Abstract
In Crithidia fasciculata, a trypanosomatid protozoan, the nuclear-encoded `28S' rRNA is multiply fragmented, comprising two large (c and d) and four small (e, f, g and j) RNA species. We have determined that the coding sequences for these RNAs (and that of the 5.8S rRNA, species i) are separated from one another by spacer sequences ranging in size from 31 to 416 bp. Coding and spacer sequences are presumably co-transcribed, with excision of the latter during post-transcriptional processing generating a highly fragmented large subunit (LSU) rRNA. Secondary structure modelling indicates that the C. fasciculata LSU rRNA complex (seven segments, including 5.8S rRNA) is held together in part by long-range intermolecular base pairing interactions that are characteristic of intramolecular interactions in the covalently continuous LSU (23S) rRNA of Escherichia coli. At least one functionally critical region (encompassing the α-sarcin cleavage site) is contained in a small RNA species (f) rather than in one of the two large RNAs. Within a proposed secondary structure model of C. fasciculata LSU rRNA, discontinuities between the different segments (created by spacer excision) map to regions that are highly variable in structure in covalently continuous LSU rRNAs. We suggest that `rRNA genes in pieces' and discontinuous rRNAs may represent an evolutionarily ancient pattern.
Keywords: Crithidia fasciculata, rRNA genes, spacers
Full text
PDF
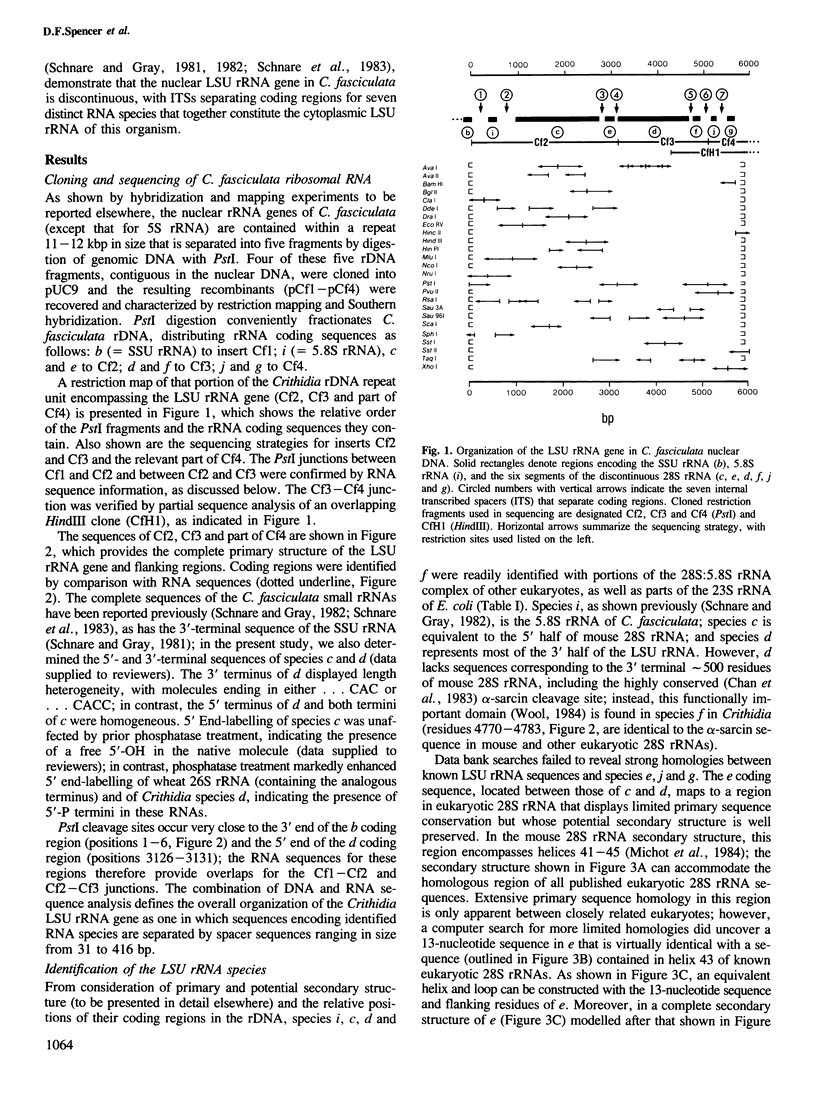


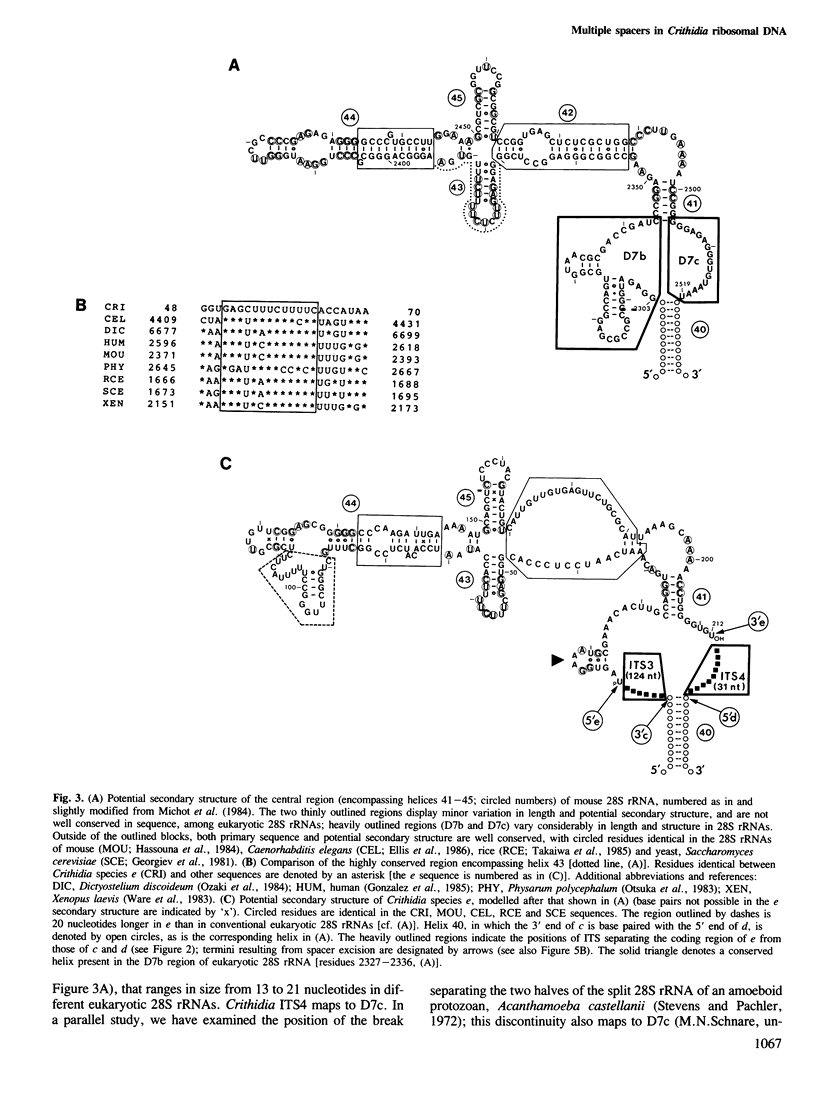
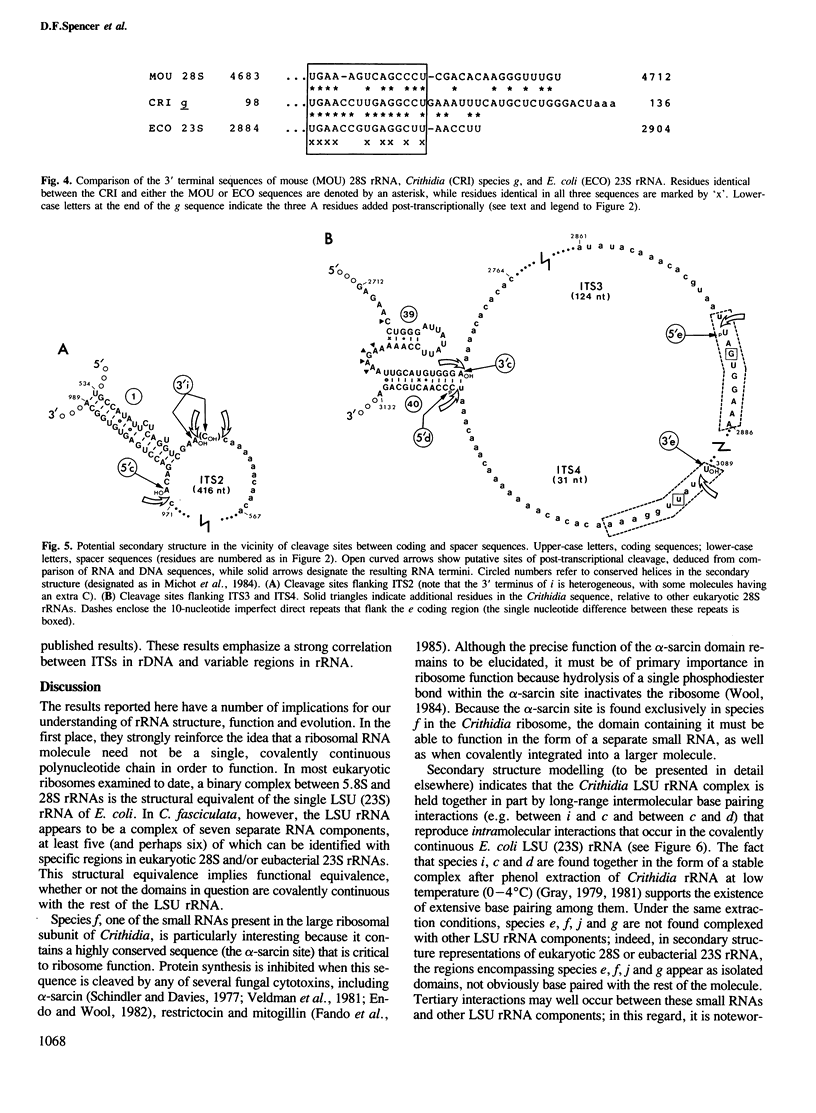
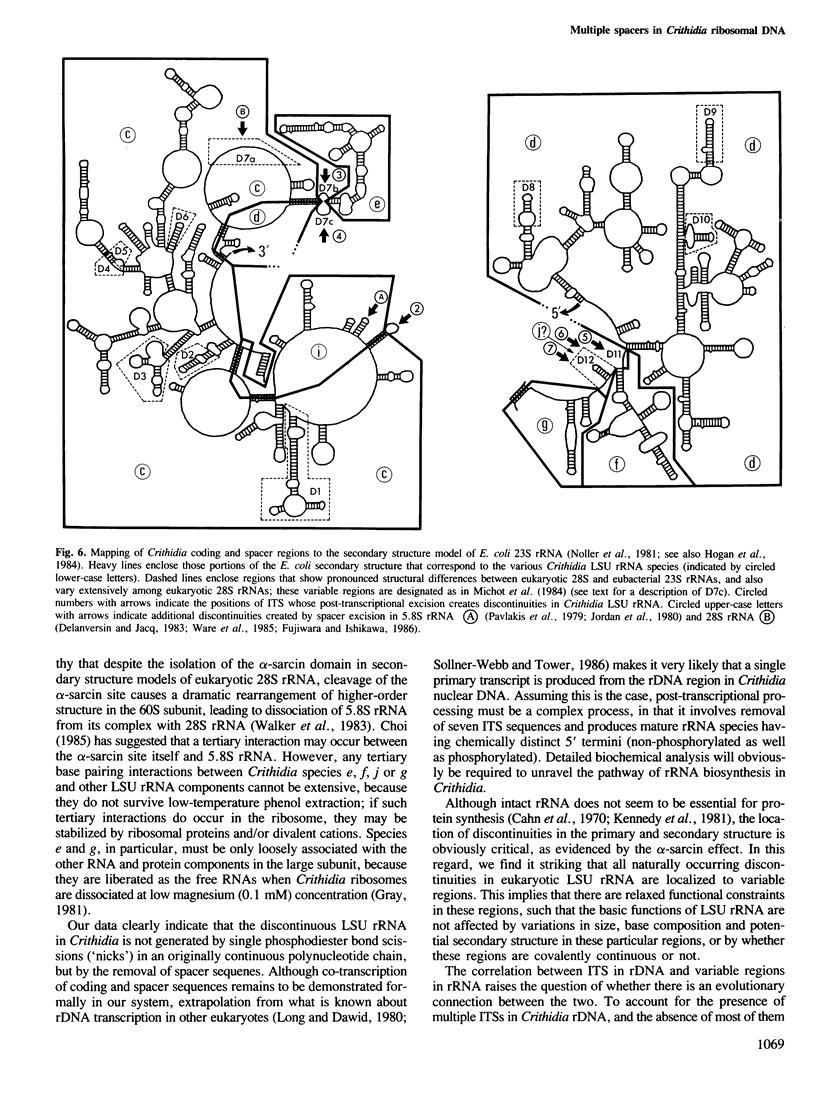


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brimacombe R. The secondary structure of ribosomal RNA, and its organization within the ribosomal subunits. Biochem Soc Symp. 1982;47:49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F., Schachter E. M., Rich A. Polypeptide synthesis with ribonuclease-digested ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;209(2):512–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90748-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano P., Londei P., Mazzei F., Biagini R. Size heterogeneity of ribosomal RNA in eukaryote evolution--2. rRNA molecular weights in species containing discontinuous large ribosomal subunit RNA. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;73(2):435–449. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Endo Y., Wool I. G. The sequence of the nucleotides at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in rat 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12768–12770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. C. Structural organization of ribosomal RNAs from Novikoff hepatoma. I. Characterization of fragmentation products from 40 S subunit. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12769–12772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. G., Tague B. W., Ware V. C., Gerbi S. A. Xenopus laevis 28S ribosomal RNA: a secondary structure model and its evolutionary and functional implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6197–6220. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley J. S., Turner M. J. 6.5 S RNA; preliminary characterisation of unusual small RNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1980 Apr;1(2):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(80)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kelly J. M. Mature 23 SrRNA of prokaryotes appears homologous with the precursor of 25--28 rRNA of eukaryotes: comments on the evolution of 23--28 rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80652-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Kelly J. M. Structural aspects of eukaryotic ribosomes. Biochem Soc Symp. 1982;47:11–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delanversin G., Jacq B. Séquence de la région de la coupure centrale du précurseur de l'ARN ribosomique 26S de Drosophile. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1983;296(22):1041–1044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Sulston J. E., Coulson A. R. The rDNA of C. elegans: sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2345–2364. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fando J. L., Alaba I., Escarmis C., Fernandez-Luna J. L., Mendez E., Salinas M. The mode of action of restrictocin and mitogillin on eukaryotic ribosomes. Inhibition of brain protein synthesis, cleavage and sequence of the ribosomal RNA fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):29–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ishikawa H. Molecular mechanism of introduction of the hidden break into the 28S rRNA of insects: implication based on structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6393–6401. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev O. I., Nikolaev N., Hadjiolov A. A., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 4. Complete sequence of the 25 S rRNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6953–6958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The ribosomal RNA of the trypanosomatid protozoan Crithidia fasciculata: physical characteristics and methylated sequences. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):914–926. doi: 10.1139/o79-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Unusual pattern of ribonucleic acid components in the ribosome of Crithidia fasciculata, a trypanosomatid protozoan. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.4.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson J. H., Sogin M. L. Length variation in eukaryotic rRNAs: small subunit rRNAs from the protists Acanthamoeba castellanii and Euglena gracilis. Gene. 1986;44(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Georgiev O. I., Nosikov V. V., Yavachev L. P. Primary and secondary structure of rat 28 S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3677–3693. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández R., Nava G., Castañeda M. Small-size ribosomal RNA species in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Aug;8(4):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan J. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Probing the conformation of 26S rRNA in yeast 60S ribosomal subunits with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3330–3335. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Latil-Damotte M., Jourdan R. Coding and spacer sequences in the 5.8S-2S region of Sciara coprophila ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3565–3573. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy T. D., Hanley-Bowdoin L. K., Lane B. G. Structural integrity of DNA and translational integrity of ribosomes in nuclease-treated cell-free protein synthesizing systems prepared from wheat germ and rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5802–5809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei P., Cammarano P., Mazzei F., Romeo A. Size heterogeneity of ribosomal RNA in eukaryote evolution--1. rRNA molecular weights in species containing intact large ribosomal subunit RNA. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;73(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90308-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. M., Spencer D. F., Doolittle W. F., Gray M. W. Nucleotide sequences of wheat-embryo cytosol 5-S and 5.8-S ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):561–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Secondary structure of mouse 28S rRNA and general model for the folding of the large rRNA in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4259–4279. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. A 5.8 S rRNA-like sequence in prokaryotic 23 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. Evolutionary relationship between eukaryotic 29--32 S nucleolar rRNA precursors and the prokaryotic 23 S rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jul 5;143(2):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Kop J., Wheaton V., Brosius J., Gutell R. R., Kopylov A. M., Dohme F., Herr W., Stahl D. A., Gupta R. Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6167–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., McCarroll R., Sogin M. L. Secondary structure of the Dictyostelium discoideum small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):8037–8049. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.8037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka T., Nomiyama H., Yoshida H., Kukita T., Kuhara S., Sakaki Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 26S rRNA gene of Physarum polycephalum: its significance in gene evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3163–3167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki T., Hoshikawa Y., Iida Y., Iwabuchi M. Sequence analysis of the transcribed and 5' non-transcribed regions of the ribosomal RNA gene in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4171–4184. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis G. N., Jordan B. R., Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N. Sequence and secondary structure of Drosophila melanogaster 5.8S and 2S rRNAs and of the processing site between them. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2213–2238. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler D. G., Davies J. E. Specific cleavage of ribosomal RNA caused by alpha sarcin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):1097–1110. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Collings J. C., Gray M. W. Structure and evolution of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene of Crithidia fasciculata. Curr Genet. 1986;10(5):405–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00418414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of Crithidia fasciculata small ribosomal subunit RNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Nucleotide sequence of an exceptionally long 5.8S ribosomal RNA from Crithidia fasciculata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2085–2092. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Heinonen T. Y., Young P. G., Gray M. W. A discontinuous small subunit ribosomal RNA in Tetrahymena pyriformis mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5187–5193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Heinonen T. Y., Young P. G., Gray M. W. Phenylalanine and tyrosine transfer RNAs encoded by Tetrahymena pyriformis mitochondrial DNA: primary sequence, post-transcriptional modifications, and gene localization. Curr Genet. 1985;9(5):389–393. doi: 10.1007/BF00421610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Spencer D. F., Gray M. W. Primary structures of four novel small ribosomal RNAs from Crithidia fasciculata. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;61(1):38–45. doi: 10.1139/o83-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Simpson A. G. Kinetoplast RNA of Leishmania tarentolae. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Elwood H. J., Gunderson J. H. Evolutionary diversity of eukaryotic small-subunit rRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. F., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Pronounced structural similarities between the small subunit ribosomal RNA genes of wheat mitochondria and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Pachler P. F. Discontinuity of 26 s rRNA in Acanthamoeba castellani. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90475-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler P., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C. A general secondary-structure model for procaryotic and eucaryotic RNAs from the small ribosomal subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;120(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Oono K., Iida Y., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a rice 25S.rRNA gene. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vossbrinck C. R., Woese C. R. Eukaryotic ribosomes that lack a 5.8S RNA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):287–288. doi: 10.1038/320287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. A., Endo Y., Wheat W. H., Wool I. G., Pace N. R. Location of 5.8 S rRNA contact sites in 28 S rRNA and the effect of alpha-sarcin on the association of 5.8 S rRNA with 28 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware V. C., Renkawitz R., Gerbi S. A. rRNA processing: removal of only nineteen bases at the gap between 28S alpha and 28S beta rRNAs in Sciara coprophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3581–3597. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware V. C., Tague B. W., Clark C. G., Gourse R. L., Brand R. C., Gerbi S. A. Sequence analysis of 28S ribosomal DNA from the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7795–7817. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker R. H. New concepts of kingdoms or organisms. Evolutionary relations are better represented by new classifications than by the traditional two kingdoms. Science. 1969 Jan 10;163(3863):150–160. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3863.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


