Abstract
The insect-specific transcription factor Broad-Complex (BR-C) is transcriptionally activated by the steroid 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) and regulates the expression of many target genes involved in insect growth and development. However, although the transcriptional regulation of BR-C proteins has been well studied, how BR-C is regulated at post-transcription and -translation levels is poorly understood. To this end, using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis, we identified residue Ser-186 as a phosphorylation site of BR-C in silkworm. Site-directed mutagenesis and treatment with specific kinase activators and inhibitors indicated that the Ser-186 residue in silkworm BR-C is phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA). Immunostaining assays disclosed that PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C has no effect on its nuclear import. However, luciferase reporter analysis, electrophoretic mobility shift assays, and chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that the PKA phosphorylation event suppresses the transcriptional activation of silkworm BR-C target genes and that this inhibition was caused by repression of BR-C binding to its DNA targets. Of note, both in vitro and ex vivo experiments disclosed that a continuous 20E signal inhibits the PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation and also the cAMP/PKA pathway, indicating that 20E's inhibitory effect on PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C contributes to maintaining BR-C transcriptional activity. In conclusion, our findings indicate that PKA-mediated phosphorylation inhibits silkworm BR-C activity by interfering with its binding to DNA and that 20E signaling relieves PKA-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C, thereby maintaining its transcriptional activity.
Keywords: gene transcription, phosphorylation, post-translational modification (PTM), protein kinase A (PKA), signal transduction, 20-hydroxyecdysone, Broad-Complex, suppression
Introduction
Broad-Complex (BR-C) 3 protein is characterized as an insect-specific transcription factor that contains two C2H2 zinc fingers and a Bric-a-brac/Tramtrack/Broad-Complex (BTB) domain (1, 2). BR-C is predominantly involved in the signaling of 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) and juvenile hormone (JH), two key hormones necessary for insect growth and development (3, 4), and regulates a variety of developmental processes, including embryogenesis, larval molting, metamorphosis, and reproduction (5).
The transcriptional cascade involving insect BR-C proteins has been well studied. Previous reports demonstrated that 20E bound to the complex of ecdysone receptor (EcR) and ultraspiracle (USP) to activate the transcription of BR-C, one of the early response genes of 20E, which in turn directly regulates the transcription of the downstream target genes, such as cuticle protein genes (5, 6), caspase genes (7), and glue protein genes (8). Conversely, 20E-induced BR-C expression can be inhibited by the transcription factor Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1), a JH-induced repressor of insect metamorphosis (9, 10).
Recently, several studies have assessed the nuclear translocation and translational modification of the insect BR-C protein. For example, in the silkworm (Bombyx mori), the receptor for activated protein kinase C 1 (RACK1) protein, a scaffolding/anchoring protein involved in protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent phosphorylation, was identified as an interacting partner of the BTB domain of BR-C (5). The interaction between BR-C and RACK1 in silkworm may be involved in PKC-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C and is required for nuclear import and subsequent transcriptional activity of BR-C. In the cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera), JH was shown to induce the phosphorylation of a newly identified isoform of BR-C protein to inhibit 20E-mediated metamorphosis (11). However, the detailed molecular mechanism underlying post-translational modification, especially phosphorylation of insect BR-C proteins, remains unclear.
In the present study we investigated whether and how silkworm BR-C is phosphorylated. Interestingly, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis found that Ser-186 of silkworm BR-C is a phosphorylation site, and it was predicted to be phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA). Furthermore, we demonstrated that PKA-triggered phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C reduces its transcriptional activity and is suppressed by 20E, and the unphosphorylated silkworm BR-C promotes the expression of its downstream genes.
Results
LC-MS/MS identification of BR-C Ser-186 as a phosphorylation site
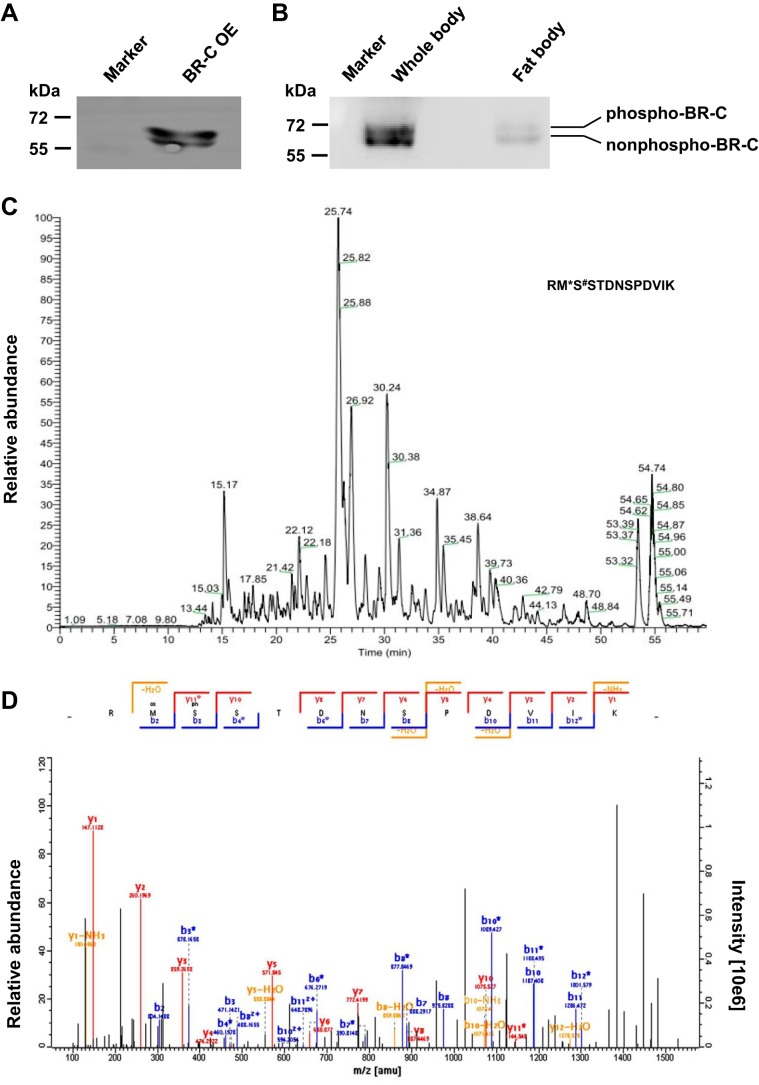
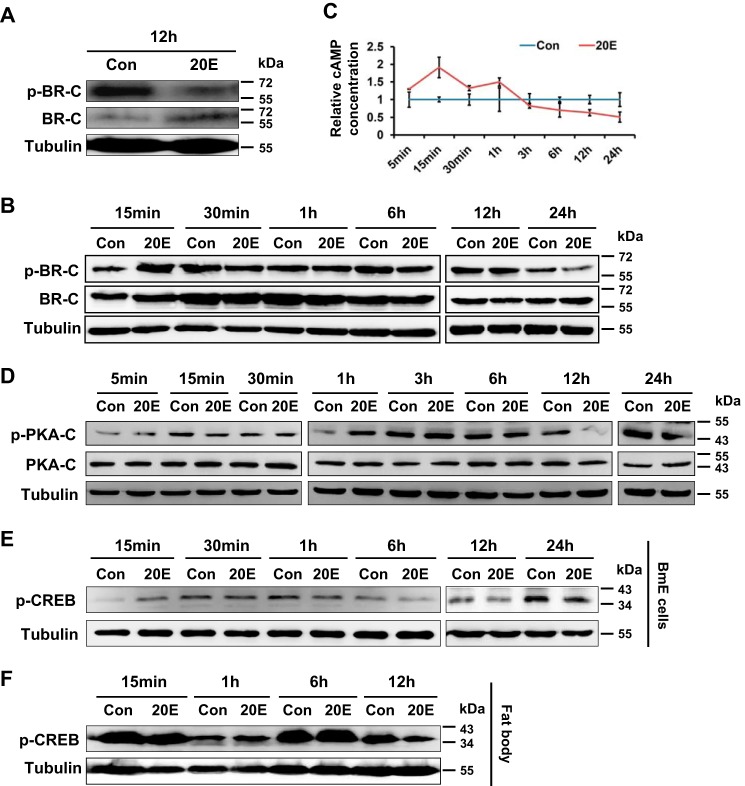
Previous studies have shown that the insect BR-C protein, which is involved in the 20E signaling pathway, may be phosphorylated (5, 11). To determine whether and how BR-C is phosphorylated, we first assessed the potential post-translational modification of silkworm BR-C by Western blot analysis with an antibody against silkworm BR-C. The results showed that in the total proteins prepared from silkworm embryo-derived BmE cells transiently overexpressing exogenous silkworm BR-C gene, two prominent protein bands with a molecular mass of ∼60 kDa could be detected as expected (Fig. 1A). The lower and upper bands were likely the non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated forms of silkworm BR-C proteins, respectively. In whole bodies and fat bodies of silkworm larvae at the late stage of the last instar when 20E titer is being elevated, two similar protein bands could also be detected (Fig. 1B).
Figure 1.
Ser-186 of BR-C was identified as a phosphorylation site by LC-MS/MS. A, the pSL1180-BR-C overexpression vector was transiently transfected into silkworm BmE cells. Total proteins isolated from these cells were used to perform Western-blotting analysis with a polyclonal antibody against BR-C. OE, overexpression. B, protein expression levels of BR-C in whole bodies and fat bodies from silkworm larvae at the late stage of the last instar were analyzed. C and D, LC-MS/MS analysis of BR-C phosphorylation. BR-C protein was immunoprecipitated from BR-C-overexpressing BmE cells using an anti-BR-C antibody and was subsequently analyzed by LC-MS/MS (C). The phosphorylated peptides that were enriched by TiO2 filler in silkworm were used to identify the BR-C phosphorylation site via LC-MS/MS analysis (D).
We further aimed to identify the phosphorylation site of silkworm BR-C using LC-MS/MS analysis. From silkworm BmE cells that transiently overexpressed the silkworm BR-C gene, we prepared total proteins and performed an immunoprecipitation experiment with anti-BR-C antibody. The BR-C proteins were separated from the immunoprecipitates by SDS-PAGE and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. As shown in Fig. 1C, different peptide peaks were observed in the first MS scan. Subsequent tandem MS analysis identified a phosphorylated peptide, RMS↓STDNSPDVIK, in which the Ser-186 residue, which is not located in the BTB domain or the zinc finger domain of silkworm BR-C, was phosphorylated. In addition, in our previous report (12) we extracted total proteins from the fat bodies of silkworm larvae on day 3 of the 5th instar and enriched phosphorylated peptides via TiO2 enrichment. The resulting phosphopeptides were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Intriguingly, the Ser-186 residue of silkworm BR-C was also identified as its phosphorylation site in this assay (Fig. 1D).
In vitro verification of Ser-186 as the BR-C phosphorylation site
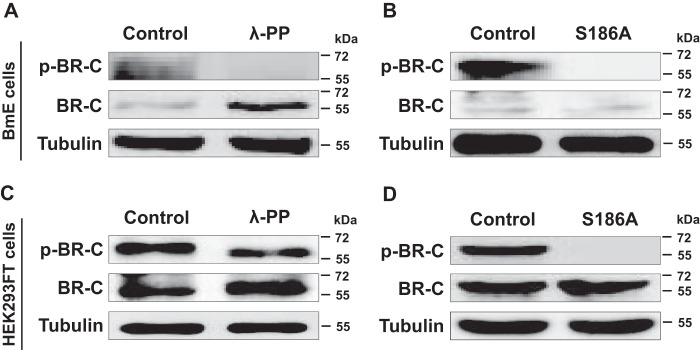
Given that the Ser-186 residue was identified as a phosphorylation site for silkworm BR-C by LC-MS/MS analysis, we designed a phospho-BR-C antibody against this site on silkworm BR-C. To further validate this phosphorylation site, we performed a dephosphorylation assay in vitro. Total proteins were harvested from the silkworm BmE cells overexpressing silkworm BR-C and were subsequently treated with λ-protein phosphatase (λ-PP). Western blot analysis revealed that the BR-C phosphorylation level was sharply decreased and was undetectable compared with that of the control (Fig. 2A), whereas the amount of total BR-C proteins was elevated. When Ser-186 was mutated to Ala (S186A), the phosphorylated form of the silkworm BR-C protein could not be detected (Fig. 2B).
Figure 2.
Ser-186 of BR-C was confirmed in vitro as a phosphorylated site. A, changes in the phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C protein after λ-PP treatment in silkworm BmE cells. The protein extracted from BmE cells overexpressing BR-C was treated with λ-PP for 0.5 h and subsequently assayed via Western blotting using anti-BR-C and anti-p-BR-C antibodies. B, changes in the phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C protein after S186A mutation in BmE cells. BR-C with the S186A mutation was overexpressed in the BmE cells for 48 h, and the extracted total proteins were used in Western-blotting experiments. C, phosphorylation changes of silkworm BR-C protein after λ-PP treatment of human HEK293FT cells overexpressing intact BR-C. D, phosphorylation change of silkworm BR-C protein with the S186A mutation in human HEK293FT cells.
To eliminate the possible effects of endogenous BR-C in silkworm BmE cells, we also conducted a dephosphorylation experiment in human HEK293FT cells. The results revealed that the levels of phosphorylated silkworm BR-C protein were substantially decreased and even eliminated after λ-PP treatment and S186A mutation, respectively (Fig. 2, C and D). Taken together, our data demonstrated that silkworm BR-C could be phosphorylated at Ser-186.
PKA mediated BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186
Generally, Ser residues can be phosphorylated by PKA, PKB, PKC, or other protein kinases (13–15). To determine which protein kinase phosphorylates the Ser-186 residue of silkworm BR-C, we first performed an analysis of the phosphorylation sites of BR-C using online computational programs NetPhosK 1.0 Server and The CUCKOO Workgroup (gps.biocuckoo.org/index.php) 4 (47). The results revealed that BR-C Ser-186 is likely a PKA phosphorylation site (data not shown).
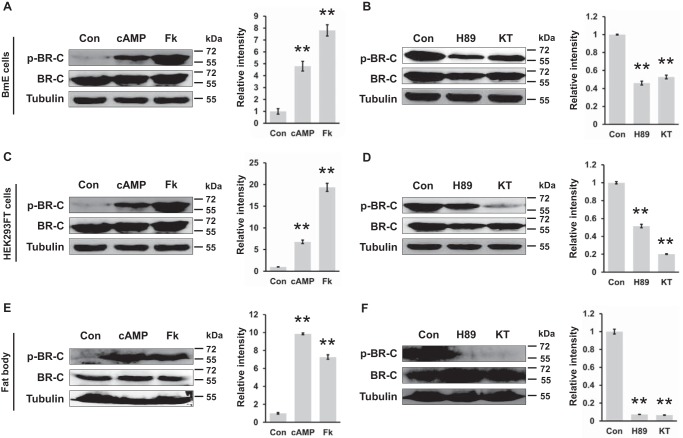
We further measured changes in silkworm BR-C phosphorylation after treatments with specific activators and inhibitors of PKA in vitro and ex vivo. Using previously reported protocols (16, 17), we treated the silkworm BmE cells overexpressing BR-C with two PKA activators, namely, cAMP and forskolin, and two inhibitors, namely, H89 and KT5720, and then BR-C phosphorylation levels were examined by Western blot assays with the p-BR-C antibody against the Ser-186 site. Compared with a control treated by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the phosphorylation levels of BR-C were increased >2-fold after PKA activator (cAMP or forskolin) treatment (Fig. 3A). In contrast, after treatment with PKA inhibitors (H89 or KT5720), the phosphorylation of BR-C was significantly decreased (Fig. 3B). Similar changes in BR-C phosphorylation levels in response to PKA activators or inhibitors were observed in human HEK293FT cells (Fig. 3, C and D).
Figure 3.
Ser-186 of BR-C was characterized as a PKA phosphorylation site. A, at 48 h after transfection with the overexpression vector pSL1180-BR-C, the BmE cells were treated with 160 nm cAMP or 20 μm forskolin for 12 h; Fk, forskolin. DMSO treatment was used as a control (Con). B, inhibition of PKA activity by H89 or KT5720 treatment attenuated phosphorylation of BR-C at Ser-186. The BR-C-overexpressing BmE cells were treated with 20 μm H89 or 100 nm KT5720 for 4 h; KT, KT5720. C, activation of PKA in HEK293FT cells overexpressing BR-C. D, inhibition of PKA in BR-C-overexpressing HEK293FT cells. E, the dissected fat body of the wandering silkworm was treated with cAMP or forskolin ex vivo for 6 h and subsequently homogenized for a Western-blotting assay. F, inhibition of the PKA pathway ex vivo. All Western-blotting signals were analyzed, and densitometric analysis of the protein bands from the Western blots was performed using ImageJ software. Values are represented as the mean ± S.E. (error bars); *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus controls.
Moreover, an ex vivo organ culture experiment with fat bodies from silkworm larvae was conducted. Consistent with the above observations, the BR-C phosphorylation level in the cultured fat bodies was increased by PKA activators (Fig. 3E) and eliminated by PKA inhibitors (Fig. 3F). Given that the PKA catalytic subunit PKA-C is involved in phosphorylating target proteins directly (18–20), we further examined whether PKA-C can directly interact with silkworm BR-C. Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) assay revealed that BR-C can interact with PKA-C weakly, suggesting that PKA might directly phosphorylate silkworm BR-C (supplemental Fig. S1). Taken together, our data strongly indicate that silkworm BR-C is phosphorylated by PKA at Ser-186.
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186 did not affect its nuclear import
Previous investigations have demonstrated that the phosphorylation of proteins contributes to their subcellular localization (21, 22). Given that silkworm BR-C is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors, we examined whether PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186 is required for nuclear localization of BR-C. First, we mutated Ser-186 to Ala (A) to block BR-C phosphorylation or to Glu (E) to mimic forced BR-C phosphorylation. Notably, immunostaining analyses of silkworm BmN4-SID1 cells revealed that, compared with the intact BR-C, neither the S186A mutation nor the S186E mutation could disrupt the nuclear localization of BR-C (Fig. 4A). In addition, because two PKA inhibitors, H89 and KT5720, can effectively decrease BR-C phosphorylation levels, we further assessed the effects of these PKA inhibitors on the nuclear import of BR-C in BmN4-SID1 cells. The results showed that BR-C was normally located in the nucleus after PKA inhibitor treatments (Fig. 4B). These observations indicate that PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation was not essential for its subcellular localization.
Figure 4.
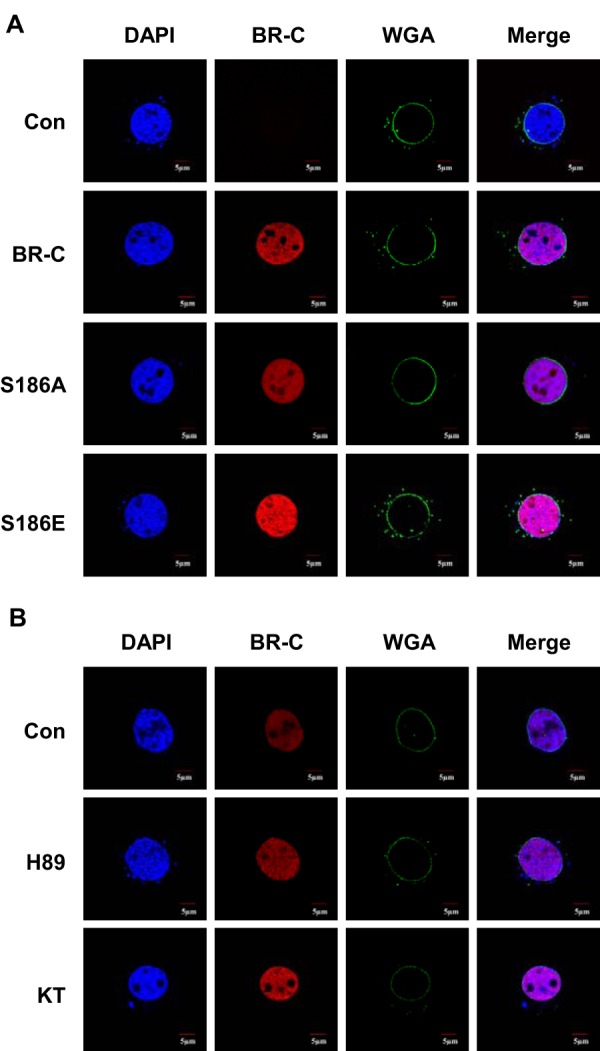
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation did not influence its nuclear import. A, the two mutant constructs pSL1180-BR-C S186A (A, blocks phosphorylation) and pSL1180-BR-C S186E (E, mimics phosphorylation) were transfected into BmN4-SID1 cells. Two days after transfection the localization of the BR-C protein was analyzed by immunostaining and confocal microscopy. Intact silkworm BR-C was used as a control. B, 2 days after transfection with the overexpression vector pSL1180-BR-C, the BmN4-SID1 cells were treated with PKA inhibitors for 4 h, and the fluorescence signals were detected with confocal microscopy. DMSO treatment was used as a control (Con). KT, KT5720. Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) is used in nuclear membrane staining.
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186 inhibited its transcriptional activity by abolishing BR-C-binding ability to the promoters of its targets
Phosphorylation of transcription factors is required for their nuclear import and transcriptional activity (23–26). We further evaluated the effects of BR-C phosphorylation on its transcriptional activity using a dual luciferase reporter assay. The cuticle protein gene WCP10 and the sericin-1 gene (Ser1) are two direct downstream targets that are positively and negatively regulated by silkworm BR-C, respectively (6, 27, 28); thus, we analyzed luciferase expression driven by the promoters of either the WCP10 or Ser1 genes after BR-C overexpression in silkworm BmE cells as an indicator of BR-C transcriptional activity. Our results showed that, compared with the empty control without BR-C overexpression, the S186A mutation of BR-C, which mimicked dephosphorylation, enhanced WCP10 promoter-driven luciferase expression (Fig. 5A). However, mimicked phosphorylation resulting from the S186E mutation led to a loss of WCP10 promoter activity, with levels comparable with that of the empty control (Fig. 5A). For the promoter of the Ser1 gene, whose expression is inhibited by BR-C, we confirmed that the activity of the Ser1 promoter was decreased after S186A mutation but was increased after S186E mutation (Fig. 5B). Moreover, we observed that either cAMP or forskolin could inhibit the WCP10 promoter activity (Fig. 5C).
Figure 5.
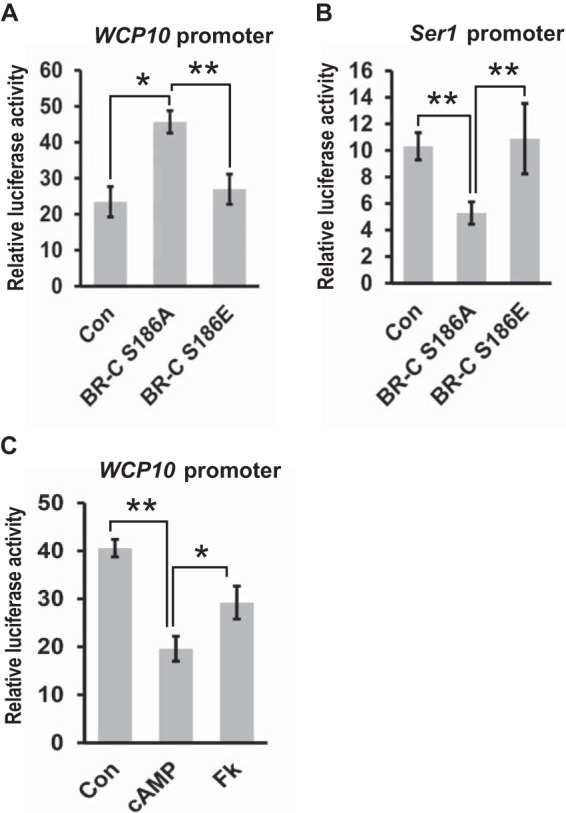
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation suppressed its transcriptional activity. A, effects of silkworm BR-C mutants on luciferase activity driven by the WCP10 promoters. The two mutant forms S186A and S186E were co-transfected into BmE cells with WCP10-luc. 48 h after transfection, cells were collected for luciferase activity analysis. The empty overexpression vector pSL1180 was used as a control, and a pRL-TK vector containing the Renilla luciferase coding gene was used as an internal reference. Data represent the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus the internal reference. B, effects of BR-C mutants on luciferase activity driven by the Ser1 promoters. C, BmE cells were co-transfected with pSL1180-BR-C and WCP10-luc for 48 h and then treated with 160 nm cAMP or 20 μm forskolin for 12 h. Cells were collected for luciferase activity measurement. FK, forskolin; Con, Control.
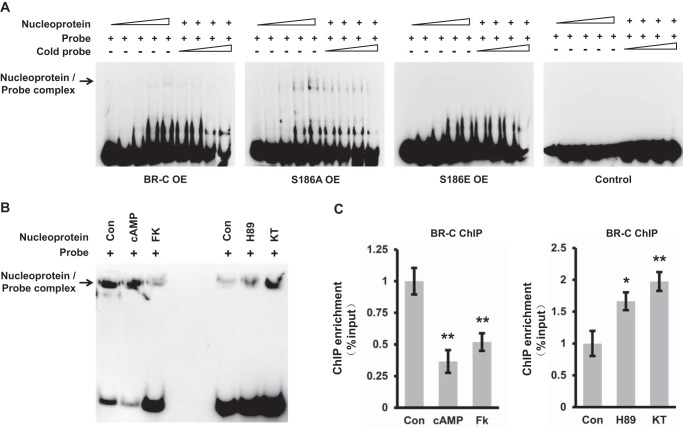
We further examined by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-qPCR whether PKA phosphorylation-induced transcriptional activity inhibition of silkworm BR-C was caused by decreasing its DNA-binding ability. The results demonstrated that the nucleoproteins extracted from BmE cells overexpressing either intact BR-C or S186A mutation can bind to the biotin-labeled probes covering cis-regulatory element (CRE) for BR-C in silkworm WCP10 promoter in a dose-dependent manner, and this binding was competitively suppressed by the unlabeled probe (Fig. 6A). As expected, the S186A mutation, which mimics dephosphorylation, exhibited higher DNA-binding ability than intact BR-C. Moreover, nucleoproteins extracted from the BmE cells overexpressing BR-C with S186E mutation had no affinity with the probe for WCP10 promoter (Fig. 6A). Compared with intact BR-C, BR-C with S186A mutation exhibited a higher ability to bind the WCP10 promoter. Meanwhile, ex vivo culture experiments of fat body from wandering silkworm revealed that the DNA-binding ability of silkworm BR-C was significantly eliminated by PKA activators and improved by PKA inhibitors in silkworm fat body (Fig. 6B). Further ChIP-qPCR assay in ex vivo cultured epidermis of the wandering silkworm also revealed that the ability of BR-C binding to the WCP10 promoter was inhibited by PKA activators but was promoted by PKA inhibitors (Fig. 6C). Our data together demonstrate that PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186 suppressed its transcriptional activities on the target genes by abolishing its DNA-binding activity but was not involved in the regulation of nuclear import of BR-C itself.
Figure 6.
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation inhibited its DNA-binding ability. A, effects of the mutations of PKA phosphorylation site within silkworm BR-C on the DNA-binding ability of BR-C. The nucleoproteins were separately extracted from silkworm BmE cells overexpressing (OE) either intact BR-C or mutated BR-C (S186A and S186E). EMSA confirmed that intact BR-C or S186A mutant can directly bind to the biotin-labeled probes covering the BR-C CRE in WCP10 promoter, but S186E mutant lost the ability to bind the biotin-labeled probes. Unlabeled probes were used for competition analysis. B, effects of PKA activators and inhibitors on the DNA-binding ability of silkworm BR-C. The ex vivo cultured fat body from the wandering silkworm was separately treated with PKA activators (cAMP and forskolin) or inhibitors (H89 and KT5720) for 6 h and was subsequently collected for extracting nucleoprotein for EMSA. C, ChIP-qPCR assays in ex vivo cultured epidermis, from the silkworm at wandering, with treatment of either PKA activators or PKA inhibitors. The ChIP readings were normalized to input. Values are represented as the mean ± S.E. (error bars); *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus controls. FK, forskolin; KT, KT5720; Con, Control.
20E inhibited BR-C phosphorylation and the cAMP/PKA pathway
Given that BR-C is a 20E primary response gene (29, 30) and PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation represses transcriptional activity of BR-C, we investigated whether 20E is also involved in PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation. To test this hypothesis, we ex vivo cultured fat bodies isolated from silkworm larvae at the beginning of the wandering stage and conducted 20E treatment. Intriguingly, Western blot analysis using an anti-p-BR-C antibody targeting the PKA phosphorylation site Ser-186 demonstrated that in ex vivo cultured silkworm larval fat bodies that were treated with 20E, BR-C phosphorylation was decreased 12 h after 20E treatment (Fig. 7A). In silkworm BmE cells, BR-C phosphorylation was elevated at 15 min but was substantially inhibited after 6 h (Fig. 7B).
Figure 7.
PKA-mediated BR-C phosphorylation and the cAMP/PKA pathway were attenuated by 20E. A, fat bodies were isolated from wandering silkworm individuals and then treated ex vivo with 2 μm 20E for 12 h. The change in BR-C phosphorylation level after 20E treatment was examined. B, after being transfected with pSL1180-BR-C for 24 h, the BmE cells were treated with 2 μm 20E and then collected to analyze BR-C phosphorylation level. C, BmE cells were treated with 2 μm 20E, and the intracellular cAMP was measured. D, effect of 2 μm 20E on PKA-C phosphorylation in BmE cells for various time periods. E, effect of 2 μm 20E on CREB protein phosphorylation in BmE cells. F, effect of 20E on CREB protein phosphorylation in ex vivo cultured fat bodies from the wandering silkworm individuals. DMSO treatment was used as a control. Con, control.
Generally, PKA is activated by cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) as a second messenger, which is produced in cells in response to hormones and nutrients, and its catalytic subunit PKA-C induces the phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element-binding (CREB) protein (18–20). Therefore, we further examined whether 20E is involved in cAMP-dependent PKA activation. We first assessed time-course changes in cAMP intracellular levels after in vitro 20E treatment. Silkworm BmE cells were continuously treated with exogenous 20E at a concentration of 2 μm for different times from 5 min to 24 h. Subsequent measurement of endogenous cAMP revealed that compared with DMSO treatment as a control, 20E application increased cAMP production in the early stages from 5 min to 1 h but inhibited cAMP levels in the late stages from 1 h to 24 h (Fig. 7C).
Moreover, the phosphorylation of PKA-C and CREB protein in response to 20E stimuli was further investigated. As shown in Fig. 7D, phosphorylation of PKA-C was significantly suppressed during the period from 6 h to 24 h after 20E treatment. Similarly, compared with DMSO treatment as a control, 20E treatment also reduced the phosphorylation levels of CREB protein, a marker of PKA activation, in silkworm BmE cells (Fig. 7E) and in ex vivo cultured fat bodies (Fig. 7F). Taken together, our data revealed that 20E can repress, at least to some extent, the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway.
Discussion
The insect transcription factor BR-C is a 20E primary response gene and mediates cross-talk between 20E and JH to modulate growth and development (4). Previous extensive studies in insects have predominantly focused on deciphering endocrine hormone regulation of BR-C transcription, identifying BR-C downstream targets, and characterizing BR-C function in various biological processes (4, 5). In this study we demonstrate the importance of PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C.
A striking finding of the present study is that silkworm BR-C can be post-translationally phosphorylated by the Ser/Thr protein kinase PKA at Ser-186. Previously, an interaction between the silkworm BR-C with the RACK1 protein was shown to be required for PKC-mediated BR-C phosphorylation (5) as well as for JH-modulated PKC-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C in the cotton bollworm (11). In addition, PKC has been confirmed to modulate the phosphorylation of the Drosophila USP protein, a key component of the 20E receptor complex EcR/USP (31, 32). We first identified Ser-186 of silkworm BR-C as a PKA phosphorylation site by LS-MS analysis and subsequent biochemical examinations. Our findings, together with existing evidence, strongly indicate that Ser/Thr protein kinases post-translationally modulate 20E signaling in insects.
Generally, the phosphorylation of transcription factors can affect their nuclear import and/or transcriptional activity (33–36). We found that PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C at Ser-186 suppressed its transcriptional activity by abolishing the DNA-binding ability but had no effect on its nuclear localization. Similarly, PKA-mediated phosphorylation can also inhibit the activity of other transcription factors, such as Yap4 in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (37) and serum response factor (SRF) in mice (38). Therefore, we proposed that BR-C plays transcriptional regulatory roles in the absence of PKA-mediated phosphorylation. Moreover, we previously reported that either the disruption of the PKC/RACK1 pathway or the mutation of potential PKC phosphorylation sites of silkworm BR-C substantially blocked its nuclear import (5). Taken together, our findings indicate that silkworm BR-C may be independently phosphorylated by PKA and PKC and that these two types of phosphorylation play distinct roles in BR-C function.
Insect BR-C transcription is activated by endogenous 20E signaling and is subsequently involved in developmental control (4, 5). We observed that a continuous 20E signal could inhibit PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C, which is similar to the findings of 20E inhibition on PKC-mediated phosphorylation of the new isoform (BrZ7) of H. armigera BR-C (11). Notably, our data reveal that the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway was enhanced by 20E treatment at the early response stage, consistent with a previous report showing that the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway is enhanced by 20E in H. armigera (39). Nevertheless, the cAMP/PKA pathway was attenuated at the late-response stage after 20E application. Given that in silkworm the elevation of 20E titer is generally maintained for 24 h during larval molting and 48 h during larval-pupal transition (40) and the transcription of 20E receptor gene EcR was significantly increased 24 h after 20E application in ovary-derived BmN4 cells (41), we hypothesized that continuous 20E signaling could inhibit PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C to a great extent by impairing the cAMP/PKA pathway.
In conclusion, this study elucidated PKA-mediated phosphorylation of silkworm BR-C. Based on the present data and previously reported evidence, we propose a model of the roles of silkworm BR-C phosphorylation in 20E signaling. As shown in Fig. 8, 20E induces the transcription of the silkworm BR-C gene at specific stages, such as larval molting and metamorphosis. Subsequently, the PKC-phosphorylated BR-C protein is translocated into the nucleus to regulate the transcription of downstream target genes. Meanwhile, continuous 20E signaling inhibits not only the cAMP/PKA pathway but also PKA-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C protein, thereby maintaining transcriptional activity of BR-C. Because the production and subsequent signaling pathway of 20E exhibits a stage-dependent fluctuation, namely, being elevated before larval molting and pupation but decreased during the feeding period (4, 40, 42, 43), we hypothesized that PKA-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C protein may be triggered by unknown activators to facilitate rapid inactivation of the BR-C-mediated 20E signaling pathway. Undoubtedly, further work will be needed to clarify how and why PKA-mediated phosphorylation of the BR-C protein is activated.
Figure 8.
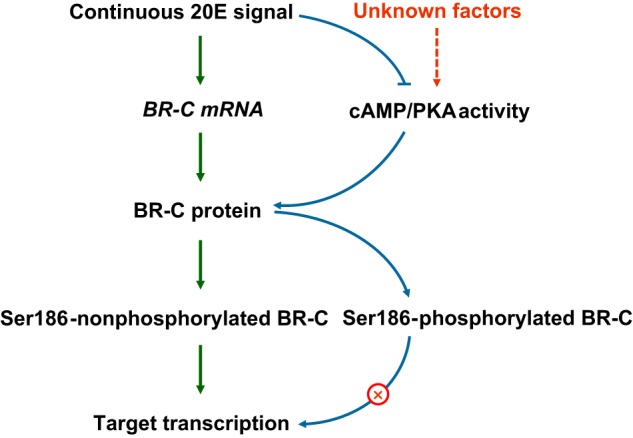
A model of PKA-mediated phosphorylation of BR-C involved in the 20E pathway. As an early response gene of 20E in the silkworm, BR-C is transcriptionally triggered by the presence of 20E. The subsequently translated BR-C protein initiates the transcription of the downstream genes that are involved in metamorphosis as long as Ser-186 remains unphosphorylated. Activated PKA promotes BR-C phosphorylation at Ser-186, which in turn blocks the transcriptional activity of BR-C. Continued 20E signaling during insect development inhibits cAMP/PKA signaling, which may contribute to the maintenance of BR-C transcriptional activity.
Experimental procedures
Insects and cell lines
The Chinese silkworm strain Dazao was reared on fresh mulberry leaves at 25 °C with a photoperiod of 12 h light/12 h dark. In addition, two silkworm cell lines, BmE cells originally derived from embryos and BmN4-SID1 cells (harboring the Caenorhabditis elegans SID1 gene) derived from the ovary, were cultured in Grace's medium (Gibco) and IPL-41 medium (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Life Technologies) at 27 °C. HEK293FT cells derived from human embryonic kidney cells that stably express the SV40 large T antigen were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Gibco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C in humidified air containing 5% CO2.
Protein purification and LC-MS/MS analysis
The pSL1180-BR-C construct for overexpressing the silkworm BR-C Z2 isoform (hereafter referred to as BR-C) was transfected into silkworm BmE cells. The cells were harvested at 48 h after transfection and then lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (50 mm Tris HCl (pH 8), 150 mm NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS) supplemented with 1 mm PMSF on ice. The cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with monoclonal antibodies against silkworm BR-C. The immunoprecipitated BR-C protein complexes were eluted and separated using SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining. The protein bands were retrieved and were further subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis by Shanghai Applied Protein Technology (Shanghai, China).
In addition, in our previous report (12) we extracted total proteins from the fat bodies of five silkworm larvae. The collected fat bodies were first homogenized in RIPA lysis buffer, which contained a mixture of proteinase inhibitors, on ice. The homogenates were centrifuged for 15 min at 17,000 rpm and 4 °C, and the supernatant containing total proteins was collected. Then, the purified total proteins were digested with trypsin, and the phosphorylated peptides were enriched using a TitansphereTM Phos-TiO Kit (GL Sciences, Tokyo, Japan). The enriched phosphorylated peptides were also subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis by Shanghai Applied Protein Technology.
Western blotting and antibodies
Total proteins were prepared following the abovementioned procedure and methods described previously (44) from silkworm cells or individuals that were treated with various reagents, including PKA activators (cAMP, Sigma; forskolin, Beyotime, Shanghai, China), PKA inhibitors (H89, Beyotime; KT5720, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), the dephosphorylation enzyme λ-PP (New England Biolabs), and 20E (Sigma). A total of 100 μg of total proteins were loaded on the SDS-PAGE gels, and subsequent Western blot analysis was performed as described previously (44). Rabbit anti-p-BR-C antibody against the PKA-phosphorylated Ser-186 of silkworm BR-C protein was prepared by Jingjie PTM-BioLab (Hangzhou, China) and diluted at a ratio of 1:10,000 for use. The other antibodies used in the present study are as follows: rabbit anti-BR-C (1:10,000; Zoonbio Biotechnology, China), rabbit anti-p-CREB (1:1000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit anti-PKA-C (1:5000, Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-p-PKA-C (1:5000, Cell Signaling), and mouse anti-tubulin (1:20,000, Beyotime).
ImageJ-based quantitative analysis of Western-blotting data
Quantitative analysis of the visible bands in Western-blotting experiments was performed by using the ImageJ program (45). According to the program instruction, the procedure was briefly described as the following: (a) converting the analyzed file to Grayscale format and subtracting the background with an value of 50; (b) converting the analyzed file to bright band and calculating the density information of a band by hand-drawing an area corresponding to its borders (the information contains area size, mean gray value, minimum and maximum gray value, and integrated density (IntDen); (c) extracting the IntDen values of all the measured bands; (d) dividing the p-BR-C IntDen value by the amounts of the total proteins loading on the SDS-PAGE gels and performing normalization analysis.
Drug treatment and 20E application
Two types of PKA activators, cAMP (Sigma) and forskolin (Beyotime), and two types of PKA inhibitors, H89 (Beyotime) and KT5720 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), were used in the BR-C phosphorylation assays. Briefly, BmE cells overexpress BR-C or fat bodies of silkworm larvae were treated with 160 μm cAMP or 20 μm forskolin separately for 12 h to activate PKA phosphorylation. For the PKA inhibition assays, cells or fat bodies were incubated with H89 or KT5720 at a concentration of 20 μm and 100 nm for 4 h. After the drug treatment, the cells were harvested, and a Western blot assay or a dual luciferase assay was performed. Based on the same procedure, 2 μm 20E was used in cells or for an ex vivo analysis of the silkworm fat body. DMSO treatment was used as a control.
Site-directed mutagenesis
The open reading frame (ORF) of the silkworm BR-C gene was cloned into the pMD19T simple plasmid, which was then used as a template for PKA phosphorylation site mutation. According to the protocol of the MutanBEST Kit (TaKaRa, Japan), the amino acid Ser-186, a PKA phosphorylation site, was changed to Glu (E) or Ala (A), which mimicked phosphorylation or de-phosphorylation, respectively. The modified BR-C ORF sequences were separately subcloned into the pSL1180 vector. These constructs were used for subsequent experiments, including Western blotting, subcellular localization, and the dual luciferase assay.
Subcellular localization
For the subcellular localization assay of the silkworm BR-C protein, BmN4-SID1 cells were seeded onto coverslips in 24-well plates. After 12 h of culture, pSL1180, pSL1180-BR-C, and the constructs containing mutated BR-C proteins were separately transfected into BmN4-SID1 cells at 1 μg per well. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were washed with PBS (pH 7.4) 3 times and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min. Subsequently, the cells were incubated with anti-BR-C antibody (1:500) for 2 h and then with anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 594 antibody (1:1,000, Life Technologies) for 1 h. Then the cells were stained with DAPI (1:1,000, Life Technologies) and Alexa Fluor 488 wheat germ agglutinin, which was used in nuclear membrane staining (1:1,000, Molecular probe). Finally, after washing with PBS three times, the coverslips were mounted on glass slides, and fluorescence signals were captured using confocal microscopy (Fv1000, Olympus, Japan) with excitation wavelengths of 488 and 594 nm.
Dual luciferase assay
The effects of the PKA phosphorylation site mutation or other reagent treatments on BR-C transcriptional activity were analyzed using the dual luciferase assay system (Promega). Briefly, the promoters of two genes directly targeted by silkworm BR-C, namely, the wing cuticle protein gene WCP10 and the sericin-1 gene Ser1, were separately subcloned into a pGL3 basic vector containing the firefly luciferase gene to form two constructs, WCP10-luc and Ser1-luc, respectively. In addition, a pRL-TK vector containing the Renilla luciferase gene was used as an internal control. The overexpression constructs, including pSL1180, pSL1180-BR-C, and the BR-C mutation vectors, were co-transfected with WCP10-luc or Ser1-luc into silkworm BmE cells, separately. At 48 h after transfection, we harvested the cells and measured the relative luciferase activity by normalizing the firefly luciferase level to the Renilla luciferase level. For reagents treatment, pSL1180-BR-C was separately co-transfected with WCP10-luc into silkworm BmE cells, and these cells were incubated with PKA activator for 12 h. Subsequently, the relative luciferase activity was measured using a microplate reader (Synergy H1, BioTek).
EMSA
To test the DNA-binding ability of silkworm BR-C, EMSA experiments were performed as described previously (44). Briefly, based on our online prediction and previous report (6), specific probes covering the CRE for BR-C in silkworm WCP10 promoter were prepared and labeled with biotin at the 5′ end. The sequence of this specific probe is AATTAGAATGAGTCTAATAAATAGTATATTATGGTCAATC. Following the manufacturer's instructions of the EMSA/Gel-Shift Kit (Beyotime), the nucleoproteins extracted from silkworm BmE cells overexpressing either intact or mutated BR-C or from fat body of wandering silkworm with drug treatment were incubated with 100 nm labeled probes. For competition assays, a 5∼50-fold molar excess of the unlabeled probes were incubated for binding with nucleoproteins before the adding of the labeled probes. Subsequently, the mixture was electrophoresed in 5% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels in TBE buffer (45 mm Tris borate and 1 mm EDTA, pH 8.3) and transferred onto nylon membrane to perform chromogenic reaction.
ChIP assays
ChIP assays coupled with quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) were performed to further confirm the DNA-binding ability of silkworm BR-C. According to the manufacturer's instructions of EZ ChIPTM Immunoprecipitation Kit (Millipore) and a previous report (46), ex vivo cultured epidermis from the wandering silkworms were treated by PKA-specific inhibitors or activators and were subsequently fixed with 37% formaldehyde to cross-link chromatin. The cross-linked chromatin was then sonicated to shear into DNA fragments of 200–1000 bp in length. The complexes immunoprecipitated by anti-BR-C antibody were then enriched by Protein G magnetic Dynabeads (Invitrogen). Finally, the purified DNA samples were analyzed by quantitative PCR with specific primer pair covering the CREs of BR-C in silkworm WCP10 promoter: 5′-ACTTACATCAGTCATTGTCCTC-3′ (forward) and 5′-CGTTGAATCATTTCGCGTAG-3′ (reverse). All reactions were performed in triplicate.
Co-IP analysis
CO-IP experiments were conducted to determine the potential interactions between silkworm BR-C and PKA. The BmE cells overexpressing silkworm BR-C were collected and lysed in Nonidet P-40 buffer (50 mm Tris (pH7.4), 150 mm NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40) plus 1 mm protein inhibitor phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride (Beyotime). Subsequently, the cell lysates were centrifuged, and the supernatants were incubated with Protein G magnetic Dynabeads (Invitrogen) that were cross-linked by anti-BR-C antibody or rabbit IgG under a condition of gentle rotation for 6 h at 4 °C. After several washings, the captured protein complex were eluted with SDT buffer (4% (w/v) SDS, 100 mm Tris/HCl (pH 7.4)) and denatured by boiling beads for 5 min. Finally, the immunoprecipitated proteins complex was detected by Western blotting with anti-PKA-C antibody.
In vitro dephosphorylation assay
To verify the roles of PKA in BR-C phosphorylation, we performed an in vitro dephosphorylation assay. Briefly, silkworm BmE cells that overexpressed BR-C or fat bodies of silkworm larvae were collected and lysed for 20 min in RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime). After protein purification and quantification, 2 μg of each sample was co-incubated with λ-protein phosphatase at 30 °C for 30 min and then boiled with 5× protein loading buffer for 5 min. The products were used to measure BR-C phosphorylation via Western-blotting analysis with anti-BR-C and anti-p-BR-C antibodies.
cAMP measurement
The silkworm BmE cells were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured for 12 h. Then, after independent treatments with 2 μm 20E for different gradient times, the BmE cells were separately harvested and washed in PBS 3 times. Then the cells were thoroughly lysed in cell lysis buffer 5 (R&D Systems) on ice for two freeze/thaw cycles. After centrifugation at 600 × g for 10 min, supernatants were collected for cAMP assays with a cAMP Assay Kit (R&D Systems). All experiments were independently repeated three times.
Author contributions
D. C. and Q. X. designed the study. W. Q. performed most of the experiments. X. G., T. Z., L. W., X. Y., Z. L., Y. Y., L. S., J. P., and P. W. helped with the experiments. D. C. and W. Q. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272503, 31572464, and 31172267) and the municipal graduate student research innovation project of Chongqing (CYB14047). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
This article contains supplemental Fig. S1.
Please note that the JBC is not responsible for the long-term archiving and maintenance of this site or any other third party hosted site.
- BR-C
- Broad-Complex
- BTB
- Bric-a-brac/Tramtrack/Broad-Complex
- 20E
- 20-hydroxyecdysone
- co-IP
- co-immunoprecipitation
- JH
- juvenile hormone
- EcR
- ecdysone receptor
- USP
- ultraspiracle
- RACK1
- receptor for activated protein kinase C 1
- qPCR
- quantitative PCR
- CRE
- cis-regulatory element
- CREB protein
- cyclic AMP response element-binding protein
- RIPA buffer
- radioimmune precipitation assay buffer
- λ-PP
- λ-protein phosphatase.
References
- 1. DiBello P. R., Withers D. A., Bayer C. A., Fristrom J. W., and Guild G. M. (1991) The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics 129, 385–397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Zollman S., Godt D., Privé G. G., Couderc J. L., and Laski F. A. (1994) The BTB domain, found primarily in zinc finger proteins, defines an evolutionarily conserved family that includes several developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 10717–10721 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Jindra M., Palli S. R., and Riddiford L. M. (2013) The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 58, 181–204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dubrovsky E. B. (2005) Hormonal cross talk in insect development. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 16, 6–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Cheng D., Qian W., Wang Y., Meng M., Wei L., Li Z., Kang L., Peng J., and Xia Q. (2014) Nuclear import of transcription factor BR-C is mediated by its interaction with RACK1. PloS ONE 9, e109111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wang H. B., Iwanaga M., and Kawasaki H. (2009) Activation of BMWCP10 promoter and regulation by BR-C Z2 in wing disc of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39, 615–623 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cakouros D., Daish T., Martin D., Baehrecke E. H., and Kumar S. (2002) Ecdysone-induced expression of the caspase DRONC during hormone-dependent programmed cell death in Drosophila is regulated by Broad-Complex. J. Cell Biol 157, 985–995 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. von Kalm L., Crossgrove K., Von Seggern D., Guild G. M., and Beckendorf S. K. (1994) The Broad-Complex directly controls a tissue-specific response to the steroid hormone ecdysone at the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. EMBO J. 13, 3505–3516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kayukawa T., Minakuchi C., Namiki T., Togawa T., Yoshiyama M., Kamimura M., Mita K., Imanishi S., Kiuchi M., Ishikawa Y., and Shinoda T. (2012) Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 11729–11734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kayukawa T., Nagamine K., Ito Y., Nishita Y., Ishikawa Y., and Shinoda T. (2016) Kruppel homolog 1 inhibits insect metamorphosis via direct transcriptional repression of broad-complex, a pupal specifier gene. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 1751–1762 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Cai M. J., Liu W., Pei X. Y., Li X. R., He H. J., Wang J. X., and Zhao X. F. (2014) Juvenile hormone prevents 20-hydroxyecdysone-induced metamorphosis by regulating the phosphorylation of a newly identified broad protein. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 26630–26641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Song L., Wang F., Dong Z., Hua X., and Xia Q. (2017) Label-free quantitative phosphoproteomic profiling of cellular response induced by an insect cytokine paralytic peptide. J. Proteomics 154, 49–58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Wagner L., Laczy B., Tamaskó M., Mazák I., Markó L., Molnár G. A., Wagner Z., Mohás M., Cseh J., Fekete A., and Wittmann I. (2007) Cigarette smoke-induced alterations in endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation: role of protein kinase C. Endothelium 14, 245–255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Ditlevsen D. K., Køhler L. B., Pedersen M. V., Risell M., Kolkova K., Meyer M., Berezin V., and Bock E. (2003) The role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in neural cell adhesion molecule-mediated neuronal differentiation and survival. J. Neurochem. 84, 546–556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Michell B. J., Chen Z. p., Tiganis T., Stapleton D., Katsis F., Power D. A., Sim A. T., and Kemp B. E. (2001) Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17625–17628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Wang W., Jobbagy Z., Bird T. H., Eiden M. V., and Anderson W. B. (2005) Cell signaling through the protein kinases cAMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase Cϵ, and RAF-1 regulates amphotropic murine leukemia virus envelope protein-induced syncytium formation. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 16772–16783 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Di Giacomo M., Camaioni A., Klinger F. G., Bonfiglio R., and Salustri A. (2016) Cyclic AMP-elevating agents promote cumulus cell survival and hyaluronan matrix stability, thereby prolonging the time of mouse oocyte fertilizability. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 3821–3836 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Fimia G. M., and Sassone-Corsi P. (2001) Cyclic AMP signalling. J. cell Sci. 114, 1971–1972 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Daniel P. B., Walker W. H., and Habener J. F. (1998) Cyclic AMP signaling and gene regulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 18, 353–383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Sassone-Corsi P. (2012) The cyclic AMP pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, a011148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Diamond M. I., Cai S., Boudreau A., Carey C. J. Jr, Lyle N., Pappu R. V., Swamidass S. J., Bissell M., Piwnica-Worms H., and Shao J. (2015) Subcellular localization and Ser-137 phosphorylation regulate tumor-suppressive activity of profilin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 9075–9086 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Ibañez I. L., Bracalente C., Notcovich C., Tropper I., Molinari B. L., Policastro L. L., and Durán H. (2012) Phosphorylation and subcellular localization of p27Kip1 regulated by hydrogen peroxide modulation in cancer cells. PloS ONE 7, e44502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Horovitz-Fried M., Jacob A. I., Cooper D. R., and Sampson S. R. (2007) Activation of the nuclear transcription factor SP-1 by insulin rapidly increases the expression of protein kinase C delta in skeletal muscle. Cell. Signal. 19, 556–562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Carvalho J., Bertram P. G., Wente S. R., and Zheng X. F. (2001) Phosphorylation regulates the interaction between Gln3p and the nuclear import factor Srp1p. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25359–25365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Brownawell A. M., Kops G. J., Macara I. G., and Burgering B. M. (2001) Inhibition of nuclear import by protein kinase B (Akt) regulates the subcellular distribution and activity of the forkhead transcription factor AFX. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3534–3546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Gradin K., Takasaki C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., and Sogawa K. (2002) The transcriptional activation function of the HIF-like factor requires phosphorylation at a conserved threonine. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23508–23514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Ye L., Qian Q., Zhang Y., You Z., Che J., Song J., and Zhong B. (2015) Analysis of the sericin1 promoter and assisted detection of exogenous gene expression efficiency in the silkworm Bombyx mori L. Sci. Rep. 5, 8301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Tripoulas N., and Samols D. (1986) Developmental and hormonal regulation of sericin RNA in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Dev. Biol. 116, 328–336 [Google Scholar]
- 29. Muramatsu D., Kinjoh T., Shinoda T., and Hiruma K. (2008) The role of 20-hydroxyecdysone and juvenile hormone in pupal commitment of the epidermis of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Mech. Dev. 125, 411–420 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Beckstead R. B., Lam G., and Thummel C. S. (2005) The genomic response to 20-hydroxyecdysone at the onset of Drosophila metamorphosis. Genome Biol. 6, R99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Wang S., Wang J., Sun Y., Song Q., and Li S. (2012) PKC-mediated USP phosphorylation at Ser35 modulates 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling in Drosophila. J. Proteome Res. 11, 6187–6196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sun X., and Song Q. (2006) PKC-mediated USP phosphorylation is required for 20E-induced gene expression in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 62, 116–127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Maneechotesuwan K., Yao X., Ito K., Jazrawi E., Usmani O. S., Adcock I. M., and Barnes P. J. (2009) Suppression of GATA-3 nuclear import and phosphorylation: a novel mechanism of corticosteroid action in allergic disease. PLoS Med. 6, e1000076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Liu L., McBride K. M., and Reich N. C. (2005) STAT3 nuclear import is independent of tyrosine phosphorylation and mediated by importin-α3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 8150–8155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Harreman M. T., Kline T. M., Milford H. G., Harben M. B., Hodel A. E., and Corbett A. H. (2004) Regulation of nuclear import by phosphorylation adjacent to nuclear localization signals. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 20613–20621 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Tagawa T., Kuroki T., Vogt P. K., and Chida K. (1995) The cell cycle-dependent nuclear import of v-Jun is regulated by phosphorylation of a serine adjacent to the nuclear localization signal. J. Cell Biol. 130, 255–263 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Pereira J., Pimentel C., Amaral C., Menezes R. A., and Rodrigues-Pousada C. (2009) Yap4 PKA- and GSK3-dependent phosphorylation affects its stability but not its nuclear localization. Yeast 26, 641–653 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Blaker A. L., Taylor J. M., and Mack C. P. (2009) PKA-dependent phosphorylation of serum response factor inhibits smooth muscle-specific gene expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29, 2153–2160 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Jing Y. P., Wang D., Han X. L., Dong D. J., Wang J. X., and Zhao X. F. (2016) The steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone enhances gene transcription through the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 12771–12785 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Mizoguchi A., Ohashi Y., Hosoda K., Ishibashi J., and Kataoka H. (2001) Developmental profile of the changes in the prothoracicotropic hormone titer in hemolymph of the silkworm Bombyx mori: correlation with ecdysteroid secretion. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 31, 349–358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Qian W., Kang L., Zhang T., Meng M., Wang Y., Li Z., Xia Q., and Cheng D. (2015) Ecdysone receptor (EcR) is involved in the transcription of cell cycle genes in the silkworm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 3335–3349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Puri P., Little-Ihrig L., Chandran U., Law N. C., Hunzicker-Dunn M., and Zeleznik A. J. (2016) Protein kinase A: a master kinase of granulosa cell differentiation. Sci. Rep. 6, 28132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. King-Jones K., and Thummel C. S. (2005) Nuclear receptors: a perspective from Drosophila. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 311–323 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Meng M., Cheng D. J., Peng J., Qian W. L., Li J. R., Dai D. D., Zhang T. L., and Xia Q. Y. (2015) The homeodomain transcription factors Antennapedia and POU-M2 regulate the transcription of the steroidogenic enzyme gene Phantom in the silkworm. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 24438–24452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Schneider C. A., Rasband W. S., and Eliceiri K. W. (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lorenzin F., Benary U., Baluapuri A., Walz S., Jung L. A., von Eyss B., Kisker C., Wolf J., Eilers M., and Wolf E. (2016) Different promoter affinities account for specificity in MYC-dependent gene regulation. eLife 5, e15161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. IC4R Project Consortium, Hao L., Zhang H., Zhang Z., Hu S., and Xue Y. (2016) Information Commons for Rice (IC4R). Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D1172–D1180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.