Abstract
Protein II isolated from porcine intestinal epithelium is a Ca2+-modulated lipid-binding protein. The amino acid sequence of porcine protein II reported here sheds new light on the properties of a multigene protein family which includes the tyrosine kinase substrates of the sarc gene (p36) and of the EGF-receptor (p35). The sequence consolidates the structural principle in which an amino-terminal tailpiece of variable length is followed by a core built from four internally homologous segments for those proteins in the 35-40 kd range. Sequence data also show that the core can now be described as two domains each containing one low and one high homology segment. This view accounts for two Ca2+ sites, lipid aggregation and F-actin bundling--when present--and suggests that properties of the cores in which protein II differs from p36 and p35 arise primarily from segments 1 and 2. The protease-sensitive tailpiece of protein II is very short and lacks the phosphorylatable tyrosine present in the larger tail domains of p36 and p35. It harbors, however, like the p36 domain, the major site for in vitro phosphorylation by the Ca2+- and lipid-activated protein kinase C. In protein II this site is most likely threonine 6. The sequence alignment also explains why protein II does not interact with a unique p11, a property probably specific for p36. Our results further suggest that liver endonexin may reflect two protein species both closely related to protein II.
Full text
PDF


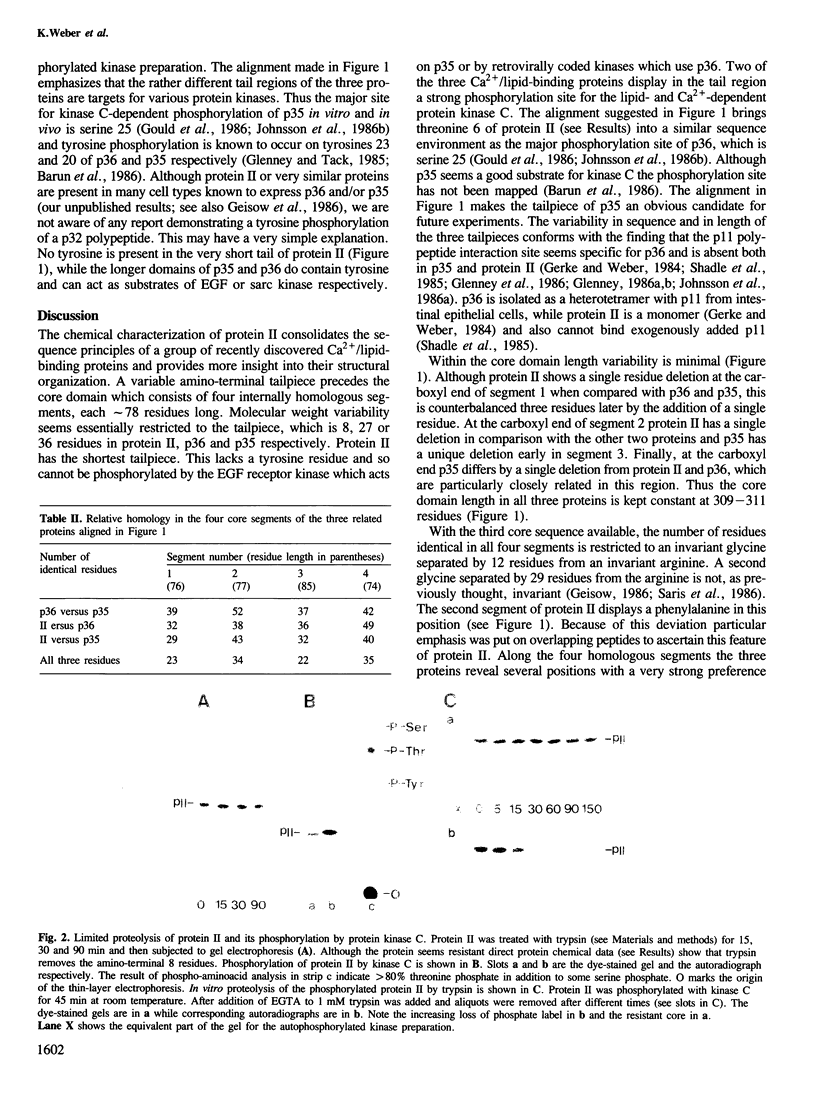


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen S., Fava R. A. Internalization of functional epidermal growth factor:receptor/kinase complexes in A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12351–12358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Dowling L. G., Sando J. J., Villar-Palasi C., Whipple J. H., Zaks W. J. Characterization of the chromobindins. Soluble proteins that bind to the chromaffin granule membrane in the presence of Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14664–14674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. A., Crumpton M. J. Identification of calcium-binding proteins associated with the lymphocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Tomasiewicz H. G., Erikson R. L. Biochemical characterization of a 34-kilodalton normal cellular substrate of pp60v-src and an associated 6-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Common domain structure of Ca2+ and lipid-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Fritsche U., Hexham J. M., Dash B., Johnson T. A consensus amino-acid sequence repeat in Torpedo and mammalian Ca2+-dependent membrane-binding proteins. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):636–638. doi: 10.1038/320636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M., Childs J., Dash B., Harris A., Panayotou G., Südhof T., Walker J. H. Cellular distribution of three mammalian Ca2+-binding proteins related to Torpedo calelectrin. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2969–2974. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02242.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Calcium-dependent conformational changes in the 36-kDa subunit of intestinal protein I related to the cellular 36-kDa target of Rous sarcoma virus tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1688–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Identity of p36K phosphorylated upon Rous sarcoma virus transformation with a protein purified from brush borders; calcium-dependent binding to non-erythroid spectrin and F-actin. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):227–233. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. The regulatory chain in the p36-kd substrate complex of viral tyrosine-specific protein kinases is related in sequence to the S-100 protein of glial cells. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2917–2920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Boudreau M., Galyean R., Hunter T., Tack B. Association of the S-100-related calpactin I light chain with the NH2-terminal tail of the 36-kDa heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10485–10488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr Phosphorylation of p36 in vitro with pp60src. Regulation by Ca2+ and phospholipid. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7884–7888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Phospholipid-dependent Ca2+ binding by the 36-kDa tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) and its 33-kDa core. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7247–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. The 46,000-dalton tyrosine protein kinase substrate is widespread, whereas the 36,000-dalton substrate is only expressed at high levels in certain rodent tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):487–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Isacke C. M., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 is also a substrate for protein kinase C in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2738–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hexham J. M., Totty N. F., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Homology between the subunits of S100 and a 10kDa polypeptide associated with p36 of pig lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Matsuda K., Notsu Y., Hattori T., del Carmine R. Phosphorylation at a tyrosine residue of lipomodulin in mitogen-stimulated murine thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4717–4721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N., Nguyen Van P., Söling H. D., Weber K. Functionally distinct serine phosphorylation sites of p36, the cellular substrate of retroviral protein kinase; differential inhibition of reassociation with p11. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3455–3460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N., Vandekerckhove J., Van Damme J., Weber K. Binding sites for calcium, lipid and p11 on p36, the substrate of retroviral tyrosine-specific protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):361–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Creutz C. E. Cell biology. Consensus in exocytosis. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):573–573. doi: 10.1038/320573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Saris C. J., Hunter T., Hicks L. J., Noonan D. J., Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Primary structure of bovine calpactin I heavy chain (p36), a major cellular substrate for retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases: homology with the human phospholipase A2 inhibitor lipocortin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4497–4503. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Dedman J. R. Calcium-dependent protein binding to phenothiazine columns. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9663–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S. Organization, chemistry, and assembly of the cytoskeletal apparatus of the intestinal brush border. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:209–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Gallagher C. J., Crumpton M. J. Cellular distribution of p68, a new calcium-binding protein from lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):945–952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K. Epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):81–84. doi: 10.1038/321081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of the calcium-dependent 35,000-dalton substrate in intact A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8233–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadle P. J., Gerke V., Weber K. Three Ca2+-binding proteins from porcine liver and intestine differ immunologically and physicochemically and are distinct in Ca2+ affinities. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16354–16360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadle P. J., Weber K. Calcium binding protein from porcine intestine binds to phosphatidylserine vesicles in the presence of calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 12;897(3):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. L., Dedman J. R. An immunological comparison of several novel calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15815–15818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Ebbecke M., Walker J. H., Fritsche U., Boustead C. Isolation of mammalian calelectrins: a new class of ubiquitous Ca2+-regulated proteins. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1103–1109. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Glenney J. R., Jr Microfilament-membrane interaction: the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells as a model. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Nov 4;299(1095):207–214. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Johnsson N. Repeating sequence homologies in the p36 target protein of retroviral protein kinases and lipocortin, the p37 inhibitor of phospholipase A2. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]