Abstract
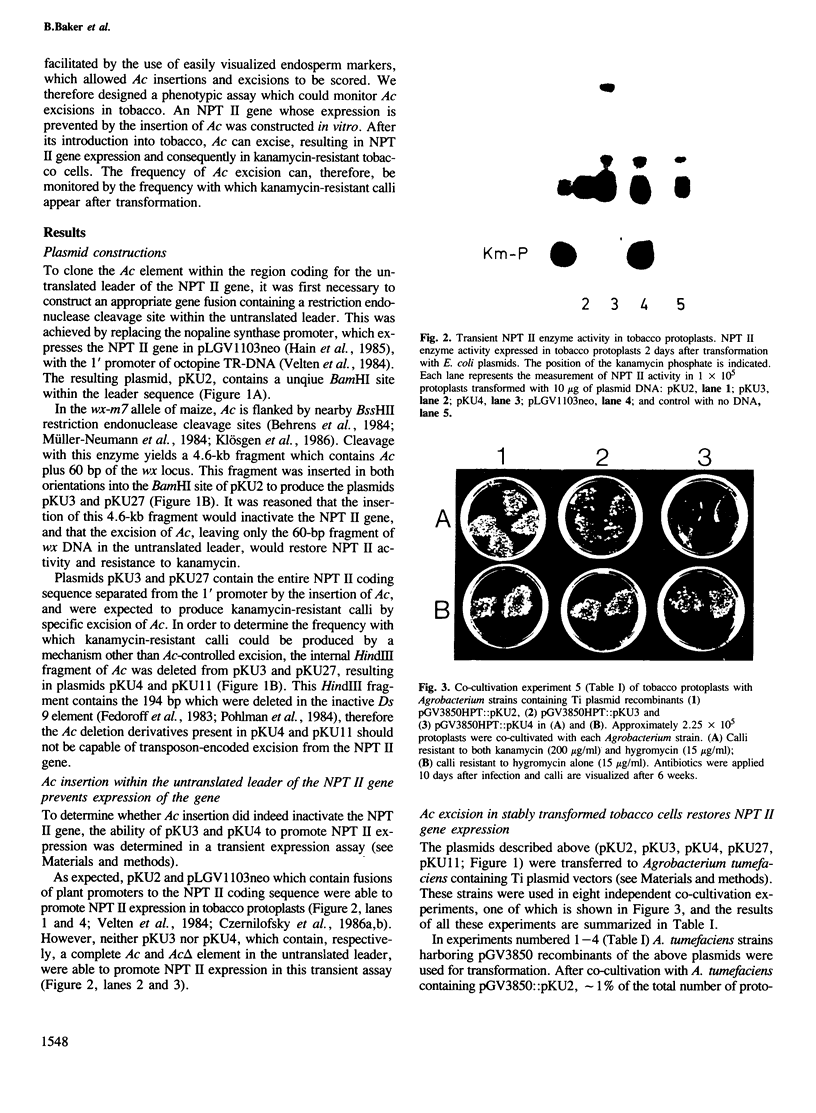
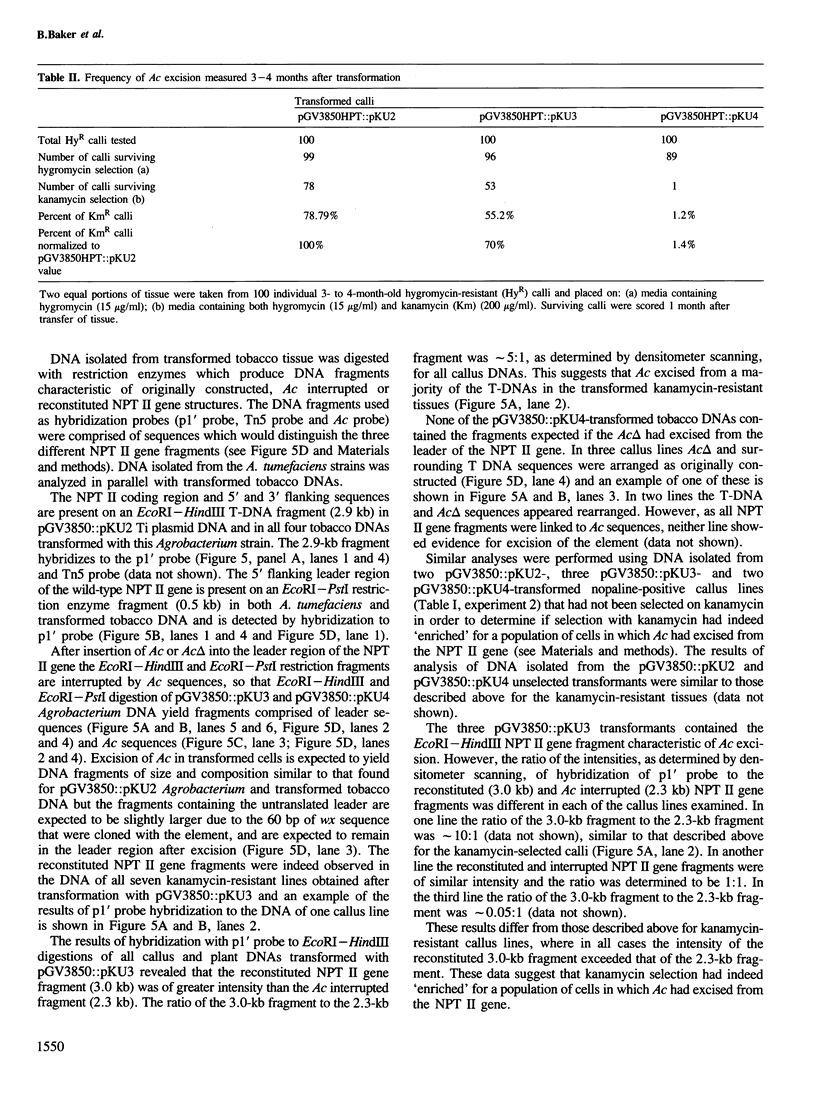
We describe a phenotypic assay designed to detect excision of the maize controlling element Ac from a selectable marker gene, neomycin phosphotransferase II (NPT II). An NPT II gene which expresses kanamycin resistance in tobacco cells, and contains a unique restriction enzyme site in the untranslated leader region, was constructed. Ac, or a defective Ac element (Ac△), was inserted into the leader region of this gene. The transposon insertions inactivated the NPT II gene as determined by transient NPT II expression assays. The three plasmids were inserted into the T DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid vectors, and transferred to tobacco protoplasts. The transformed protoplasts were selected with 100 or 200 µg/ml kanamycin. Protoplasts transformed by the NPT II gene interrupted by Ac formed ˜25% as many calli resistant to 100 or 200 µg/ml kanamycin as protoplasts transformed by the uninterrupted NPT II gene. Protoplasts transformed by the NPT II gene interrupted by Ac△ did not form any calli resistant to 200 µg/ml of kanamycin when transformed under similar conditions. Southern blot hybridization analyses of seven kanamycin-resistant calli or plants obtained after transformation by the NPT II gene interrupted by Ac revealed that in all cases Ac had excised, restoring the structure of the NPT II gene. This assay is therefore useful to monitor the activity of a transposable element such as Ac and to define the regions of this element involved in transposition activity.
Keywords: Ac-transposition, tobacco transformation, gene tagging, transposon insertion
Full text
PDF

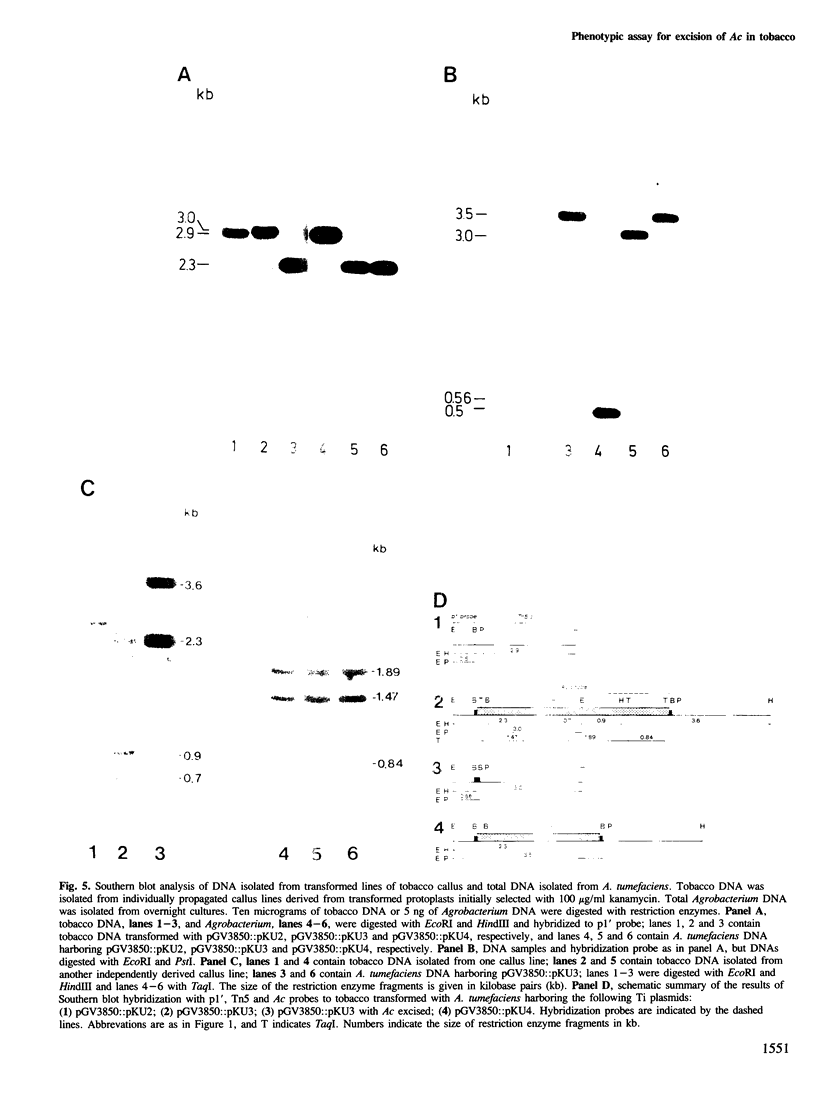



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B., Schell J., Lörz H., Fedoroff N. Transposition of the maize controlling element "Activator" in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4844–4848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Hain R., Baker B., Wirtz U. Studies of the structure and functional organization of foreign DNA integrated into the genome of Nicotiana tabacum. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):473–482. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Hain R., Herrera-Estrella L., Lörz H., Goyvaerts E., Baker B. J., Schell J. Fate of selectable marker DNA integrated into the genome of Nicotiana tabacum. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):101–113. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Starlinger P. Barbara McClintock's controlling elements: now at the DNA level. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Tillmann E., Starlinger P. DNA sequence of the maize transposable element Dissociation. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):127–130. doi: 10.1038/307127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V., Furtek D. B., Nelson O. E. Cloning of the bronze locus in maize by a simple and generalizable procedure using the transposable controlling element Activator (Ac). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joos H., Timmerman B., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Genetic analysis of transfer and stabilization of Agrobacterium DNA in plant cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2151–2160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Carpenter R., Sommer H., Saedler H., Coen E. S. Molecular analysis of instability in flower pigmentation of Antirrhinum majus, following isolation of the pallida locus by transposon tagging. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1625–1630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCLINTOCK B. Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:13–47. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly C., Shepherd N. S., Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Bertram I., Robertson D. S., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Molecular cloning of the a1 locus of Zea mays using the transposable elements En and Mu1. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):877–882. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Fedoroff N. V., Messing J. The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss B., Sprengel R., Will H., Schaller H. A new sensitive method for qualitative and quantitative assay of neomycin phosphotransferase in crude cell extracts. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedler H., Nevers P. Transposition in plants: a molecular model. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):585–590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Cuypers H., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Plant transposable elements generate the DNA sequence diversity needed in evolution. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):591–597. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D., Gerlach W. L., Peacock W. J., Schwartz D. Molecular analysis of ds controlling element mutations at the adh1 locus of maize. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1265–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4642.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haute E., Joos H., Maes M., Warren G., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Intergeneric transfer and exchange recombination of restriction fragments cloned in pBR322: a novel strategy for the reversed genetics of the Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):411–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velten J., Velten L., Hain R., Schell J. Isolation of a dual plant promoter fragment from the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P., Joos H., Genetello C., Leemans J., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]