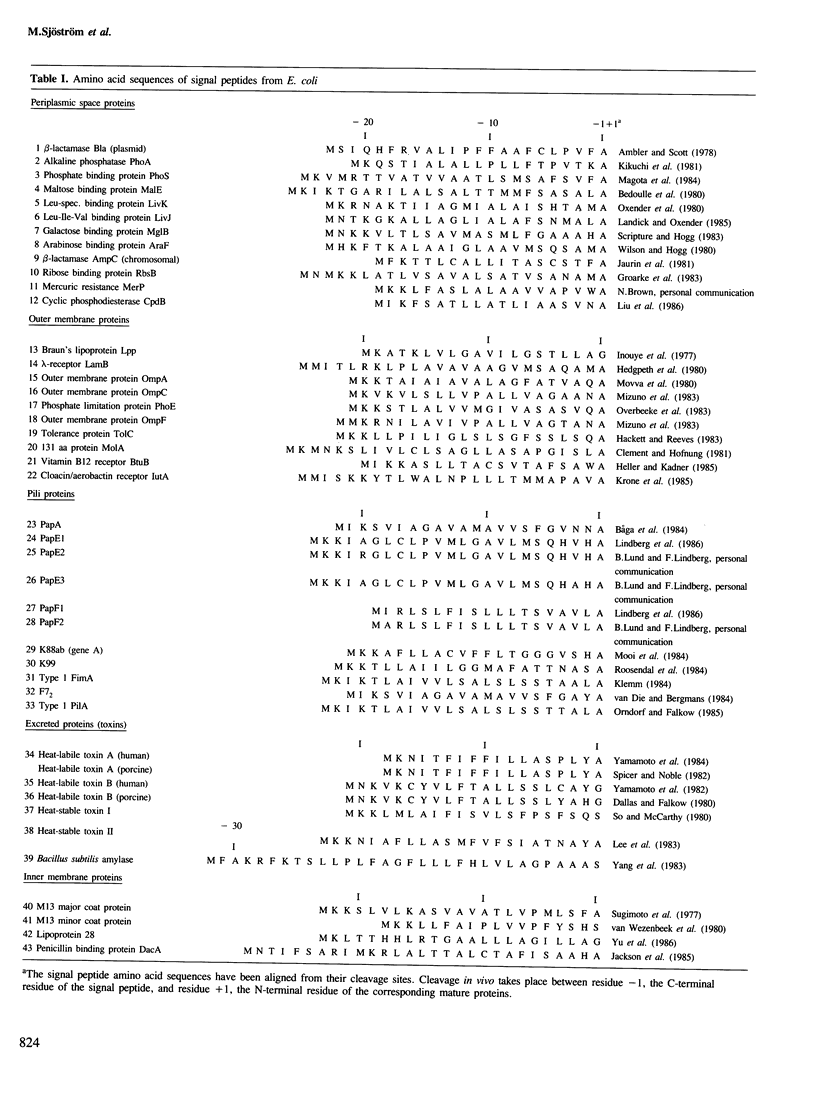
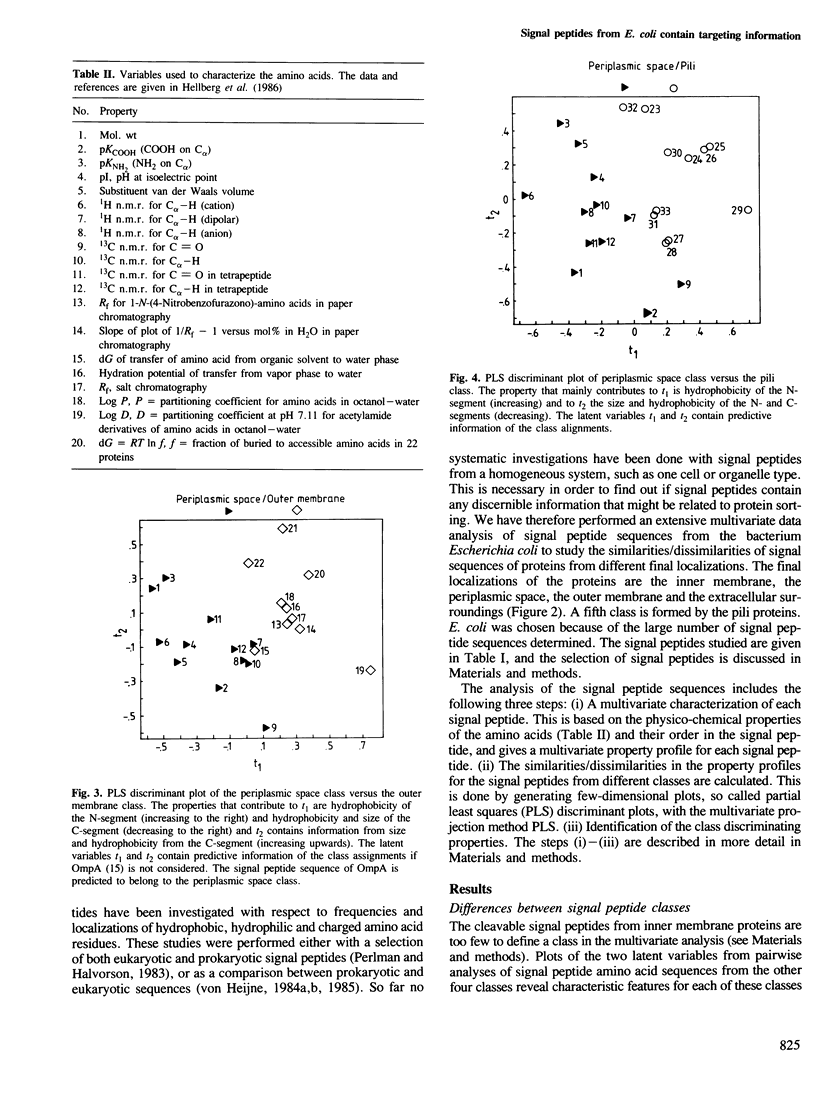
With few exceptions, the signal peptides from proteins inserted into, or translocated through, the membranes of gram-negative bacteria or the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotes have no sequence homologies. Therefore these signal peptides have not been considered to contain information related to the different final localizations of the proteins. In this study, 43 signal peptide amino acid sequences from proteins with different final localizations in Escherichia coli have been subjected to a multivariate data analysis. Each amino acid residue was characterized by 20 physico-chemical properties, yielding a multivariate property profile for each peptide. The similarities/dissimilarities in the property profiles for the signal peptides from different classes were compared with each other by generating few-dimensional partial least squares (PLS) discriminant plots. With this approach, signal peptides from proteins localized to the periplasmic space (PS), the outer membrane (OM), and the extracellular surroundings (excreted proteins), were separated into distinct groups. Signal peptides from pili proteins were not separated from the OM signal peptides and only partly from the PS signal peptides, but were clearly different from the signal peptides of the excreted proteins. Signal peptides from inner membrane proteins were similar to those of the PS peptides. The size and the hydrophobicity of different peptide segments were responsible for the separation of the signal peptide classes. For example, the hydrophobicity of the N-terminal segment of the signal peptides increased with an increased distance from the cytoplasm of the final localization for the corresponding proteins. Thus, many signal peptides from proteins with different final localizations in E. coli have different discernible physico-chemical profiles.
Full text
PDF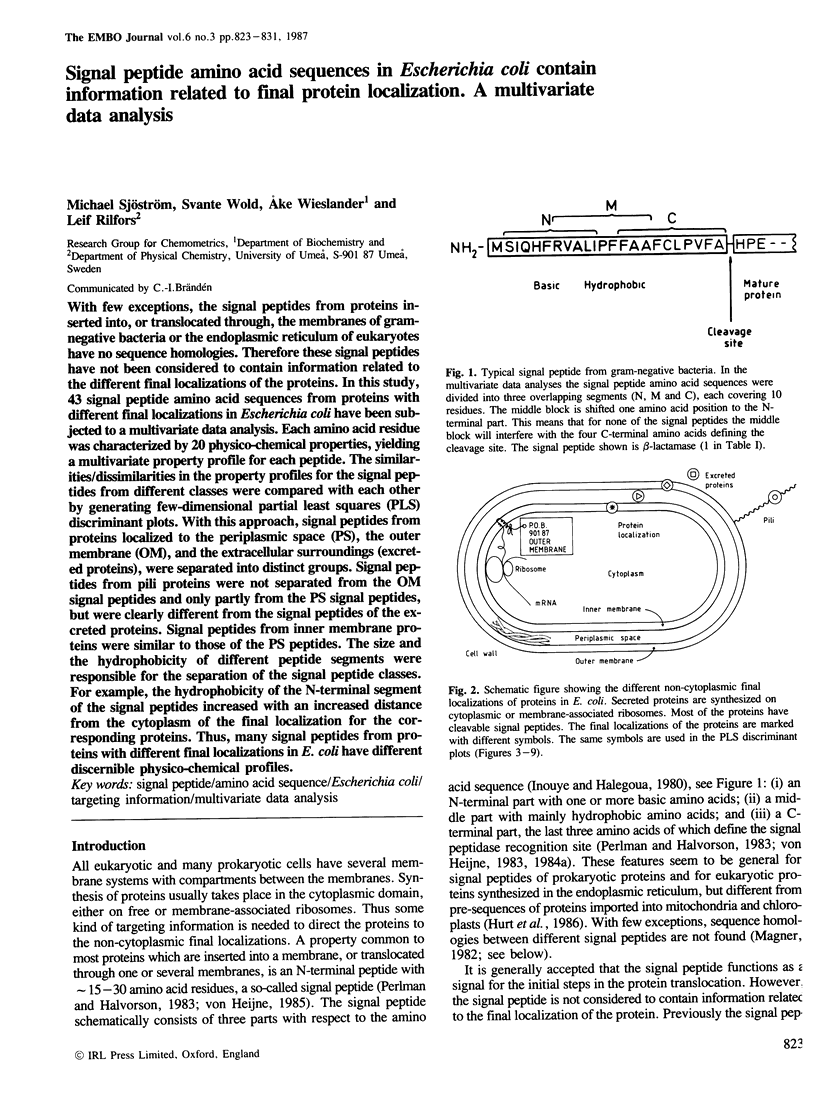


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Scott G. K. Partial amino acid sequence of penicillinase coded by Escherichia coli plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedouelle H., Bassford P. J., Jr, Fowler A. V., Zabin I., Beckwith J., Hofnung M. Mutations which alter the function of the signal sequence of the maltose binding protein of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):78–81. doi: 10.1038/285078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
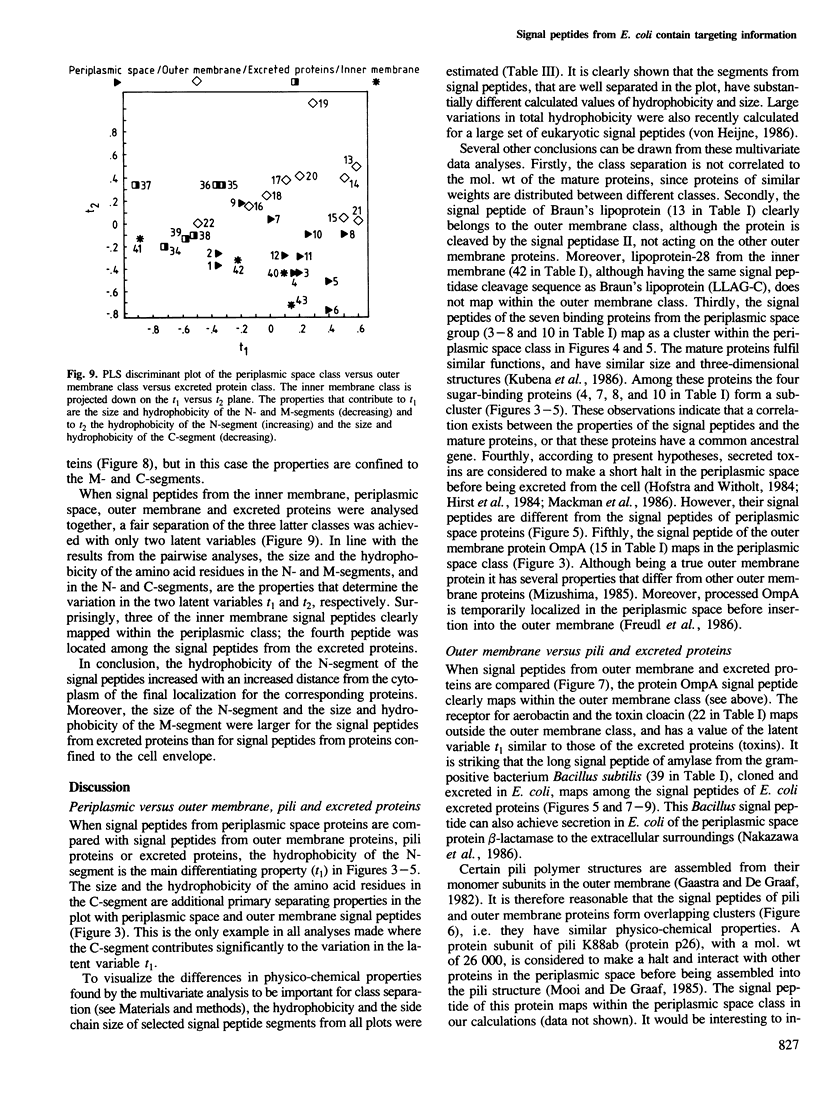
- Båga M., Normark S., Hardy J., O'Hanley P., Lark D., Olsson O., Schoolnik G., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence of the papA gene encoding the Pap pilus subunit of human uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):330–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.330-333.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clément J. M., Hofnung M. Gene sequence of the lambda receptor, an outer membrane protein of E. coli K12. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Boeke J. D., Model P. Fine structure of a membrane anchor domain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Model P. An artificial anchor domain: hydrophobicity suffices to stop transfer. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty H., Yamada H., Caffrey P., Owen P. Identification, immunochemical characterization, and purification of a major lipoprotein antigen associated with the inner (cytoplasmic) membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1072–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1072-1082.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudl R., Schwarz H., Stierhof Y. D., Gamon K., Hindennach I., Henning U. An outer membrane protein (OmpA) of Escherichia coli K-12 undergoes a conformational change during export. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11355–11361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaastra W., de Graaf F. K. Host-specific fimbrial adhesins of noninvasive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):129–161. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.129-161.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghrayeb J., Inouye M. Nine amino acid residues at the NH2-terminal of lipoprotein are sufficient for its modification, processing, and localization in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):463–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghrayeb J., Kimura H., Takahara M., Hsiung H., Masui Y., Inouye M. Secretion cloning vectors in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2437–2442. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groarke J. M., Mahoney W. C., Hope J. N., Furlong C. E., Robb F. T., Zalkin H., Hermodson M. A. The amino acid sequence of D-ribose-binding protein from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12952–12956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J., Reeves P. Primary structure of the tolC gene that codes for an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6487–6495. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Clement J. M., Marchal C., Perrin D., Hofnung M. DNA sequence encoding the NH2-terminal peptide involved in transport of lambda receptor, an Escherichia coli secretory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2621–2625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellberg S., Sjöström M., Wold S. The prediction of bradykinin potentiating potency of pentapeptides. An example of a peptide quantitative structure-activity relationship. Acta Chem Scand B. 1986 Feb;40(2):135–140. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.40b-0135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller K., Kadner R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the vitamin B12 receptor protein in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):904–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.904-908.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R., Boos W. Translational control of exported proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):462–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.462-466.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst T. R., Sanchez J., Kaper J. B., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J. Mechanism of toxin secretion by Vibrio cholerae investigated in strains harboring plasmids that encode heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7752–7756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Wright A. Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5107–5111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstra H., Witholt B. Kinetics of synthesis, processing, and membrane transport of heat-labile enterotoxin, a periplasmic protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15182–15187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Soltanifar N., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rochaix J. D., Schatz G. The cleavable pre-sequence of an imported chloroplast protein directs attached polypeptides into yeast mitochondria. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1343–1350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. E., Pratt J. M., Stoker N. G., Holland I. B. An inner membrane protein N-terminal signal sequence is able to promote efficient localisation of an outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2377–2383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03942.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T., Edlund T., Normark S. The E. coli beta-lactamase attenuator mediates growth rate-dependent regulation. Nature. 1981 Mar 19;290(5803):221–225. doi: 10.1038/290221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the amino-terminal region of alkaline phosphatase structural gene (phoA) of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5671–5678. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. The fimA gene encoding the type-1 fimbrial subunit of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence and primary structure of the protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubena B. D., Luecke H., Rosenberg H., Quiocho F. A. Crystallization and x-ray diffraction studies of a phosphate-binding protein involved in active transport in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7995–7996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Nishikawa K., Takahashi S., Ooi T. Correspondence of homologies in amino acid sequence and tertiary structure of protein molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 18;701(2):242–252. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Oxender D. L. The complete nucleotide sequences of the Escherichia coli LIV-BP and LS-BP genes. Implications for the mechanism of high-affinity branched-chain amino acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8257–8261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Moseley S. L., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Gyles C. L., So M. Characterization of the gene encoding heat-stable toxin II and preliminary molecular epidemiological studies of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin II producers. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.264-268.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lund B., Normark S. Gene products specifying adhesion of uropathogenic Escherichia coli are minor components of pili. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1891–1895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Burns D. M., Beacham I. R. Isolation and sequence analysis of the gene (cpdB) encoding periplasmic 2',3'-cyclic phosphodiesterase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):1002–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.1002-1010.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Secretion of haemolysin by Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:159–181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magner J. A. Information in the signal peptide? J Theor Biol. 1982 Dec 21;99(4):831–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magota K., Otsuji N., Miki T., Horiuchi T., Tsunasawa S., Kondo J., Sakiyama F., Amemura M., Morita T., Shinagawa H. Nucleotide sequence of the phoS gene, the structural gene for the phosphate-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):909–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.909-917.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. DNA sequence of the promoter region of the ompC gene and the amino acid sequence of the signal peptide of pro-OmpC protein of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 10;151(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., de Graaf F. K. Molecular biology of fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:119–138. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooi F. R., van Buuren M., Koopman G., Roosendaal B., de Graaf F. K. K88ab gene of Escherichia coli encodes a fimbria-like protein distinct from the K88ab fimbrial adhesin. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):482–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.482-487.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movva N. R., Nakamura K., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence of the signal peptide of ompA protein, a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):27–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahari K., Kanaya S., Munakata K., Aoyagi Y., Mizushima S. Secretion into the culture medium of a foreign gene product from Escherichia coli: use of the ompF gene for secretion of human beta-endorphin. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3589–3592. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Takano T., Sohma A., Yamane K. Secretion activities of Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase signal peptides of different lengths in Escherichia coli cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):624–631. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80465-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence of pilA, the gene encoding the structural component of type 1 pili in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):454–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.454-457.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Bergmans H., van Mansfeld F., Lugtenberg B. Complete nucleotide sequence of phoE, the structural gene for the phosphate limitation inducible outer membrane pore protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L., Anderson J. J., Daniels C. J., Landick R., Gunsalus R. P., Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Amino-terminal sequence and processing of the precursor of the leucine-specific binding protein, and evidence for conformational differences between the precursor and the mature form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2005–2009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. M., Jackson M. E., Holland I. B. The C terminus of penicillin-binding protein 5 is essential for localisation to the E. coli inner membrane. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2399–2405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04510.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scripture J. B., Hogg R. W. The nucleotide sequences defining the signal peptides of the galactose-binding protein and the arabinose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10853–10855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström M., Wold S. A multivariate study of the relationship between the genetic code and the physical-chemical properties of amino acids. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):272–277. doi: 10.1007/BF02099756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneath P. H. Relations between chemical structure and biological activity in peptides. J Theor Biol. 1966 Nov;12(2):157–195. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So M., McCarthy B. J. Nucleotide sequence of the bacterial transposon Tn1681 encoding a heat-stable (ST) toxin and its identification in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4011–4015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Noble J. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Nucleotide sequence of the A subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5716–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Okamoto T., Takanami M. Studies on bacteriophage fd DNA. IV. The sequence of messenger RNA for the major coat protein gene. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):487–507. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara M., Hibler D. W., Barr P. J., Gerlt J. A., Inouye M. The ompA signal peptide directed secretion of Staphylococcal nuclease A by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2670–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., van Tol H., Lugtenberg B. The ultimate localization of an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12 is not determined by the signal sequence. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1275–1279. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. Asymmetric orientation of a phage coat protein in cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4749–4753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Hogg R. W. The NH2-terminal sequence of a precursor form of the arabinose binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6745–6750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Ryoji M., Kaji A., Yokota T., Takano T. Sequence analysis of the heat-labile enterotoxin subunit B gene originating in human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):506–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.506-509.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Yokota T. Primary structure of heat-labile enterotoxin produced by Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5037–5044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Galizzi A., Henner D. Nucleotide sequence of the amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):237–249. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatvin M. B., Smith K. M., Siegel F. L. Translocation of nascent non-signal sequence protein in heated Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8070–8075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Inouye S., Inouye M. Lipoprotein-28, a cytoplasmic membrane lipoprotein from Escherichia coli. Cloning, DNA sequence, and expression of its gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2284–2288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Die I., Bergmans H. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the F72 fimbrial subunit of a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wezenbeek P. M., Hulsebos T. J., Schoenmakers J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the filamentous bacteriophage M13 DNA genome: comparison with phage fd. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):129–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Analysis of the distribution of charged residues in the N-terminal region of signal sequences: implications for protein export in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2315–2318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Towards a comparative anatomy of N-terminal topogenic protein sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



