Abstract
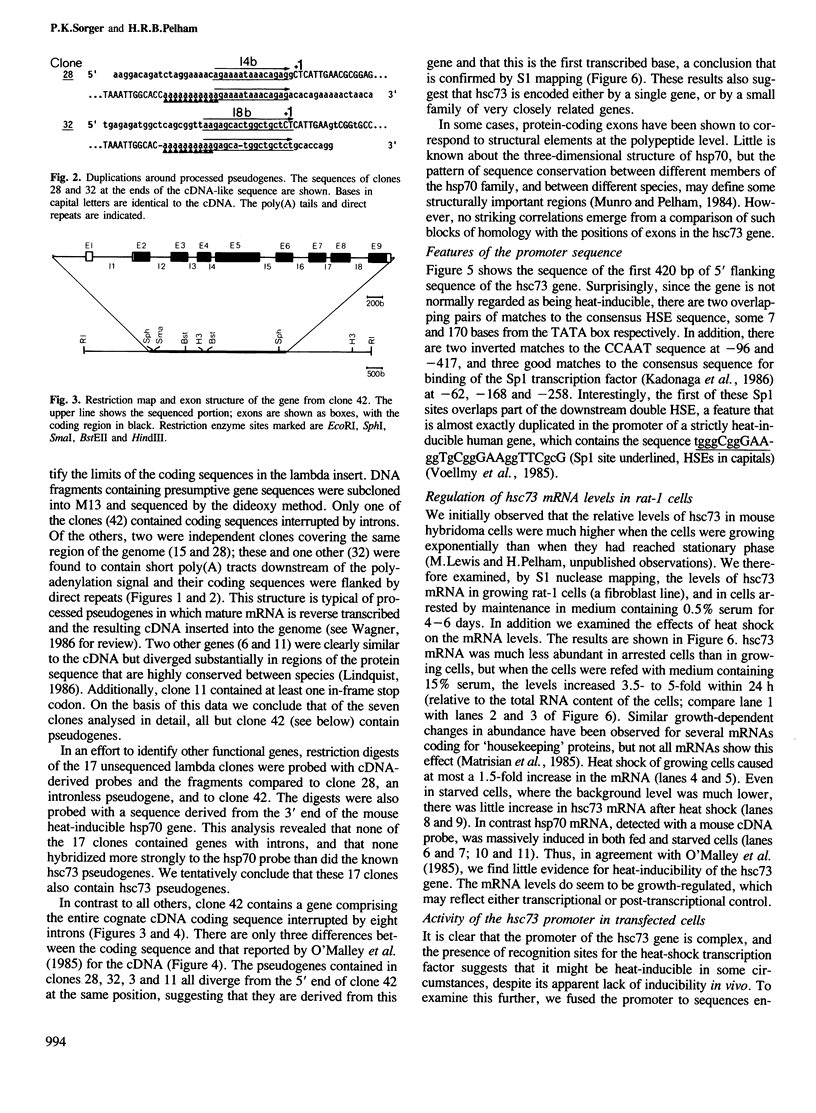
The isolation and complete DNA sequence of a rat genomic clone encoding hsc73, the major hsp70-like protein found in growing cells is described. Unlike the heat-inducible genes characterized so far, the hsc73 gene is interrupted by introns, and there are also numerous intronless hsc73 pseudogenes in the rat genome. We show that the levels of hsc73 mRNA are approximately 5-fold higher in rapidly growing tissue-culture cells than in cells whose growth has been arrested by serum starvation. The abundance of hsc73 mRNA is not significantly increased by heat shock of either fed or starved cells. The hsc73 promoter contains putative binding sites for transcription factor Sp1, two CCAAT boxes and, surprisingly, two matches to the consensus heat-shock regulatory element. When fused to the CAT gene and transfected into COS or HeLa cells, the promoter is constitutively active, showing only a small induction by heat shock. Deletion of some constitutive elements makes it more strongly heat-inducible. The gene thus appears to be subject to more than one form of regulation, mediated by different promoter elements that are intermingled.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensaude O., Babinet C., Morange M., Jacob F. Heat shock proteins, first major products of zygotic gene activity in mouse embryo. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):331–333. doi: 10.1038/305331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. A CCAAT box confers cell-type-specific regulation on the Xenopus hsp70 gene in oocytes. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Transcription and DNA sequence of the BamHI L fragment of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1083–1090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappell T. G., Welch W. J., Schlossman D. M., Palter K. B., Schlesinger M. J., Rothman J. E. Uncoating ATPase is a member of the 70 kilodalton family of stress proteins. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Ingolia T. D., Manseau L. J. Expression of Drosophila heat-shock cognate genes during heat shock and development. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):418–426. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations in cognate genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae hsp70 result in reduced growth rates at low temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3517–3524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. The heat shock response. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(3):239–280. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Moran L. A. Molecular cloning and analysis of DNA complementary to three mouse Mr = 68,000 heat shock protein mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2102–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morange M., Diu A., Bensaude O., Babinet C. Altered expression of heat shock proteins in embryonal carcinoma and mouse early embryonic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):730–735. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mues G. I., Munn T. Z., Raese J. D. A human gene family with sequence homology to Drosophila melanogaster Hsp70 heat shock genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):874–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Mauron A., Barchas J. D., Kedes L. Constitutively expressed rat mRNA encoding a 70-kilodalton heat-shock-like protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3476–3483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Schmid S. L. Enzymatic recycling of clathrin from coated vesicles. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90852-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuey D. J., Parker C. S. Binding of Drosophila heat-shock gene transcription factor to the hsp 70 promoter. Evidence for symmetric and dynamic interactions. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7934–7940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungewickell E. The 70-kd mammalian heat shock proteins are structurally and functionally related to the uncoating protein that releases clathrin triskelia from coated vesicles. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3385–3391. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Ahmed A., Schiller P., Bromley P., Rungger D. Isolation and functional analysis of a human 70,000-dalton heat shock protein gene segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4949–4953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Morimoto R. I. Transcription of the human hsp70 gene is induced by serum stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




