Abstract
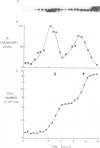
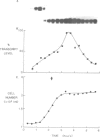
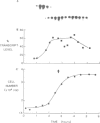
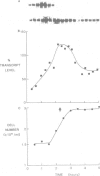
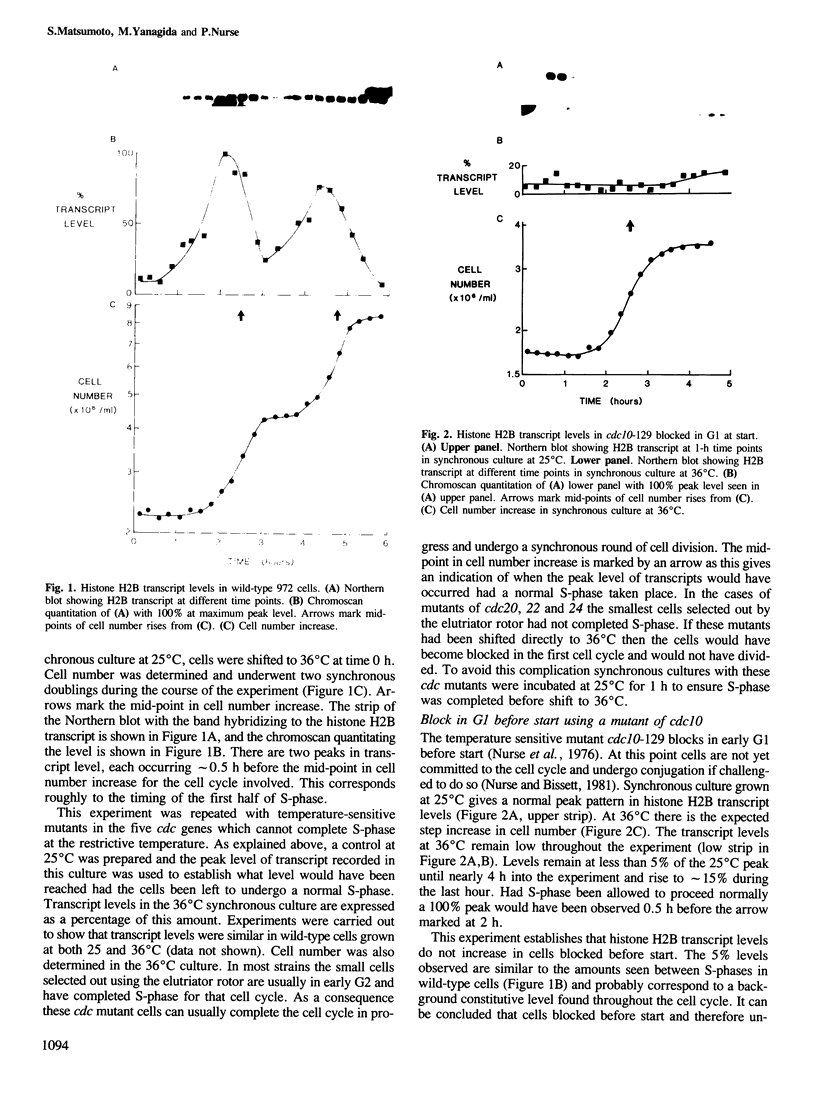
The level of histone H2B transcripts peak during S-phase of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The pattern of transcript accumulation has been monitored in temperature-sensitive mutants which block at different times during the cell cycle, at start in G1 where the cell becomes committed to the mitotic cycle, in G1 after start, and during S-phase. Cells blocked before start using cdc10-129 do not accumulate histone H2B transcripts, but cells blocked after start using cdc22-C11 do show accumulation. Transcript levels increase in another mutant cdc20-M10 which also blocks in G1. These experiments establish that histone H2B transcripts increase in level in preparation for S-phase during late G1 before any DNA synthesis. Passage of start begins a sequence of events leading to S-phase which includes an increase in histone H2B transcript levels. In the cdc20 and cdc22 mutants transcript levels do not decrease normally suggesting that the signals which lead to the fall in level are not given in these G1-arrested cells. The mutants cdc17-K42 (defective in DNA ligase) and cdc24-M38 block in late S-phase after the DNA content has doubled. Histone H2B transcripts increase normally but remain at a high level. In these mutants even though DNA content has doubled, the mechanisms which lead to a fall in transcript levels appear not to be brought into play.
Keywords: histone, transcription, cell cycle, yeast, start
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Grafsky A., Lee A. S. Isolation of a mammalian sequence capable of conferring cell cycle regulation to a heterologous gene. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.4059922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aves S. J., Durkacz B. W., Carr A., Nurse P. Cloning, sequencing and transcriptional control of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc10 'start' gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):457–463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capasso O., Heintz N. Regulated expression of mammalian histone H4 genes in vivo requires a trans-acting transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5622–5626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkacz B., Carr A., Nurse P. Transcription of the cdc2 cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):369–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Identification of promoter elements necessary for transcriptional regulation of a human histone H4 gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):380–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Transcription of human histone genes in extracts from synchronized HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2713–2717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Bromley S., Osley M. A. Periodic transcription of yeast histone genes. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. R., Marashi F., Baserga R., Stein J., Stein G. Expression of histone genes in a G1-specific temperature-sensitive mutant of the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3731–3735. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yanagida M. Histone gene organization of fission yeast: a common upstream sequence. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3531–3538. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. Temperature-sensitive lethal mutants in the structural gene for DNA ligase in the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Nurse P. Cell division cycle mutants altered in DNA replication and mitosis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00422777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):547–551. doi: 10.1038/256547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P., Nasmyth K. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):167–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00268085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Gould J., Kim S., Kane M. Y., Hereford L. Identification of sequences in a yeast histone promoter involved in periodic transcription. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Multiple sequence elements are required for maximal in vitro transcription of a human histone H2B gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3329–3340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]